Forces and Motion Commotion 2012
... 1. Describe and measure motion using the concept of a reference point. 2. Describe and measure speed and be able to calculate speed. (Know what 2 factors –distance and time—on which speed depends.) 3. Graph motion showing changes in distance as a function of time (This means know how to graph speed! ...
... 1. Describe and measure motion using the concept of a reference point. 2. Describe and measure speed and be able to calculate speed. (Know what 2 factors –distance and time—on which speed depends.) 3. Graph motion showing changes in distance as a function of time (This means know how to graph speed! ...
P5 Key facts sheets: RAG - North Leamington School
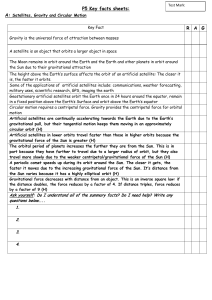
... Refractive index is a measure of the amount of refraction after a boundary Refractive index = c ÷ v (where c = speed of light in a vacuum, v = speed of light in the medium. e.g. glass) Dispersion happens when light is refracted. This is where refraction splits light into all the spectral colours and ...
... Refractive index is a measure of the amount of refraction after a boundary Refractive index = c ÷ v (where c = speed of light in a vacuum, v = speed of light in the medium. e.g. glass) Dispersion happens when light is refracted. This is where refraction splits light into all the spectral colours and ...
Document
... at the top of a cliff, swings down at the end of a rope, releases it, and falls into the water below. There are two paths by which the person can enter the water. Suppose he enters the water at a speed of 10.0 m/s via path 1. How fast is he moving on path 2 when he releases the rope at a height of 3 ...
... at the top of a cliff, swings down at the end of a rope, releases it, and falls into the water below. There are two paths by which the person can enter the water. Suppose he enters the water at a speed of 10.0 m/s via path 1. How fast is he moving on path 2 when he releases the rope at a height of 3 ...
Physics Review Powerpoint
... An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion continues in motion with constant velocity (that is, constant speed in a straight line) unless it experiences a net external force. Also known as the “Law of Inertia” ...
... An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion continues in motion with constant velocity (that is, constant speed in a straight line) unless it experiences a net external force. Also known as the “Law of Inertia” ...
Ch. 2-3
... 2. Newton was the first to discover the notion of _________ or an object’s resistance to motion. 3. During free fall an object accelerates toward the Earth at this rate: __________ 4. Velocity differs from speed in that velocity has a ___________. 5. Newton’s Second Law states the acceleration is __ ...
... 2. Newton was the first to discover the notion of _________ or an object’s resistance to motion. 3. During free fall an object accelerates toward the Earth at this rate: __________ 4. Velocity differs from speed in that velocity has a ___________. 5. Newton’s Second Law states the acceleration is __ ...
Student notes Chap 1 & 2
... km/h to zero in 0.1 s is equal to 14 times the force that gravity exerts on the person • belt loosens a little as it restrains the person, increasing the time it takes to slow the person down • this reduces force exerted on the person • safety belt also prevents the person from being thrown out of t ...
... km/h to zero in 0.1 s is equal to 14 times the force that gravity exerts on the person • belt loosens a little as it restrains the person, increasing the time it takes to slow the person down • this reduces force exerted on the person • safety belt also prevents the person from being thrown out of t ...
Physics 122 – Review Sheets
... A 12.0 W lamp operates on a 6.0 V circuit. What current flows through it? How much energy would be used in 5.0 min.? (2.0 A, 3.6 x 103 J) ...
... A 12.0 W lamp operates on a 6.0 V circuit. What current flows through it? How much energy would be used in 5.0 min.? (2.0 A, 3.6 x 103 J) ...
Unit 5 Problem Set
... P4. A fire hose sends 20.0 kg of water per second onto a burning building. The water strikes the roof horizontally at 40.0 m/s and is deflected 60.0° as shown in Figure P6.17. What are the magnitude and direction of the force exerted by the water on the roof? [Hint: Treat the horizontal and vertical ...
... P4. A fire hose sends 20.0 kg of water per second onto a burning building. The water strikes the roof horizontally at 40.0 m/s and is deflected 60.0° as shown in Figure P6.17. What are the magnitude and direction of the force exerted by the water on the roof? [Hint: Treat the horizontal and vertical ...
PHY203F08 Exam 3 Name
... 3. A pitcher throws a baseball with a speed of 27 m/s. After being struck by a bat the ball travels in the opposite direction with a speed of 40 m/s. If the ball has a mass of 0.11 kg and is in contact with the bat for 3.0 ms, the average force exerted by the bat on the ball is A) 0.99 kN B) 4.8 kN ...
... 3. A pitcher throws a baseball with a speed of 27 m/s. After being struck by a bat the ball travels in the opposite direction with a speed of 40 m/s. If the ball has a mass of 0.11 kg and is in contact with the bat for 3.0 ms, the average force exerted by the bat on the ball is A) 0.99 kN B) 4.8 kN ...
Unit 4 SG
... stops for 4 seconds to drink water, and then takes off running at 4 m/s for 2 seconds. ...
... stops for 4 seconds to drink water, and then takes off running at 4 m/s for 2 seconds. ...
Honors Physics Midterm
... 17. A centrifuge is spinning with an initial angular velocity of 600 revolutions per minute. The motor is turned off, and the centrifuge stops spinning after 100 seconds. What is the angular acceleration of the centrifuge? a) -6 rad/s 2 b) -0.16 rad/s2 c) -0.628 rad/s2 d) -1.59 rad/s2 18. A CD start ...
... 17. A centrifuge is spinning with an initial angular velocity of 600 revolutions per minute. The motor is turned off, and the centrifuge stops spinning after 100 seconds. What is the angular acceleration of the centrifuge? a) -6 rad/s 2 b) -0.16 rad/s2 c) -0.628 rad/s2 d) -1.59 rad/s2 18. A CD start ...