Midterm Exam 1
... History of astronomy from ancient Greeks until mid-1600’s. – What did the ancient Greeks have right? What did they have wrong? – How we went from geocentric (Earth at center) models to heliocentric (Sun at center) models of Solar System. – Ptolemy’s system – epicycles, etc. Why were these complicati ...
... History of astronomy from ancient Greeks until mid-1600’s. – What did the ancient Greeks have right? What did they have wrong? – How we went from geocentric (Earth at center) models to heliocentric (Sun at center) models of Solar System. – Ptolemy’s system – epicycles, etc. Why were these complicati ...
stphysic - The Skeptic Tank
... concept of relativity that we have today. I believe it will seem quite reasonable. I state it as it appears in a physics book by Serway: "the laws of physics are the same in every inertial frame of reference." What it means is that if you observer any physical laws for a given situation in your fra ...
... concept of relativity that we have today. I believe it will seem quite reasonable. I state it as it appears in a physics book by Serway: "the laws of physics are the same in every inertial frame of reference." What it means is that if you observer any physical laws for a given situation in your fra ...
Final Review: Problems
... 12. An apple drops from a tree and hits the ground in 1.5 seconds. What is its speed just before it hits the ground? 13. A rock gets thrown from a cliff that is 70 m high with a speed of 5 m/s. (ignore air resistance) a. How much time does it take for the rock to reach the ground? b. How far does th ...
... 12. An apple drops from a tree and hits the ground in 1.5 seconds. What is its speed just before it hits the ground? 13. A rock gets thrown from a cliff that is 70 m high with a speed of 5 m/s. (ignore air resistance) a. How much time does it take for the rock to reach the ground? b. How far does th ...
slides - UMD Physics
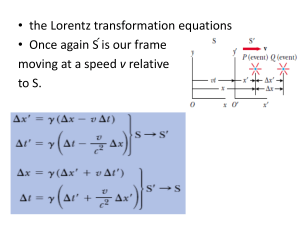
... in which the two events (emission and detection) are measured with the same clock. In this case, this is called the proper time and is notated as notated as . MORE time passes per tick in frame S in which the clock is moving than in the stationary frame S’. ...
... in which the two events (emission and detection) are measured with the same clock. In this case, this is called the proper time and is notated as notated as . MORE time passes per tick in frame S in which the clock is moving than in the stationary frame S’. ...
Speed/Motion Notes!
... What is the acceleration of a roller coaster that starts with a velocity of 4 m/s and accelerates to 22m/s in 3 sec.? A=(22m/s-4m/s)/3s A=18m/s//3s A=6m/s/s or 6m/s2 ...
... What is the acceleration of a roller coaster that starts with a velocity of 4 m/s and accelerates to 22m/s in 3 sec.? A=(22m/s-4m/s)/3s A=18m/s//3s A=6m/s/s or 6m/s2 ...
PHY 108 – Atoms to Galaxies
... No experiment performed within a sealed room moving at an unchanging velocity can tell you whether you are standing still or moving. ...
... No experiment performed within a sealed room moving at an unchanging velocity can tell you whether you are standing still or moving. ...
Newton`s Laws First Law --an object at rest tends to stay at rest AND
... directions If teams pull with the same force, in opposite directions, net force on the rope is ZERO and ---> Rope doesn’t move ...
... directions If teams pull with the same force, in opposite directions, net force on the rope is ZERO and ---> Rope doesn’t move ...
Motion Dukes oHazzard 08t
... Velocity- describes the speed and direction of something • You can change velocity without changing speed if you turn a corner. • If you travel at 10mph on Lombard street your speed stays the same. 2.) Does velocity change? ...
... Velocity- describes the speed and direction of something • You can change velocity without changing speed if you turn a corner. • If you travel at 10mph on Lombard street your speed stays the same. 2.) Does velocity change? ...
Notes
... Gauss’ law for magnetism states the magnetic flux through any closed surface is zero. This implies there are no magnetic monopoles (analogs to isolated electric charges). ...
... Gauss’ law for magnetism states the magnetic flux through any closed surface is zero. This implies there are no magnetic monopoles (analogs to isolated electric charges). ...
Clocks/meter sticks - University of Colorado Boulder
... A light wave traveling at speed c with respect to faraway stars is heading in the opposite direction. According to Einstein’s relativity, what is the speed of the light wave as viewed from the earth? (Further assume the earth is not accelerating). a) c ...
... A light wave traveling at speed c with respect to faraway stars is heading in the opposite direction. According to Einstein’s relativity, what is the speed of the light wave as viewed from the earth? (Further assume the earth is not accelerating). a) c ...
Document
... say that the speed should be the sum of the two speeds, or 1.50c. This answer must be incorrect because it contradicts the assertion that no material object can travel faster than the speed of light. • Let two frames or reference be labelled b and d, and suppose that frame d is moving at velocity vd ...
... say that the speed should be the sum of the two speeds, or 1.50c. This answer must be incorrect because it contradicts the assertion that no material object can travel faster than the speed of light. • Let two frames or reference be labelled b and d, and suppose that frame d is moving at velocity vd ...
Light and Optics
... a car that can go from rest to 60km/h in 3.2 seconds. 3. What is the difference between speed and velocity? 4. What is a motion diagram? Draw one and explain it. 5. Be able to use the 4 “more complicated” equations to solve for v0 or v1, or d1, or t, or a. Problem: If a Ferrari, with an initial velo ...
... a car that can go from rest to 60km/h in 3.2 seconds. 3. What is the difference between speed and velocity? 4. What is a motion diagram? Draw one and explain it. 5. Be able to use the 4 “more complicated” equations to solve for v0 or v1, or d1, or t, or a. Problem: If a Ferrari, with an initial velo ...
1) A car starts to accelerate from rest with a=0
... 2) A canon is shot under an angle of 30.00 with respect to the ground with an initial velocity of 49.0 m/s. At what horizontal distance away from the cannon does the cannon ball reach its highest point? a) 50 m b) 106 m c) 212 m d) 245 m e) none of the above 3) A mass of 7.0 kg lying on a slope (370 ...
... 2) A canon is shot under an angle of 30.00 with respect to the ground with an initial velocity of 49.0 m/s. At what horizontal distance away from the cannon does the cannon ball reach its highest point? a) 50 m b) 106 m c) 212 m d) 245 m e) none of the above 3) A mass of 7.0 kg lying on a slope (370 ...