Physics
... Q. 2. Under what condition is the scalar product of two non-zero vectors zero ? Q. 3. A body just starts to move when 15 N forces is applied . If 10 N forces is applied on it . Find force of friction . Q. 4. When momentum of a body is doubled , how will its Kinetic-energy changes? Q. 5. Write equati ...
... Q. 2. Under what condition is the scalar product of two non-zero vectors zero ? Q. 3. A body just starts to move when 15 N forces is applied . If 10 N forces is applied on it . Find force of friction . Q. 4. When momentum of a body is doubled , how will its Kinetic-energy changes? Q. 5. Write equati ...
Chapter 2 Study Guide
... 1. When designing an experiment, what is the manipulated and responding variable? 2. Manipulated variable: ___________________________________ when graphing, __ axis. 3. Responding variable: ___________________________________ when graphing, __ axis. 4. What are some examples of data in an experimen ...
... 1. When designing an experiment, what is the manipulated and responding variable? 2. Manipulated variable: ___________________________________ when graphing, __ axis. 3. Responding variable: ___________________________________ when graphing, __ axis. 4. What are some examples of data in an experimen ...
Einstein`s special theory of relativity
... Example 2 The mean lifetime of an elementary particle called muon is 2.2 10 6 s as measured in a frame of reference that it is at rest. What will be its mean lifetime as measured in an earth laboratory if it is travelling at half of the speed of light relative to the earth? ...
... Example 2 The mean lifetime of an elementary particle called muon is 2.2 10 6 s as measured in a frame of reference that it is at rest. What will be its mean lifetime as measured in an earth laboratory if it is travelling at half of the speed of light relative to the earth? ...
More Energy Practice Problems
... 7. A body of mass 100 g is attached to a hanging spring whose force constant is 10 N/m. The body is lifted until the spring is in its unstretched state. The body is then released. Calculate the speed of the body when it strikes a table 15 cm below the release point. 8. A 10 kg packet is fired vertic ...
... 7. A body of mass 100 g is attached to a hanging spring whose force constant is 10 N/m. The body is lifted until the spring is in its unstretched state. The body is then released. Calculate the speed of the body when it strikes a table 15 cm below the release point. 8. A 10 kg packet is fired vertic ...
Which will fall faster?
... How many meters will an object fall in 1 second? • 9.8 meters • Every 1 second, speed will increase by 9.8 m/s ...
... How many meters will an object fall in 1 second? • 9.8 meters • Every 1 second, speed will increase by 9.8 m/s ...
Introduction and Describing Motion
... http://physics.nist.gov/cuu/Units/index.html Fundamental physical constants: ...
... http://physics.nist.gov/cuu/Units/index.html Fundamental physical constants: ...
Homework 1. Estimate the speed of the planet mercury? Compare
... Why don’t we fall into the sun? Assume that the earth suddenly stopped moving. Then, assuming (unrealistically) that our acceleration towards the sun is constant thereafter, how long would it take us to reach the sun? Solution: • The acceleration is ...
... Why don’t we fall into the sun? Assume that the earth suddenly stopped moving. Then, assuming (unrealistically) that our acceleration towards the sun is constant thereafter, how long would it take us to reach the sun? Solution: • The acceleration is ...
Motion and Speed
... An object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will continue moving at a constant velocity unless acted upon by a net force. ...
... An object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will continue moving at a constant velocity unless acted upon by a net force. ...
Speed
... time: s (second) acceleration: m/s/s or m/s2 Speed is the rate at which an object moves. Average speed = total distance total time Velocity: The speed of an object in a particular direction. The rate of change of an object’s position. Constant velocity: an object’s velocity is constant only if its s ...
... time: s (second) acceleration: m/s/s or m/s2 Speed is the rate at which an object moves. Average speed = total distance total time Velocity: The speed of an object in a particular direction. The rate of change of an object’s position. Constant velocity: an object’s velocity is constant only if its s ...
A Brief History of Planetary Science
... The intensity depends on how much energy the wave delivers, which depends on the energy density and the speed: I = uc = (½e0Erms2 + ½e0Erms2)c I = ce0Erms2 ...
... The intensity depends on how much energy the wave delivers, which depends on the energy density and the speed: I = uc = (½e0Erms2 + ½e0Erms2)c I = ce0Erms2 ...
Relativity1
... proposed in the 19th century that light propagates through ether—some sort of medium— although nobody knew what this ether was. It was supposed that this ether might be at rest with respect to the solar system, or maybe the galaxy. In any case, the Earth would move through this ether, and we should ...
... proposed in the 19th century that light propagates through ether—some sort of medium— although nobody knew what this ether was. It was supposed that this ether might be at rest with respect to the solar system, or maybe the galaxy. In any case, the Earth would move through this ether, and we should ...
Chapter 2 - Net Start Class
... Average Speed describes speed of motion when speed is changing. Average Speed is the distance traveled divided by the time of travel. It can be calculated using the relationship among speed distance and time. If Mr. Van Fleet rides his bicycle to work, and he lives 10 miles away, how fast did he tra ...
... Average Speed describes speed of motion when speed is changing. Average Speed is the distance traveled divided by the time of travel. It can be calculated using the relationship among speed distance and time. If Mr. Van Fleet rides his bicycle to work, and he lives 10 miles away, how fast did he tra ...
Notes - SFA Physics and Astronomy
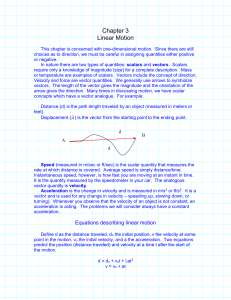
... Speed (measured in m/sec or ft/sec) is the scalar quantity that measures the rate at which distance is covered. Average speed is simply distance/time. Instantaneous speed, however, is how fast you are moving at an instant in time. It is the quantity measured by the speedometer in your car. The analo ...
... Speed (measured in m/sec or ft/sec) is the scalar quantity that measures the rate at which distance is covered. Average speed is simply distance/time. Instantaneous speed, however, is how fast you are moving at an instant in time. It is the quantity measured by the speedometer in your car. The analo ...
Time Activities - cloudfront.net
... It took Buzz Lightyear 2.5 hours to travel 600 It took Payton 4 hours to travel 165 kilometers due kilometers. North. How fast was he going in Kilometers an hour? What was the velocity of her car in Kilometers an hour? ...
... It took Buzz Lightyear 2.5 hours to travel 600 It took Payton 4 hours to travel 165 kilometers due kilometers. North. How fast was he going in Kilometers an hour? What was the velocity of her car in Kilometers an hour? ...