Lecture 35: Basics of DNA Cloning-I
... bacterial cell. Hence it can be used as a cloning vector to deliver larger DNA segments. Most of the bacteriophage genome is non-essential and can be replaced with foreign DNA. Using bacteriophage as a vector, a DNA fragment of size up to 20 kb can be transformed. Bacterial artificial chromosomes (B ...
... bacterial cell. Hence it can be used as a cloning vector to deliver larger DNA segments. Most of the bacteriophage genome is non-essential and can be replaced with foreign DNA. Using bacteriophage as a vector, a DNA fragment of size up to 20 kb can be transformed. Bacterial artificial chromosomes (B ...
DNA helix mRNA strand transcription gene A > A G > G C > C T > U
... different in the children (i.e. the frequency of recombination between those two genes). This will help us estimate p and therefore d. If we are able to determine the distance between all pairs of genes in our example genome, then we can use these distances to determine the exact sequence of the gen ...
... different in the children (i.e. the frequency of recombination between those two genes). This will help us estimate p and therefore d. If we are able to determine the distance between all pairs of genes in our example genome, then we can use these distances to determine the exact sequence of the gen ...
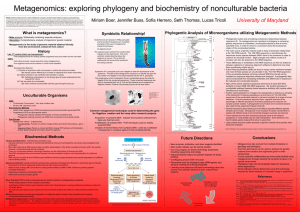
Metagenomics - University of Maryland, College Park
... • Total DNA extractions from environmental samples must be normalized to get an even representation of a particular genome • RNA recovery is similar to that of DNA except modified to minimize single-stranded polynucleotide degradation of mRNA as well as RNAse activity Genome enrichment: Sample enric ...
... • Total DNA extractions from environmental samples must be normalized to get an even representation of a particular genome • RNA recovery is similar to that of DNA except modified to minimize single-stranded polynucleotide degradation of mRNA as well as RNAse activity Genome enrichment: Sample enric ...
DNA Packaging and Ch..
... An organism’s task in managing its DNA: 1.) Efficient packaging and storage, to fit into very small spaces (2.3 million times smaller) 2.) Requires “de-packaging” of DNA to access correct genes at the correct time (gene expression). 3.) Accurate DNA replication during the Sphase of the cell-cycle. ...
... An organism’s task in managing its DNA: 1.) Efficient packaging and storage, to fit into very small spaces (2.3 million times smaller) 2.) Requires “de-packaging” of DNA to access correct genes at the correct time (gene expression). 3.) Accurate DNA replication during the Sphase of the cell-cycle. ...
Cells - Troup County High School
... new alleles are randomly formed; one can only predict offspring (using Punnett squares) • The Law of Independent Assortment: each trait is inherited independently of other traits ...
... new alleles are randomly formed; one can only predict offspring (using Punnett squares) • The Law of Independent Assortment: each trait is inherited independently of other traits ...
jan8
... Partitioning replicated chromosomes so that each daughter cell gets one copy of each chromosome The solution After replication of a chromosome… • hold the two sister chromatids together • target them to opposite poles • then separate the sisters ...
... Partitioning replicated chromosomes so that each daughter cell gets one copy of each chromosome The solution After replication of a chromosome… • hold the two sister chromatids together • target them to opposite poles • then separate the sisters ...
Bacterial transformation - BLI-Research-Synbio-2014-session-1
... together. • When DNA from two sources is joined together, the enzyme DNA ligase is used to catalyze bonding between sugar and phosphate groups in the DNA backbone. • DNA from a “foreign” source (plant, animal, viral, bacterial, yeast) is generally bonded to vector DNA. Vectors can be bacterial plasm ...
... together. • When DNA from two sources is joined together, the enzyme DNA ligase is used to catalyze bonding between sugar and phosphate groups in the DNA backbone. • DNA from a “foreign” source (plant, animal, viral, bacterial, yeast) is generally bonded to vector DNA. Vectors can be bacterial plasm ...
Chapter 12 Review PPT
... the chronological order of the important discoveries in the structure of DNA is: Chargaff’s ratios of nucleotides Franklin makes an X-ray diffraction photo of DNA Watson and Crick identify the double helix ...
... the chronological order of the important discoveries in the structure of DNA is: Chargaff’s ratios of nucleotides Franklin makes an X-ray diffraction photo of DNA Watson and Crick identify the double helix ...
point of view that is personal rather than scientific
... the chronological order of the important discoveries in the structure of DNA is: Chargaff’s ratios of nucleotides Franklin makes an X-ray diffraction photo of DNA Watson and Crick identify the double helix ...
... the chronological order of the important discoveries in the structure of DNA is: Chargaff’s ratios of nucleotides Franklin makes an X-ray diffraction photo of DNA Watson and Crick identify the double helix ...
article in press
... The complexity of higher organisms, which arises in the course of embryonic development from the much simpler fertilized egg, does not emerge by spontaneous generation nor by miracle. Such complexity must somehow be preexistent in the egg. Since the structure of organisms is genetically transmitted, ...
... The complexity of higher organisms, which arises in the course of embryonic development from the much simpler fertilized egg, does not emerge by spontaneous generation nor by miracle. Such complexity must somehow be preexistent in the egg. Since the structure of organisms is genetically transmitted, ...
DNA Replication Paper Lab
... your cut out nucleotides) to form a new right side. (Do NOT mark this side.) Tape the upright phosphoric acid and deoxyribose molecules using a ‘covalent’ bond. Tape the nitrogen bases together using ‘hydrogen’ bonds (a small piece of tape). ...
... your cut out nucleotides) to form a new right side. (Do NOT mark this side.) Tape the upright phosphoric acid and deoxyribose molecules using a ‘covalent’ bond. Tape the nitrogen bases together using ‘hydrogen’ bonds (a small piece of tape). ...
Linkage
... • “Naked” DNA taken up from solution – Bacteria must be “competent” • E. coli treated with high [Ca2] for example – DNA binds to receptor sites on surface – DNA brought into cell by active transport process ...
... • “Naked” DNA taken up from solution – Bacteria must be “competent” • E. coli treated with high [Ca2] for example – DNA binds to receptor sites on surface – DNA brought into cell by active transport process ...
Microbiology Babylon university 2nd stage pharmacy collage
... number of each chromosome (when more than one is present) per growing cell falls between one and four. Some bacterial plasmids may have as many as 30 copies in one bacterial cell, and mutations causing relaxed control of plasmid replication can result in even higher copy numbers. The replication of ...
... number of each chromosome (when more than one is present) per growing cell falls between one and four. Some bacterial plasmids may have as many as 30 copies in one bacterial cell, and mutations causing relaxed control of plasmid replication can result in even higher copy numbers. The replication of ...
Restriction Enzyme Digestion
... 2= Restriction enzyme activity is measured in “units.” One unit is defined as the amount of the enzyme required to digest 1 ug of DNA in 60 minutes. 10-fold overdigestion is recommended. In our lab, use 10 units of enzyme for DNA amounts of 1 ug or less. Add 10 units for each additional 0.1-1 ug of ...
... 2= Restriction enzyme activity is measured in “units.” One unit is defined as the amount of the enzyme required to digest 1 ug of DNA in 60 minutes. 10-fold overdigestion is recommended. In our lab, use 10 units of enzyme for DNA amounts of 1 ug or less. Add 10 units for each additional 0.1-1 ug of ...
Human Genome Project
... the DNA building blocks G and C. • In contrast, the gene-poor "deserts" are rich in the DNA building blocks A and T. GC- and AT-rich regions usually can be seen through a microscope as light and dark bands on chromosomes. • Genes appear to be concentrated in random areas along the genome, with vast ...
... the DNA building blocks G and C. • In contrast, the gene-poor "deserts" are rich in the DNA building blocks A and T. GC- and AT-rich regions usually can be seen through a microscope as light and dark bands on chromosomes. • Genes appear to be concentrated in random areas along the genome, with vast ...
Document
... Which statement best describes a population of organisms if cloning is the only method used to reproduce this population? (1) The population would be more likely to adapt to a changing environment. (2) There would be little chance for variation within the population. (3) The population would evolve ...
... Which statement best describes a population of organisms if cloning is the only method used to reproduce this population? (1) The population would be more likely to adapt to a changing environment. (2) There would be little chance for variation within the population. (3) The population would evolve ...
Document
... the DNA building blocks G and C. • In contrast, the gene-poor "deserts" are rich in the DNA building blocks A and T. GC- and AT-rich regions usually can be seen through a microscope as light and dark bands on chromosomes. • Genes appear to be concentrated in random areas along the genome, with vast ...
... the DNA building blocks G and C. • In contrast, the gene-poor "deserts" are rich in the DNA building blocks A and T. GC- and AT-rich regions usually can be seen through a microscope as light and dark bands on chromosomes. • Genes appear to be concentrated in random areas along the genome, with vast ...
GENETICS REVIEWAPRIL26
... Which statement best describes a population of organisms if cloning is the only method used to reproduce this population? (1) The population would be more likely to adapt to a changing environment. (2) There would be little chance for variation within the population. (3) The population would evolve ...
... Which statement best describes a population of organisms if cloning is the only method used to reproduce this population? (1) The population would be more likely to adapt to a changing environment. (2) There would be little chance for variation within the population. (3) The population would evolve ...
Assignment 2
... 1. Find the protein with the accession number: P23367 in the NCBI protein database. (10 points) a. How many amino acids are in the protein? b. What is the function of the protein? 2. Find the gene mutL of Escherichia coli. (15 points) a. How many records did you retrieve in the NCBI Gene database? b ...
... 1. Find the protein with the accession number: P23367 in the NCBI protein database. (10 points) a. How many amino acids are in the protein? b. What is the function of the protein? 2. Find the gene mutL of Escherichia coli. (15 points) a. How many records did you retrieve in the NCBI Gene database? b ...
Genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) Chromosome Gene Allele
... One of several alternative forms of a gene that occupies a given locus on a chromosome. Alleles can differ from one another in their phenotypic effects. At the molecular level, alleles differ from one another based on their nucleotide sequences, regardless of their effect on phenotype. ...
... One of several alternative forms of a gene that occupies a given locus on a chromosome. Alleles can differ from one another in their phenotypic effects. At the molecular level, alleles differ from one another based on their nucleotide sequences, regardless of their effect on phenotype. ...
GENETICS – BIO 300
... many other families discovered in maize autonomous elements encode information necessary for the transposition of themselves and nonautonomous members of their family ...
... many other families discovered in maize autonomous elements encode information necessary for the transposition of themselves and nonautonomous members of their family ...
Genomic library

A genomic library is a collection of the total genomic DNA from a single organism. The DNA is stored in a population of identical vectors, each containing a different insert of DNA. In order to construct a genomic library, the organism's DNA is extracted from cells and then digested with a restriction enzyme to cut the DNA into fragments of a specific size. The fragments are then inserted into the vector using DNA ligase. Next, the vector DNA can be taken up by a host organism - commonly a population of Escherichia coli or yeast - with each cell containing only one vector molecule. Using a host cell to carry the vector allows for easy amplification and retrieval of specific clones from the library for analysis.There are several kinds of vectors available with various insert capacities. Generally, libraries made from organisms with larger genomes require vectors featuring larger inserts, thereby fewer vector molecules are needed to make the library. Researchers can choose a vector also considering the ideal insert size to find a desired number of clones necessary for full genome coverage.Genomic libraries are commonly used for sequencing applications. They have played an important role in the whole genome sequencing of several organisms, including the human genome and several model organisms.