Document
... (R – Radius of the Earth) The mass m of the falling object cancels out and does not matter; therefore all objects fall at the same rate or acceleration g = GM / R2 i.e. constant acceleration due to gravity 9.8 m/sec2 ...
... (R – Radius of the Earth) The mass m of the falling object cancels out and does not matter; therefore all objects fall at the same rate or acceleration g = GM / R2 i.e. constant acceleration due to gravity 9.8 m/sec2 ...
File
... A metre stick is balanced on a knife edge at its centre. When two coins, each of mass 5 g are put one on top of the other at the 12.0 cm mark, the stick is found to be balanced at 45.0 cm. What is the mass of the metre stick? Given the moment of inertia of a disc of mass M and radius R about any of ...
... A metre stick is balanced on a knife edge at its centre. When two coins, each of mass 5 g are put one on top of the other at the 12.0 cm mark, the stick is found to be balanced at 45.0 cm. What is the mass of the metre stick? Given the moment of inertia of a disc of mass M and radius R about any of ...
Sample problems
... 12. An automobile of mass 2 000 kg moving at 20 m/s is braked suddenly with a constant braking force of 5 000 N. How far does the car travel before stopping? a. 2.5 m b. 66 m c. 80 m d. 20 m e. 102 m 13. A 5-kg object is moving at 7 m/s. A 2-N force is applied in the opposite direction of motion an ...
... 12. An automobile of mass 2 000 kg moving at 20 m/s is braked suddenly with a constant braking force of 5 000 N. How far does the car travel before stopping? a. 2.5 m b. 66 m c. 80 m d. 20 m e. 102 m 13. A 5-kg object is moving at 7 m/s. A 2-N force is applied in the opposite direction of motion an ...
here - Physics at PMB
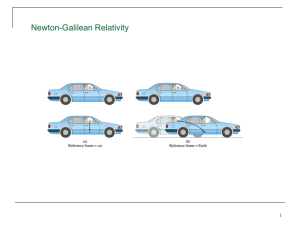
... we start measuring these properties. The Cartesian coordinate system may be considered as a frame of reference where its origin is a reference point and the x-, y-, and z-axes are the directions the object may take. In this section we will consider the motion of objects in one direction (i.e. one di ...
... we start measuring these properties. The Cartesian coordinate system may be considered as a frame of reference where its origin is a reference point and the x-, y-, and z-axes are the directions the object may take. In this section we will consider the motion of objects in one direction (i.e. one di ...
CHEM 5181 – Fall 2009
... e. What is the frequency and wavelength of a photon with an energy of 5 eV? Which region of the electromagnetic spectrum is the photon in? f. Same as previous but with 10 eV g. What is the speed of an electron with 70 eV of kinetic energy? h. What is the speed of an SF6+ ion with 70 eV of kinetic en ...
... e. What is the frequency and wavelength of a photon with an energy of 5 eV? Which region of the electromagnetic spectrum is the photon in? f. Same as previous but with 10 eV g. What is the speed of an electron with 70 eV of kinetic energy? h. What is the speed of an SF6+ ion with 70 eV of kinetic en ...
Problems for workgroup sessions during week of September 13, 2004
... from 4 to 11 hrs (c) Determine the car's average speed for its entire 11-hour motion. (d) Sketch the velocity versus time graph corresponding to this motion. (e) From the graph below, estimate the average acceleration in the interval from 1 to 3 hours. (f) At what times is the magnitude of the accel ...
... from 4 to 11 hrs (c) Determine the car's average speed for its entire 11-hour motion. (d) Sketch the velocity versus time graph corresponding to this motion. (e) From the graph below, estimate the average acceleration in the interval from 1 to 3 hours. (f) At what times is the magnitude of the accel ...
Motion - Cloudfront.net
... 1. The motion of an object over a period of time can be shown on a distance-time graph 2. Distance is plotted on the vertical axis (y) ...
... 1. The motion of an object over a period of time can be shown on a distance-time graph 2. Distance is plotted on the vertical axis (y) ...
Document
... 5. The coordinate of an object is given as a function of time by x = 4t 2 - 3t3 , where x is in meters and t is in seconds. Its average acceleration over the interval from t = 0 to t = 2s is: 6. Starting at time t = 0, and object moves along a straight line with velocity in m/s given by v(t) = 98 - ...
... 5. The coordinate of an object is given as a function of time by x = 4t 2 - 3t3 , where x is in meters and t is in seconds. Its average acceleration over the interval from t = 0 to t = 2s is: 6. Starting at time t = 0, and object moves along a straight line with velocity in m/s given by v(t) = 98 - ...
90mc
... C. The gas in Y has a higher temperature than X. D. The gas in Y has a higher pressure than X. E. The gases in X and Y are at the same temperature. ...
... C. The gas in Y has a higher temperature than X. D. The gas in Y has a higher pressure than X. E. The gases in X and Y are at the same temperature. ...
Problem 1: Kinematics (15 pts) A particle moves along a straight line
... flows east with speed VW . A boat cross the river from port A to port B. The speed of the boat relative to the water is VB . Assume VB = 2VW . State all your answers in terms of VB and D. (a) What is the direction of the boat, θ, relative to the North so that it crosses directly on a line from A to B ...
... flows east with speed VW . A boat cross the river from port A to port B. The speed of the boat relative to the water is VB . Assume VB = 2VW . State all your answers in terms of VB and D. (a) What is the direction of the boat, θ, relative to the North so that it crosses directly on a line from A to B ...
Slide 1
... Energy and free fall 11) How fast would something be moving if it accelerated at 1g, for a distance equal to the Earth’s diameter? Easy! Just balance P.E. and K.E. mgh = ½mv2 gD = ½v2 v2 = 2gD, so ...
... Energy and free fall 11) How fast would something be moving if it accelerated at 1g, for a distance equal to the Earth’s diameter? Easy! Just balance P.E. and K.E. mgh = ½mv2 gD = ½v2 v2 = 2gD, so ...
Sample Final 105_fall 2009 1. One mile is equal to 1609 meters
... 12. An automobile of mass 2 000 kg moving at 20 m/s is braked suddenly with a constant braking force of 5 000 N. How far does the car travel before stopping? a. 2.5 m b. 66 m c. 80 m d. 20 m e. 102 m 13. A 5-kg object is moving at 7 m/s. A 2-N force is applied in the opposite direction of motion an ...
... 12. An automobile of mass 2 000 kg moving at 20 m/s is braked suddenly with a constant braking force of 5 000 N. How far does the car travel before stopping? a. 2.5 m b. 66 m c. 80 m d. 20 m e. 102 m 13. A 5-kg object is moving at 7 m/s. A 2-N force is applied in the opposite direction of motion an ...
kines_lecture_four_note_Mr_Bolu_shs_306
... the same position when the body moves from one position to another, the motion is linear. ...
... the same position when the body moves from one position to another, the motion is linear. ...
c - Telkom University
... Relativistic Momentum The conservation of linear momentum requires the total change in momentum of the collision, ΔpF + ΔpM, to be zero. The addition of Equations (2.40) and (2.44) clearly does not give zero. Linear momentum is not conserved if we use the conventions for momentum from classical ...
... Relativistic Momentum The conservation of linear momentum requires the total change in momentum of the collision, ΔpF + ΔpM, to be zero. The addition of Equations (2.40) and (2.44) clearly does not give zero. Linear momentum is not conserved if we use the conventions for momentum from classical ...