* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Special Relativity
Lorentz ether theory wikipedia , lookup
History of general relativity wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of the theory of relativity wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to general relativity wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of physics wikipedia , lookup
Relational approach to quantum physics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
History of optics wikipedia , lookup
History of special relativity wikipedia , lookup
A Brief History of Time wikipedia , lookup
Speed of light wikipedia , lookup
Length contraction wikipedia , lookup
Michelson–Morley experiment wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Inertial frame of reference wikipedia , lookup
Time dilation wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Tests of special relativity wikipedia , lookup
Special relativity wikipedia , lookup
Derivations of the Lorentz transformations wikipedia , lookup
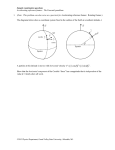
Special Relativity How does light behave in moving reference frames? Some lingering questions remain… Maxwell’s equations describe and predict electromagnetic phenomena amazingly well. but… 1) What is the medium for electromagnetic waves? 2) In what frame of reference is the speed of light 3.00 x 108 m/s? Luminiferous ether? Hypothesized as medium for light Hypothesized as frame of reference for light • Does a microwave work on a fast-moving spaceship? • Does a motor work? If there is an ether, it’s odd. • Does not noticeable interact with matter • Is it dragged by Earth or is there an ethereal wind through which the Earth (and everything else) travels? Michelson-Morley Interferometer In 1880’s, Albert Michelson and Edward Morley designed an experiment to test the speed of the ethereal wind. Swimmers’ analogy Stationary relative to ether? • waves should constructively interfere. Moving relative to ether? • waves should destructively interfere Null results Michelson and Morley discovered no evidence of the Earth’s motion through ether. Consequence of no ether 1. No ‘absolute’ frame of reference 2. If no ‘absolute’ frame, laws of physics (including electricity and magnetism) work in all reference frames 3. If laws of physics work in all reference frames, speed of light is the same in all frames of reference Speed of light is the same regardless of reference frames? Postulates of special relativity 1st postulate: All laws of nature are the same in all uniformly moving frames of reference • Sometimes called “inertial reference frames” 2nd postulate: The speed of light in empty space is the same, regardless of the motion of the source or the motion of the observer Frames of reference (with a ball) The thrower throws the ball at, say, 10 m/s in each situation. The receiver perceives the ball to travel at 1) 2) 3) 10 m/s (truck at rest) >10 m/s (moving towards) <10 m/s (moving away) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v= BLuI118nhzc Frames of reference & light 1) What happens if you travel at the speed of light and turn on a flashlight? Does that light travel at twice the speed as the ‘slow’ light? 2) Imagine an electric current traveling down a wire. It induces a magnetic field. Would you detect a magnetic field if you traveled the same speed as the electric current? Frames of reference (with a flashlight) The person on the truck shines a flashlight at the person standing on the ground. The person on the ground perceives the light to travel at 1) 2) 3) 3 x 108 m/s (truck at rest) 3 x 108 (moving towards) 3 x 108 (moving away) Explaining null results Hendrik Lorentz proposed a mathematical trick as a solution • Trick = hypothesis with no physical explanation Suppose that objects contract (i.e., shrink) in the direction of their motion What if length contraction not a trick? Einstein’s insight: if speed of light is the same in all reference frames, 1. Clocks aren’t 2. Rulers aren’t Read the original paper here: https://www.fourmilab.ch/etext s/einstein/specrel/www/ Time and distance in stationary frames Person on high-speed rocket ship measures time with a light clock, a device in which light bounces back and forth between two mirrors 𝑑 𝑑 𝑡= = 𝑣 𝑐 Time and distance in moving frames Person NOT on the ship observes the following: Moment 1 Moment 2 Moment 3 Time and distance in moving frames Person NOT on the ship observes the following: 𝑑 = 𝑐𝑡0 𝑑 = 𝑣𝑡 Moment 1 Moment 2 Moment 3 Time and distance in moving frames 𝑐𝑡 2 = 𝑐𝑡0 2 By Pythagorean Theorem So, 𝑐𝑡 2 − 𝑣𝑡 So, 𝑡 2 1 − So, 𝑡 = 𝑣2 𝑐2 = 𝑡0 2 𝑡0 2 𝑣 1− 2 𝑐2 = 𝑐𝑡0 2 + 𝑣𝑡 2 Time dilation 𝑡= 𝑡0 If physics works regardless of reference frame, then observers note that time slows downs for events in moving reference frames. • At everyday speeds (v << c), v/c ~0, so time dilation is barely noticeable. NOT “seems to slow”, but really and actually and counterintuitively slows • At relativistic speeds, (v some appreciable fraction of c), time dilation is significant. • 2 𝑣 1− 𝑐2 Length contraction Length contracts in direction of travel. 𝐿 = 𝐿𝑜 1 − 𝑣2 𝑐2 Measurement between frames Measurements of time and length between one frame of reference and another will agree only on the speed of light. Time: 𝑡 = 𝑡0 2 1− 𝑣 2 𝑐 Length: 𝐿 = 𝐿0 1 − In relativity, we see the term 1 𝑣2 1−𝑐2 𝑣2 𝑐2 occurs so frequently, we abbreviate it with the Greek letter gamma, Other implications Relativistic momentum Relativistic kinetic energy 𝑝= 𝑚𝑣 2 𝑣 1−𝑐2 KE = 𝑚𝑐 2 2 − 𝑚𝑐 2 𝑣 1−𝑐2 Using relativity to explain electromagnets Imagine an electric current traveling down a wire. It induces a magnetic field. Would you detect a magnetic field if you traveled the same speed as the electric current? Think about… Joe Burpy is 30 years old. He has a daughter who is 6 years old. If Joe leaves on a Greyhound space bus which takes a 5-year (space bus time) round trip at 0.99 c. a) How old will Joe be when he returns? b) How old will his daughter be? More… Minute Physics: • Special relativity: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ajhFNcUTJI0 • Energy & mass equivalence: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hW7DW9NI O9M • How far away is tomorrow: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=s5S-hA9uKEM • Adding velocity: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IM630Z8lho8 • Breaking speed of light: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lR4tJr7sMPM • Why you can’t go speed of light: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NnMIhxWRG Nw New York University – Physics Dept: http://www.physics.nyu.edu/~ts2/Animation/special_r elativity.html#