PHYS-2020: General Physics II Course Lecture Notes Section IX Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser
... detect it — either the Ether moved with the Earth, or the Ether didn’t exist. Einstein chose the latter and used this fact as one of the underlying principles to relativity. ...
... detect it — either the Ether moved with the Earth, or the Ether didn’t exist. Einstein chose the latter and used this fact as one of the underlying principles to relativity. ...
Review
... reference frame. Both would agree on measurements of space and time intervals between given events, so we say they share the same realm of spacetime. ...
... reference frame. Both would agree on measurements of space and time intervals between given events, so we say they share the same realm of spacetime. ...
Lecture 17
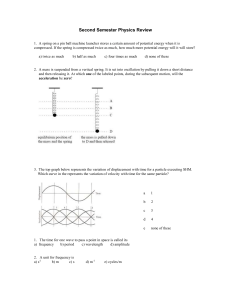
... A small wheel and a large wheel are connected by a belt. The small wheel is turned at a constant angular velocity s. How does the magnitude of the angular velocity of the large wheel L compare to that of the small wheel? ...
... A small wheel and a large wheel are connected by a belt. The small wheel is turned at a constant angular velocity s. How does the magnitude of the angular velocity of the large wheel L compare to that of the small wheel? ...
Example Midterm Solutions
... Solution: Depending on the angle of my friend’s travel, the time she measures the event to happen would be longer and the distance between the stars would appear shorter. 2. What are the two postulates of relativity? ...
... Solution: Depending on the angle of my friend’s travel, the time she measures the event to happen would be longer and the distance between the stars would appear shorter. 2. What are the two postulates of relativity? ...
PHYSICS 100
... Thin film interference occurs when light incident on a thin film is partially reflected at the top surface and partially transmitted through the film. The transmitted ray reflects off the bottom of the film and travels up and through the top of the film. The two reflected rays have a path length dif ...
... Thin film interference occurs when light incident on a thin film is partially reflected at the top surface and partially transmitted through the film. The transmitted ray reflects off the bottom of the film and travels up and through the top of the film. The two reflected rays have a path length dif ...
Student Number - Department of Mechanical Engineering
... 3. Answers are to be written in the spaces provided under each question. ...
... 3. Answers are to be written in the spaces provided under each question. ...
Electromagnetic radiation – the nature of light
... Electromagnetic radiation (sometimes abbreviated EMR) takes the form of self-propagating waves in a vacuum or in matter. EM radiation has an electric and magnetic field component which oscillate in phase perpendicular to each other and to the direction of energy propagation. ...
... Electromagnetic radiation (sometimes abbreviated EMR) takes the form of self-propagating waves in a vacuum or in matter. EM radiation has an electric and magnetic field component which oscillate in phase perpendicular to each other and to the direction of energy propagation. ...
test1
... _________________ acting on the object, and is inversely proportional to the ___________ of the object. B) Every object continues in a state of rest or of _____________ _____________ in a straight line unless acted on by a _______________ __________ ________________. This law is also known as the la ...
... _________________ acting on the object, and is inversely proportional to the ___________ of the object. B) Every object continues in a state of rest or of _____________ _____________ in a straight line unless acted on by a _______________ __________ ________________. This law is also known as the la ...
PowerPoint Lecture Chapter 3
... C. Velocity- speed of the object and its direction 1. is a vector quantity 2. Size of objects velocity is speed 3. Object will have different velocities if have different speeds or move in different directions ...
... C. Velocity- speed of the object and its direction 1. is a vector quantity 2. Size of objects velocity is speed 3. Object will have different velocities if have different speeds or move in different directions ...
exercises1
... same direction and sense of A. determine: i) In which time B reaches A; ii) which is the distance travelled for the two bodies at the moment when they meet What is the average speed of B in the section between its origin and the achievement of A. [t = 90 s; sA = 900 m= sB ; v =30 m/s] B5) ...
... same direction and sense of A. determine: i) In which time B reaches A; ii) which is the distance travelled for the two bodies at the moment when they meet What is the average speed of B in the section between its origin and the achievement of A. [t = 90 s; sA = 900 m= sB ; v =30 m/s] B5) ...
Unit B: Energy Flow in Technological Systems
... slide is 4.00 m, what is the gravitation potential energy of the child relative to the ground? ...
... slide is 4.00 m, what is the gravitation potential energy of the child relative to the ground? ...
Freefall
... • Assume no air resistance during freefall, so acceleration due to gravity is a constant 10 m/s2 • Assume object start from rest (initial velocity will be zero) • Velocity can be calculated at any instant (v=gt) • Distance traveled can be calculated at any instant (d = ½ gt2) ...
... • Assume no air resistance during freefall, so acceleration due to gravity is a constant 10 m/s2 • Assume object start from rest (initial velocity will be zero) • Velocity can be calculated at any instant (v=gt) • Distance traveled can be calculated at any instant (d = ½ gt2) ...
Blackbody Radiation
... • Blackbody radiation (and problems understanding it) actually led to quantum physics ...
... • Blackbody radiation (and problems understanding it) actually led to quantum physics ...
The Theory of Anti-Relativity, Chapter 1
... “certain complication”. It was found that when far outside the Earth’s field of influence the stars and sun are NOT VISIBLE! However, the Earth and the Moon are plainly visible. No direct light in outer space, only that made visible by gross physical matter. This gives rise to an important question, ...
... “certain complication”. It was found that when far outside the Earth’s field of influence the stars and sun are NOT VISIBLE! However, the Earth and the Moon are plainly visible. No direct light in outer space, only that made visible by gross physical matter. This gives rise to an important question, ...
$doc.title
... L ? The radiation force is exerted via Thomson scattering of photons on free electrons (cross section σ Τ ). After each scatter, a photon is equally likely to recoil forward or backward. d. The ...
... L ? The radiation force is exerted via Thomson scattering of photons on free electrons (cross section σ Τ ). After each scatter, a photon is equally likely to recoil forward or backward. d. The ...
CH11 Notes - Moline High School
... Net force – all the forces acting on an object Balanced forces – net force equal to zero - no change in motion Unbalanced forces – net forces does not equal ...
... Net force – all the forces acting on an object Balanced forces – net force equal to zero - no change in motion Unbalanced forces – net forces does not equal ...
POP4e: Ch. 1 Problems
... the top of the building before striking the ground at point B. If air resistance is negligible, what is the value of the kinetic energy of the ball at B minus the kinetic energy of the ball at A (K B - KA)? ...
... the top of the building before striking the ground at point B. If air resistance is negligible, what is the value of the kinetic energy of the ball at B minus the kinetic energy of the ball at A (K B - KA)? ...