Bacterial Genetics
... The gal gene is on one side of attλ and the bio gene (biotin synthesis) is on the other side. • Sometimes when lambda come out of the chromosome at the end of the lysogenic phase, it crosses over at the wrong point. This is very similar to the production of an F’ from an Hfr. • When this happens, a ...
... The gal gene is on one side of attλ and the bio gene (biotin synthesis) is on the other side. • Sometimes when lambda come out of the chromosome at the end of the lysogenic phase, it crosses over at the wrong point. This is very similar to the production of an F’ from an Hfr. • When this happens, a ...
Chromosomes - TeacherWeb
... (b) Growth and development. This micrograph shows a sand dollar embryo shortly after the fertilized egg divided, forming two cells (LM). ...
... (b) Growth and development. This micrograph shows a sand dollar embryo shortly after the fertilized egg divided, forming two cells (LM). ...
Issues in Biotechnology
... protein binds to the gene that codes for enzyme that will make tryptophan. When there is no tryptophan present this protein falls off the DNA allowing the gene to be expressed so more tryptophan can be made. A protein that binds to a site on DNA next to a gene and blocks the transcription of that ge ...
... protein binds to the gene that codes for enzyme that will make tryptophan. When there is no tryptophan present this protein falls off the DNA allowing the gene to be expressed so more tryptophan can be made. A protein that binds to a site on DNA next to a gene and blocks the transcription of that ge ...
Analyzing Data
... Transformation • The DNA molecule is hydrophilic (water-soluble) but cell membranes are made of a very hydrophobic lipid bilayer. Two means of artificial transformation commonly used in labs: electroporation and chemical transformation. • During electroporation, short bursts of current are passed t ...
... Transformation • The DNA molecule is hydrophilic (water-soluble) but cell membranes are made of a very hydrophobic lipid bilayer. Two means of artificial transformation commonly used in labs: electroporation and chemical transformation. • During electroporation, short bursts of current are passed t ...
pLKO.1 puro protocol
... 2. Purify the 7 kb band by gel extraction. We used The illustra™ GFX™ PCR DNA and Gel Band Purification Kit from GE Healthcare, but a gel extraction method of choice can be used. Quantify the DNA and proceed to ligation. Ligating and Transforming into Bacteria 1. We use T4 DNA ligase from Fermentas, ...
... 2. Purify the 7 kb band by gel extraction. We used The illustra™ GFX™ PCR DNA and Gel Band Purification Kit from GE Healthcare, but a gel extraction method of choice can be used. Quantify the DNA and proceed to ligation. Ligating and Transforming into Bacteria 1. We use T4 DNA ligase from Fermentas, ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Chapter 20 DNA Technology and
... The gene is inserted into a bacterial plasmid. The plasmid is returned to a bacterial cell, producing a recombinant bacterium, which reproduces to form a clone of identical cells. ...
... The gene is inserted into a bacterial plasmid. The plasmid is returned to a bacterial cell, producing a recombinant bacterium, which reproduces to form a clone of identical cells. ...
More on Genetics2013
... __________________In the process of transforming bacteria,the foreign DNA is joined to this small,circular DNA _____________________-contain genes plasmids from other species---used for making insulin…. clone A _____________is a member of a population of genetically identical cells from a single sou ...
... __________________In the process of transforming bacteria,the foreign DNA is joined to this small,circular DNA _____________________-contain genes plasmids from other species---used for making insulin…. clone A _____________is a member of a population of genetically identical cells from a single sou ...
Gene linkage and Gene maps
... Recombination frequency is dependent on the distance between the linked genes Morgan’s student, Alfred Sturtevant, developed a method for constructing a gene map(an ordered list of genetic loci along a particular chromosome) Sturtevant(1911): based on his experiments –the farther apart two genes are ...
... Recombination frequency is dependent on the distance between the linked genes Morgan’s student, Alfred Sturtevant, developed a method for constructing a gene map(an ordered list of genetic loci along a particular chromosome) Sturtevant(1911): based on his experiments –the farther apart two genes are ...
Bioterrorism and the Fermi Paradox
... escape the gravitational field of an astronomical body large enough to hold onto an atmosphere requires a huge amount of energy, and collecting that much energy in one place – another audacious upstream battle against entropy – requires the collective efforts of thousands of individuals, funded by bil ...
... escape the gravitational field of an astronomical body large enough to hold onto an atmosphere requires a huge amount of energy, and collecting that much energy in one place – another audacious upstream battle against entropy – requires the collective efforts of thousands of individuals, funded by bil ...
dna structure - Siegel Science
... diffraction to show there were two twisted strands to a DNA molecule. ...
... diffraction to show there were two twisted strands to a DNA molecule. ...
Brock Genetic Exchange in Bacteria
... Each transducing particle (TP) carries 44 kb of DNA – the Salmonella genome is app. 4400 kb in size Therefore, if the process is random 100 different transducing particles should represent the entire genome. (0.5)(1011 viruses/ml)/(100 TP [1 genome]) = 5x108 copies of the genome/ml of lysate ...
... Each transducing particle (TP) carries 44 kb of DNA – the Salmonella genome is app. 4400 kb in size Therefore, if the process is random 100 different transducing particles should represent the entire genome. (0.5)(1011 viruses/ml)/(100 TP [1 genome]) = 5x108 copies of the genome/ml of lysate ...
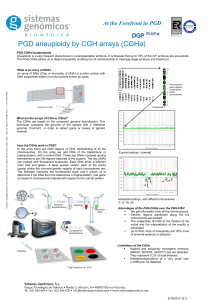
At the Forefront in PGD
... balanced abnormality. This causes, recurrent abortions and, in many cases, infertility. PGD using FISH techniques allows detect altered embryos (unbalanced) for a specific chromosomal rearrangement. However, the main limitation is that it does not provide information of the rest of chromosomes. Comb ...
... balanced abnormality. This causes, recurrent abortions and, in many cases, infertility. PGD using FISH techniques allows detect altered embryos (unbalanced) for a specific chromosomal rearrangement. However, the main limitation is that it does not provide information of the rest of chromosomes. Comb ...
Unit Title
... draw conclusions/make predictions based on hereditary evidence/data (pedigrees, punnet squares). Multicellular organisms, including humans, form from cells that contain two copies of each chromosome. This explains many features of heredity. Transmission of genetic information through sexual reprod ...
... draw conclusions/make predictions based on hereditary evidence/data (pedigrees, punnet squares). Multicellular organisms, including humans, form from cells that contain two copies of each chromosome. This explains many features of heredity. Transmission of genetic information through sexual reprod ...
Transgenic farm animals ppt. - Ms. Thomas` Foundations of
... may allow us to genetically engineer cows so they make milk that curdles more easily and consistently. This could lower the price of cheese and improve the quality. ...
... may allow us to genetically engineer cows so they make milk that curdles more easily and consistently. This could lower the price of cheese and improve the quality. ...
Amount of rearranged DNA in children affected by SLI.
... person has lots of changes. If the rearrangement disrupts an important gene then the family member is more likely to develop speech and language difficulties. The fact that affected families have more rearrangements increases the chances of an important gene being disrupted but does not determine th ...
... person has lots of changes. If the rearrangement disrupts an important gene then the family member is more likely to develop speech and language difficulties. The fact that affected families have more rearrangements increases the chances of an important gene being disrupted but does not determine th ...
Heredity and Genes
... combinations for offspring. Your genetic makeup is one of those combinations. ...
... combinations for offspring. Your genetic makeup is one of those combinations. ...
Chapter 20 Notes AP Biology I. Chapter 20.1: DNA - Pomp
... 1. Ordering of genetic markers such as RFLPs 2. Simple sequence DNA 3. Other polymorphisms-‐ about 200 per chromosome c. Physical Mapping: Ordering DNA Fragments i. The distances between markers are expressed in ...
... 1. Ordering of genetic markers such as RFLPs 2. Simple sequence DNA 3. Other polymorphisms-‐ about 200 per chromosome c. Physical Mapping: Ordering DNA Fragments i. The distances between markers are expressed in ...
Phasing Analysis Service for Whole Human Genome Sequencing
... Establishing Variant Linkage When performing whole-genome phasing, Illumina’s proprietary phasing algorithm first builds short sequence reads into the originally targeted long fragments. Next, it uses overlapping heterozygous regions to create long, molecularly phased sequence segments. The molecula ...
... Establishing Variant Linkage When performing whole-genome phasing, Illumina’s proprietary phasing algorithm first builds short sequence reads into the originally targeted long fragments. Next, it uses overlapping heterozygous regions to create long, molecularly phased sequence segments. The molecula ...
CH 11 Study Guide: DNA, RNA, and Proteins
... mRNA: carries the DNA message from the nucleus to the cytoplasm (to the ribosome) rRNA: forms the ribosome tRNA: carries amino acids to the ribosome so that proteins can be made 5. Who discovered the structure of DNA? Watson & Crick 6. IF a sequence of codons on a DNA strand is AAC TAG GGT, what is ...
... mRNA: carries the DNA message from the nucleus to the cytoplasm (to the ribosome) rRNA: forms the ribosome tRNA: carries amino acids to the ribosome so that proteins can be made 5. Who discovered the structure of DNA? Watson & Crick 6. IF a sequence of codons on a DNA strand is AAC TAG GGT, what is ...
Genomic library

A genomic library is a collection of the total genomic DNA from a single organism. The DNA is stored in a population of identical vectors, each containing a different insert of DNA. In order to construct a genomic library, the organism's DNA is extracted from cells and then digested with a restriction enzyme to cut the DNA into fragments of a specific size. The fragments are then inserted into the vector using DNA ligase. Next, the vector DNA can be taken up by a host organism - commonly a population of Escherichia coli or yeast - with each cell containing only one vector molecule. Using a host cell to carry the vector allows for easy amplification and retrieval of specific clones from the library for analysis.There are several kinds of vectors available with various insert capacities. Generally, libraries made from organisms with larger genomes require vectors featuring larger inserts, thereby fewer vector molecules are needed to make the library. Researchers can choose a vector also considering the ideal insert size to find a desired number of clones necessary for full genome coverage.Genomic libraries are commonly used for sequencing applications. They have played an important role in the whole genome sequencing of several organisms, including the human genome and several model organisms.