Quiz on Motion under gravity
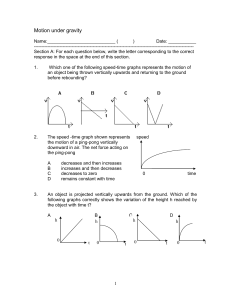
... following graphs correctly shows the variation of the height h reached by the object with time t? A ...
... following graphs correctly shows the variation of the height h reached by the object with time t? A ...
Practice - People Server at UNCW
... planet’s distance from the Sun could then be determined from Kepler’s a) first law; b) second law d) third law. _____ r) When the distance between two masses is cut in half and one of the masses is doubled, the gravitational force between them is _____ the original force. a) half b) the same as b) t ...
... planet’s distance from the Sun could then be determined from Kepler’s a) first law; b) second law d) third law. _____ r) When the distance between two masses is cut in half and one of the masses is doubled, the gravitational force between them is _____ the original force. a) half b) the same as b) t ...
2-D Motion Homework Set
... 1. Does a light ray traveling from one medium into another always bend toward the normal? 2. As light travels from a vacuum (n = 1) to a medium such as glass (n > 1), does its wavelength change? Does its velocity change? 3. What is the relationship between the velocity of light and the index of refr ...
... 1. Does a light ray traveling from one medium into another always bend toward the normal? 2. As light travels from a vacuum (n = 1) to a medium such as glass (n > 1), does its wavelength change? Does its velocity change? 3. What is the relationship between the velocity of light and the index of refr ...
89mc
... A. 50 N throughout the journey. B. more than 50 N when the lift starts, and remains steady until it comes to rest. C. less than 50 N when the lift starts, and remains steady until it comes to rest. D. more than 50 N as the lift starts, and less than 50 N as it comes to rest. E. less than 50 N as the ...
... A. 50 N throughout the journey. B. more than 50 N when the lift starts, and remains steady until it comes to rest. C. less than 50 N when the lift starts, and remains steady until it comes to rest. D. more than 50 N as the lift starts, and less than 50 N as it comes to rest. E. less than 50 N as the ...
Chapter 3
... average acceleration. Given: vi = 0 m/s Find: a = ? vf = 30 m/s t = 10 s Equation : a = vf - vi t Solve : a = (30 m/s) - (0 m/s) 10 s a = 3 m/s² ...
... average acceleration. Given: vi = 0 m/s Find: a = ? vf = 30 m/s t = 10 s Equation : a = vf - vi t Solve : a = (30 m/s) - (0 m/s) 10 s a = 3 m/s² ...
types_of_questions
... balls are at the same horizontal level at the beginning of the experiment. The same quantity of heat is supplied to both balls. The change of temperature of both balls is same. (All kinds of heat losses are negligible) (see fig.) ...
... balls are at the same horizontal level at the beginning of the experiment. The same quantity of heat is supplied to both balls. The change of temperature of both balls is same. (All kinds of heat losses are negligible) (see fig.) ...
Work & Energy
... Two blocks, A and B (mA=50 kg and mB=100 kg), are connected by a string as shown. If the blocks begin at rest, what will their speeds be after A has slid a distance s = 0.25 m? Assume the pulley and incline are frictionless. ...
... Two blocks, A and B (mA=50 kg and mB=100 kg), are connected by a string as shown. If the blocks begin at rest, what will their speeds be after A has slid a distance s = 0.25 m? Assume the pulley and incline are frictionless. ...
Document
... The root-mean-square voltages across the resistor R, capacitor C and inductor L of an RCL series circuit are respectively 4 V, 1 V and 4 V. What is the phase difference between the applied voltage and the current flowing in the circuit? ...
... The root-mean-square voltages across the resistor R, capacitor C and inductor L of an RCL series circuit are respectively 4 V, 1 V and 4 V. What is the phase difference between the applied voltage and the current flowing in the circuit? ...
Gravity PP
... – Maintained - constant force exerted on object – Force (perpendicular to the velocity as the direction of the velocity changes) – Force - directed towards the center of the circle ...
... – Maintained - constant force exerted on object – Force (perpendicular to the velocity as the direction of the velocity changes) – Force - directed towards the center of the circle ...
Special Relativity
... (Cartesian Frames S & S'. Two points in S, A and B. A is at x1 and t1, and B is at x2 and t2. A reference frame S' moving at v) Suppose the two events A and B occur simultaneously in S. If in S events would occur at a time interval dt. dt'=(dt-v.dx/cý)/(1-(vý/cý))^« However simultaneity in S means t ...
... (Cartesian Frames S & S'. Two points in S, A and B. A is at x1 and t1, and B is at x2 and t2. A reference frame S' moving at v) Suppose the two events A and B occur simultaneously in S. If in S events would occur at a time interval dt. dt'=(dt-v.dx/cý)/(1-(vý/cý))^« However simultaneity in S means t ...
Centripetal Force Mini Lab and Lecture EN
... How far does the ball travel in one rotation? How can we calculate the distance traveled by a circular path? ...
... How far does the ball travel in one rotation? How can we calculate the distance traveled by a circular path? ...
Chapter 4 Motion
... 17. Pluto is the smallest planet in the solar system. Infer whether you would feel lighter or heavier on Pluto than on Earth. Explain why. 18. How can a race-car driver keep the same engine (the force) but increase the acceleration of the car? Identify the control variable and the test variable. ...
... 17. Pluto is the smallest planet in the solar system. Infer whether you would feel lighter or heavier on Pluto than on Earth. Explain why. 18. How can a race-car driver keep the same engine (the force) but increase the acceleration of the car? Identify the control variable and the test variable. ...
Fiz 235 Mechanics 2002
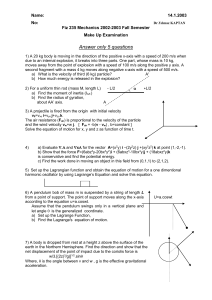
... Answer only 5 questions 1) A 20 kg body is moving in the direction of the positive x-axis with a speed of 200 m/s when due to an internal explosion, it breaks into three parts. One part, whose mass is 10 kg, moves away from the point of explosion with a speed of 100 m/s along the positive y axis. A ...
... Answer only 5 questions 1) A 20 kg body is moving in the direction of the positive x-axis with a speed of 200 m/s when due to an internal explosion, it breaks into three parts. One part, whose mass is 10 kg, moves away from the point of explosion with a speed of 100 m/s along the positive y axis. A ...