Motion and Forces
... Gravitational force is determined by the distance between the two masses. Everything falls at an acceleration of 9.8 m/s2 in the absence of air resistance Gravity is opposed by air resistance ...
... Gravitational force is determined by the distance between the two masses. Everything falls at an acceleration of 9.8 m/s2 in the absence of air resistance Gravity is opposed by air resistance ...
Speed and Velocity
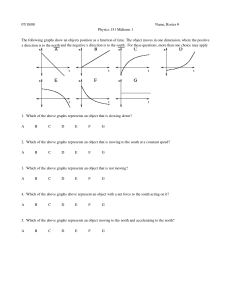
... You can show the motion of an object on a line graph in which you plot distance versus time. Time is shown on the horizontal axis, or x-axis. Distance is shown on the vertical axis, or y-axis. A point on the line represents the distance an object has traveled at a particular time. The x value of the ...
... You can show the motion of an object on a line graph in which you plot distance versus time. Time is shown on the horizontal axis, or x-axis. Distance is shown on the vertical axis, or y-axis. A point on the line represents the distance an object has traveled at a particular time. The x value of the ...
The Milky Way - Computer Science Technology
... wouldn’t have had so much trouble describing the motion of the planets, but that insight didn’t appear until three decades after the trial of Galileo. Isaac Newton started from the work of Galileo, and devised a way to explain motion and gravity that allowed astronomers to understand orbits and tide ...
... wouldn’t have had so much trouble describing the motion of the planets, but that insight didn’t appear until three decades after the trial of Galileo. Isaac Newton started from the work of Galileo, and devised a way to explain motion and gravity that allowed astronomers to understand orbits and tide ...
Conceptual Physics first Semester Review #1
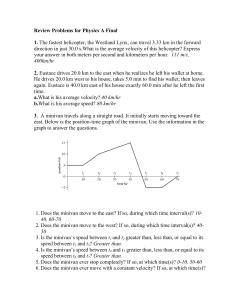
... In the graph above, what does the slope of the line represent? A. displacement B. average velocity C. acceleration D. distance 14. Displacement is a A. scalar B. vector C. distance D. force 15. A tile falls freely from rest from the roof of a building. What is the total distance the tile falls in th ...
... In the graph above, what does the slope of the line represent? A. displacement B. average velocity C. acceleration D. distance 14. Displacement is a A. scalar B. vector C. distance D. force 15. A tile falls freely from rest from the roof of a building. What is the total distance the tile falls in th ...
MOTION - pdsd.org
... 3. Tire traction: the friction between the tires and the surface of the road that allows your car to accelerate, slow down, and negotiate turns and corners. 4. Static friction: the friction between two surfaces that prevents items on less-than-perfectly-level tables and shelves from sliding off. Als ...
... 3. Tire traction: the friction between the tires and the surface of the road that allows your car to accelerate, slow down, and negotiate turns and corners. 4. Static friction: the friction between two surfaces that prevents items on less-than-perfectly-level tables and shelves from sliding off. Als ...
Circular Motion
... circular motion. It simulates a common physics demonstration involving identical masses on a horizontal turntable located at different distances from center. The initial question asks which mass will slide off the turntable first, as the rotation rate increases. As the turntable accelerates, a Frict ...
... circular motion. It simulates a common physics demonstration involving identical masses on a horizontal turntable located at different distances from center. The initial question asks which mass will slide off the turntable first, as the rotation rate increases. As the turntable accelerates, a Frict ...
Physics 150
... of the ramp. 7. A 1 kg ball is released from a height of 1 m above a trampoline. After hitting the trampoline surface, the ball rebounds to a height of 2 m. About how much energy was added to the ball by the trampoline? 8. Show that a bullet fired from a gun with muzzle speed v and a bullet dropped ...
... of the ramp. 7. A 1 kg ball is released from a height of 1 m above a trampoline. After hitting the trampoline surface, the ball rebounds to a height of 2 m. About how much energy was added to the ball by the trampoline? 8. Show that a bullet fired from a gun with muzzle speed v and a bullet dropped ...
Acceleration
... • Now consider an object thrown straight up. It will continue to move straight up, then it comes back down. • At the highest point, the object changes its direction and the objects instantaneous speed is 0 m/s. • Whether the object is moving up or down, the acceleration of the object is always 10 m ...
... • Now consider an object thrown straight up. It will continue to move straight up, then it comes back down. • At the highest point, the object changes its direction and the objects instantaneous speed is 0 m/s. • Whether the object is moving up or down, the acceleration of the object is always 10 m ...
Worksheet on W=mgh
... the force that is parallel to the object’s motion is used to determine the work on the object. Work is defined as negative when the force is in the direction opposite the displacement. Friction forces always do negative work on an object. When things move against gravity, gravity is said to do negat ...
... the force that is parallel to the object’s motion is used to determine the work on the object. Work is defined as negative when the force is in the direction opposite the displacement. Friction forces always do negative work on an object. When things move against gravity, gravity is said to do negat ...
PHE-01 (2007
... 5. (a) Calculate the gravitational force and the electrical force between two electrons 1.0 cm apart and compare them. ...
... 5. (a) Calculate the gravitational force and the electrical force between two electrons 1.0 cm apart and compare them. ...
PHE-01 (2007)
... 5. (a) Calculate the gravitational force and the electrical force between two electrons 1.0 cm apart and compare them. ...
... 5. (a) Calculate the gravitational force and the electrical force between two electrons 1.0 cm apart and compare them. ...
Physical Science Final Study Guide I KEY Name __ ___
... a. Strange intermolecular forces b. Pushing air out of the way c. Rough surfaces getting caught on each other d. Gravity 4. The 2 main kinds of friction are STATIC (not moving) and KINETIC (moving) friction 5. Give a situation where friction is good. a. STOPPING A CAR, WALKING 6. Give a situation wh ...
... a. Strange intermolecular forces b. Pushing air out of the way c. Rough surfaces getting caught on each other d. Gravity 4. The 2 main kinds of friction are STATIC (not moving) and KINETIC (moving) friction 5. Give a situation where friction is good. a. STOPPING A CAR, WALKING 6. Give a situation wh ...
264-lecture-2015-08-30
... As a photon from a remote star approaches the Sun, the photon’s speed v A. stays constant B. increases C. decreases ...
... As a photon from a remote star approaches the Sun, the photon’s speed v A. stays constant B. increases C. decreases ...
10 Motion Trial Test
... What is the potential energy of the mass before it is dropped? Assuming all the potential energy of the b object is converted to kinetic energy, what is the speed of the ball as it reaches the ground? To what form or forms of energy is the c kinetic energy of the ball converted after ...
... What is the potential energy of the mass before it is dropped? Assuming all the potential energy of the b object is converted to kinetic energy, what is the speed of the ball as it reaches the ground? To what form or forms of energy is the c kinetic energy of the ball converted after ...
FOSS Force and Motion Course Glossary
... net force: The sum of all the forces acting on a mass. newton (N): The unit used to measure force in the metric system. Newton’s laws of motion: 1. Objects remain in uniform motion (at rest or constant velocity) until acted on by a net force. 2. A net force exerted on an object results in accelerat ...
... net force: The sum of all the forces acting on a mass. newton (N): The unit used to measure force in the metric system. Newton’s laws of motion: 1. Objects remain in uniform motion (at rest or constant velocity) until acted on by a net force. 2. A net force exerted on an object results in accelerat ...
Force and Drag 1. Define the newton
... The figure below shows the horizontal forces acting on a car of mass 900 kg when it is travelling at a particular velocity on a level road. ...
... The figure below shows the horizontal forces acting on a car of mass 900 kg when it is travelling at a particular velocity on a level road. ...
Exam Review - Dublin Schools
... object. It experiences a resistance force due to friction of 13N. ...
... object. It experiences a resistance force due to friction of 13N. ...
Force and Newton`s First Law
... On earth, this is 9.8 m/s2 - Gravity constant In the absence of air resistance, all objects on Earth accelerate at the same rate, regardless of their mass. An object reaches its terminal velocity when the force of gravity is balanced by the force of air resistance ...
... On earth, this is 9.8 m/s2 - Gravity constant In the absence of air resistance, all objects on Earth accelerate at the same rate, regardless of their mass. An object reaches its terminal velocity when the force of gravity is balanced by the force of air resistance ...