The Principle of Relativity Outline
... Assuming movement is small so that the force doesn’t change appreciably, the distance moved in 3 min (180 sec) is ...
... Assuming movement is small so that the force doesn’t change appreciably, the distance moved in 3 min (180 sec) is ...
Lecture Notes: Chapter 2 Motion
... Scientists at NASA need to consider frames of reference because all objects in space are in constant motion relative to earth. They can’t just send up a satellite or spacecraft and expect it to be at the speed of the other objects. Distance An important part of describing the motion of an object ...
... Scientists at NASA need to consider frames of reference because all objects in space are in constant motion relative to earth. They can’t just send up a satellite or spacecraft and expect it to be at the speed of the other objects. Distance An important part of describing the motion of an object ...
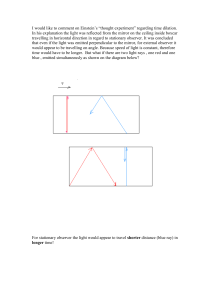
“thought experiment” regarding time dilation
... travelling in horizontal direction in regard to stationary observer. It was concluded that even if the light was emitted perpendicular to the mirror, for external observer it would appear to be travelling on angle. Because speed of light is constant, therefore time would have to be longer. But what ...
... travelling in horizontal direction in regard to stationary observer. It was concluded that even if the light was emitted perpendicular to the mirror, for external observer it would appear to be travelling on angle. Because speed of light is constant, therefore time would have to be longer. But what ...
JKDoranPaper - FSU High Energy Physics
... special relativity and know about time dilation, so they each think that the other’s clock runs slower relative to their own because they each “see” the other’s clock in motion relative to their own (Krane). Therefore, each sister expects the other to be younger when Betty returns from the planet. T ...
... special relativity and know about time dilation, so they each think that the other’s clock runs slower relative to their own because they each “see” the other’s clock in motion relative to their own (Krane). Therefore, each sister expects the other to be younger when Betty returns from the planet. T ...
Chapter 18 Test Review
... • Magnetic force: The force that pushes magnets apart or pulls them together. • Motion: object’s change in position relative to a reference point. • Gravity: The force of attraction between objects that is due to their mass. • Friction: a force that always acts to oppose motion. ...
... • Magnetic force: The force that pushes magnets apart or pulls them together. • Motion: object’s change in position relative to a reference point. • Gravity: The force of attraction between objects that is due to their mass. • Friction: a force that always acts to oppose motion. ...
Motion In Review
... that pulls us towards the earth. • It gives everything a weight • If gravity didn’t exist we would float around like astronauts in space ...
... that pulls us towards the earth. • It gives everything a weight • If gravity didn’t exist we would float around like astronauts in space ...
Relativity 1 - UCF College of Sciences
... of mechanics are true in one frame of reference. How do they look in another frame, moving with respect to the first frame? To figure out, we have to find how to get from position, velocity and acceleration in one frame to the corresponding quantities in the second frame. Obviously, the two frames m ...
... of mechanics are true in one frame of reference. How do they look in another frame, moving with respect to the first frame? To figure out, we have to find how to get from position, velocity and acceleration in one frame to the corresponding quantities in the second frame. Obviously, the two frames m ...
Waves, incl. Electromagnetic Waves, Light
... (Or: any accelerating charged particle will radiate electromagnetically) Hertz’s discovery & subsequent work started the amazing telecommunications revolution, going on unabated: radio, TV, phones, microwave transmission, fiber optics, wireless, etc….. Important comment about c (footnote on p.199) ...
... (Or: any accelerating charged particle will radiate electromagnetically) Hertz’s discovery & subsequent work started the amazing telecommunications revolution, going on unabated: radio, TV, phones, microwave transmission, fiber optics, wireless, etc….. Important comment about c (footnote on p.199) ...
Motion Review Notes - Ms. Guggenheimer`s Education Connection
... Constant Speed: When something moves at the same speed for several hours. The speed of the object does not change. To calculate the constant speed you use the formula for speed Speed = Distance Time Average Speed: is equal to the total distance traveled divided by the total time for the trip. It tak ...
... Constant Speed: When something moves at the same speed for several hours. The speed of the object does not change. To calculate the constant speed you use the formula for speed Speed = Distance Time Average Speed: is equal to the total distance traveled divided by the total time for the trip. It tak ...
DiffLinearMotion
... motion • Newton’s 1st Law of Motion: an object moving at a constant velocity or at rest will remain that way unless it is acted upon by a force • Why should we wear ...
... motion • Newton’s 1st Law of Motion: an object moving at a constant velocity or at rest will remain that way unless it is acted upon by a force • Why should we wear ...
PPL1 Intro and Describing Motion CH 1 and 2
... http://physics.nist.gov/cuu/Units/index.html Fundamental physical constants: ...
... http://physics.nist.gov/cuu/Units/index.html Fundamental physical constants: ...
The Velocity of Light - Gravitational Relativity
... originate in the subatomic electric charges in matter. This derivation of the speed of light was an incredible achievement and has been time tested for the last 150 years. However, since (1) light travels through empty space from distant celestial bodies and (2) electromagnetic fields only come from ...
... originate in the subatomic electric charges in matter. This derivation of the speed of light was an incredible achievement and has been time tested for the last 150 years. However, since (1) light travels through empty space from distant celestial bodies and (2) electromagnetic fields only come from ...
Motion and Speed
... a specific moment in time (Instantaneous Speed from your other notes). Average speed measures how far an object moves in a given amount of time. ...
... a specific moment in time (Instantaneous Speed from your other notes). Average speed measures how far an object moves in a given amount of time. ...
Click here for ppt
... air will slow down, stop, and then begin to fall with the acceleration due to gravity. When it passes the thrower, it will be traveling at the same rate at which it was thrown. ...
... air will slow down, stop, and then begin to fall with the acceleration due to gravity. When it passes the thrower, it will be traveling at the same rate at which it was thrown. ...
Definitions
... This time must be the same as O’Brien measured for the first clock or Postulate #1 would be violated. Doing the algebra, the only possible conclusion is that d as measured by O’Brien must be different than d0 as measured by Scott: ...
... This time must be the same as O’Brien measured for the first clock or Postulate #1 would be violated. Doing the algebra, the only possible conclusion is that d as measured by O’Brien must be different than d0 as measured by Scott: ...
If the displacement of an object, x, is related to
... Note the following mathematical expression: y = x 2 . Which one of the statements below is most consistent with this expression? a. if y doubles, then x quadruples b. y is greater than x c. if x doubles, then y doubles d. if x doubles, then y quadruples ...
... Note the following mathematical expression: y = x 2 . Which one of the statements below is most consistent with this expression? a. if y doubles, then x quadruples b. y is greater than x c. if x doubles, then y doubles d. if x doubles, then y quadruples ...
相對論簡介
... Light • This is required by the first postulate • Confirmed experimentally in many ways • Explains the null result of the MichelsonMorley experiment • Relative motion is unimportant when measuring the speed of light – We must alter our common-sense notions of space and time ...
... Light • This is required by the first postulate • Confirmed experimentally in many ways • Explains the null result of the MichelsonMorley experiment • Relative motion is unimportant when measuring the speed of light – We must alter our common-sense notions of space and time ...
Life in the Universe
... Early 1800s, the French philosopher (founder of sociology), Auguste Comte claimed that humanity will never know about the nature and composition of stars because stars are so far away… Only thing we can “see” from stars is their light. How can one understand properties of stars (such as temperat ...
... Early 1800s, the French philosopher (founder of sociology), Auguste Comte claimed that humanity will never know about the nature and composition of stars because stars are so far away… Only thing we can “see” from stars is their light. How can one understand properties of stars (such as temperat ...
Set #1
... everyday phenomena can be derived from relativity. For example, magnetism can be described as arising from electrostatics plus special relativity applied to the slow-moving charges in wires.) ( v / c 3.16 1018. ; v / c 9.26 108. ; v / c 2.87 106 . ; v / c 104. ) SEC. 38-3 . THE PRIN ...
... everyday phenomena can be derived from relativity. For example, magnetism can be described as arising from electrostatics plus special relativity applied to the slow-moving charges in wires.) ( v / c 3.16 1018. ; v / c 9.26 108. ; v / c 2.87 106 . ; v / c 104. ) SEC. 38-3 . THE PRIN ...
Lecture 8, PPT version
... BUT: time is running more slowly on the railway car, so the force felt by the brick on the car lasts for less time than for the brick on the railway platform (say, 1 billionth of a second versus 2 billionths of a second)! ...
... BUT: time is running more slowly on the railway car, so the force felt by the brick on the car lasts for less time than for the brick on the railway platform (say, 1 billionth of a second versus 2 billionths of a second)! ...