Microsoft Word - Mapping-Traits-in-Dogs
... Ostrander, Ph.D., chief of the Cancer Genetics Branch in NHGRI's Division of Intramural Research. "We think this approach will help pinpoint multiple genes involved in complex human conditions, such as cancer, heart disease, diabetes and obesity." Artificial selection, at the heart of breeding for d ...
... Ostrander, Ph.D., chief of the Cancer Genetics Branch in NHGRI's Division of Intramural Research. "We think this approach will help pinpoint multiple genes involved in complex human conditions, such as cancer, heart disease, diabetes and obesity." Artificial selection, at the heart of breeding for d ...
"Frontmatter". In: Plant Genomics and Proteomics
... single model or small number of models, will be important in developing an understanding of the functional and evolutionary constraints on genome size in plants. Despite this enormous variation in DNA content per cell, it is generally accepted that most plants have about the same number of genes and ...
... single model or small number of models, will be important in developing an understanding of the functional and evolutionary constraints on genome size in plants. Despite this enormous variation in DNA content per cell, it is generally accepted that most plants have about the same number of genes and ...
View PDF - Genetics
... Plastids carry reduced genomes that reflect an evolutionary history of extensive gene loss and transfer to the nucleus since their ancient endosymbiotic origin roughly one billion years ago (Timmis et al. 2004; Keeling 2010; Gray and Archibald 2012). Many of the proteins encoded by genes that have ...
... Plastids carry reduced genomes that reflect an evolutionary history of extensive gene loss and transfer to the nucleus since their ancient endosymbiotic origin roughly one billion years ago (Timmis et al. 2004; Keeling 2010; Gray and Archibald 2012). Many of the proteins encoded by genes that have ...
SEARCH_16S: A new algorithm for identifying 16S
... http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/RNAmmer/. I downloaded these predictions on 15th Dec. 2016 and found that the files were dated 14th Jan. 2014 despite the statement on that page that it is updated daily. Only 978 genomes were included, far fewer than the 6,487 complete genome assemblies currently avai ...
... http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/RNAmmer/. I downloaded these predictions on 15th Dec. 2016 and found that the files were dated 14th Jan. 2014 despite the statement on that page that it is updated daily. Only 978 genomes were included, far fewer than the 6,487 complete genome assemblies currently avai ...
Ezekiel Code with DNA Molecule: Fifteen Similarities
... Ezekiel described the four living creatures: “Their wings were spread out upward; … one touching the wing of another creature on either side.” “and each had two wings covering its body”. The biological scientist described the four nucleotides in a DNA molecule: One kind of the chemical bonds is betw ...
... Ezekiel described the four living creatures: “Their wings were spread out upward; … one touching the wing of another creature on either side.” “and each had two wings covering its body”. The biological scientist described the four nucleotides in a DNA molecule: One kind of the chemical bonds is betw ...
Lecture Presentation to accompany Principles of Life
... Concept 9.3 Mutations Are Heritable Changes in DNA ...
... Concept 9.3 Mutations Are Heritable Changes in DNA ...
Horizontal transfer of non-LTR retrotransposons: artifact or rare event
... Malik et al. (1999) first used the term “clade” for groups of non-LTR retrotransposons, which have high phylogenetic support, share the same structural features, and are estimated to date back to the Precambrian time (older than ~570 Myr). Based on the phylogenetic analysis of RT domains, 23 diverse ...
... Malik et al. (1999) first used the term “clade” for groups of non-LTR retrotransposons, which have high phylogenetic support, share the same structural features, and are estimated to date back to the Precambrian time (older than ~570 Myr). Based on the phylogenetic analysis of RT domains, 23 diverse ...
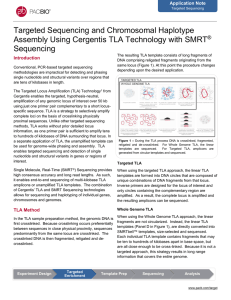
Application Note: Targeted sequencing and chromosomal haplotype
... Each individual TLA template contains fragments that may be ten to hundreds of kilobases apart in base space, but are all close enough to be cross-linked. Because it is not a targeted approach, this strategy results in long range information that covers the entire genome. ...
... Each individual TLA template contains fragments that may be ten to hundreds of kilobases apart in base space, but are all close enough to be cross-linked. Because it is not a targeted approach, this strategy results in long range information that covers the entire genome. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - LSU Museum of Natural Science
... copy of chromosome 4 had attached to the end of chromosome 2. It lost its centromere. Diagram all members of chromosomes II and IV during synapsis in Meiosis I -chromosomes replicated -two pairs of sister chromatids for II -one pair of sister chromatids for IV ...
... copy of chromosome 4 had attached to the end of chromosome 2. It lost its centromere. Diagram all members of chromosomes II and IV during synapsis in Meiosis I -chromosomes replicated -two pairs of sister chromatids for II -one pair of sister chromatids for IV ...
PDF
... cus, and several eukaryotic genomes. ung gene was determined and is presented in this paper. The open reading frame of the gene, confirmed by N-terminal protein sequence analysis, codes for a protein of25,664 Da DNA glycosylases excise damaged or unconventional bases which contains a single cysteine ...
... cus, and several eukaryotic genomes. ung gene was determined and is presented in this paper. The open reading frame of the gene, confirmed by N-terminal protein sequence analysis, codes for a protein of25,664 Da DNA glycosylases excise damaged or unconventional bases which contains a single cysteine ...
Risks from GMOs due to Horizontal Gene Transfer
... Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) is the stable transfer of genetic material from one organism to another without reproduction or human intervention. Transfer occurs by the passage of donor genetic material across cellular boundaries, followed by heritable incorporation to the genome of the recipient o ...
... Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) is the stable transfer of genetic material from one organism to another without reproduction or human intervention. Transfer occurs by the passage of donor genetic material across cellular boundaries, followed by heritable incorporation to the genome of the recipient o ...
Ada Hamosh - scientia.global
... and then trying to determine how those samples related to each other, over time building up a map of related data points that could be used to pick out where on the genome the disease-causing mutation must lie. The advent of full-genome sequencing changed this immensely – geneticists now sequence DN ...
... and then trying to determine how those samples related to each other, over time building up a map of related data points that could be used to pick out where on the genome the disease-causing mutation must lie. The advent of full-genome sequencing changed this immensely – geneticists now sequence DN ...
OMIM® – The Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man
... and then trying to determine how those samples related to each other, over time building up a map of related data points that could be used to pick out where on the genome the disease-causing mutation must lie. The advent of full-genome sequencing changed this immensely – geneticists now sequence DN ...
... and then trying to determine how those samples related to each other, over time building up a map of related data points that could be used to pick out where on the genome the disease-causing mutation must lie. The advent of full-genome sequencing changed this immensely – geneticists now sequence DN ...
General - Bioinformatics Research Group at SRI International
... Phase II: Prune pathways unlikely to be present No/few unique enzymes Most pathway steps present because they are used in another pathway Pathway very unlikely to be present in this organism ...
... Phase II: Prune pathways unlikely to be present No/few unique enzymes Most pathway steps present because they are used in another pathway Pathway very unlikely to be present in this organism ...
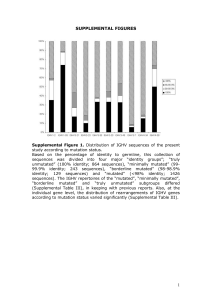
Supplementary Figures (doc 928K)
... The second example provides us with the opportunity to make some important remarks regarding the clustering procedure. Level 0 clusters are guaranteed to contain sequences that all share patterns between themselves, but are not guaranteed to contain all samples that display above-threshold identity ...
... The second example provides us with the opportunity to make some important remarks regarding the clustering procedure. Level 0 clusters are guaranteed to contain sequences that all share patterns between themselves, but are not guaranteed to contain all samples that display above-threshold identity ...
A unique pattern of intrastrand anomalies in base
... The polytene chromosomes are then fragmented, and ∼95% or more of the original micronuclear DNA sequence complexity is eliminated. These eliminated sequences are the spacers in micronuclear DNA between the successive genes. The ∼5% of sequence complexity that remains forms the gene-size molecules of ...
... The polytene chromosomes are then fragmented, and ∼95% or more of the original micronuclear DNA sequence complexity is eliminated. These eliminated sequences are the spacers in micronuclear DNA between the successive genes. The ∼5% of sequence complexity that remains forms the gene-size molecules of ...
02Spermatogenesistxt
... 12B2 The maturing spermatids remain attached by cytoplasmic bridges as they mature => syncytium ...
... 12B2 The maturing spermatids remain attached by cytoplasmic bridges as they mature => syncytium ...
Solutions to Genetics Day 6 Interpretation Questions
... Any change that prevents transposase from being expressed, any change that interferes with phage adsorption, any change that allowed the λ phage to form a lysogene or lyse the cells could have prevented random insertion from occurring. How was the non-random insertion of DNA into the bacterial genom ...
... Any change that prevents transposase from being expressed, any change that interferes with phage adsorption, any change that allowed the λ phage to form a lysogene or lyse the cells could have prevented random insertion from occurring. How was the non-random insertion of DNA into the bacterial genom ...
Kreitman review on positive selection
... referred to as polymorphism, and a nucleotide variation that distinguishes two alleles from different species, sometimes called the divergence or fixed differences, can be a subtle one. Polymorphism and divergence data can be viewed as providing information about evolution at different time depths i ...
... referred to as polymorphism, and a nucleotide variation that distinguishes two alleles from different species, sometimes called the divergence or fixed differences, can be a subtle one. Polymorphism and divergence data can be viewed as providing information about evolution at different time depths i ...
Differential roles of TGIF family genes in mammalian reproduction Open Access
... conserved downstream and upstream genes in most of species. Human genomic sequence encompassing MYOM1 (partial sequence and not shown)-TGIF1-DLGAP1 (chr18: 3,395,327-3,507,935) compared to the mouse (chr17: 71,147,775-71,255,269), opossum (chr3: 269,037,689269,144,991), platypus (Contig3116: 1-55,20 ...
... conserved downstream and upstream genes in most of species. Human genomic sequence encompassing MYOM1 (partial sequence and not shown)-TGIF1-DLGAP1 (chr18: 3,395,327-3,507,935) compared to the mouse (chr17: 71,147,775-71,255,269), opossum (chr3: 269,037,689269,144,991), platypus (Contig3116: 1-55,20 ...
Biomart/ GENOME ALIGNMENT III
... evolutionary history of species and in identifying functional regions in genomes. The possibilities for identifying regions under selection are enhanced with the addition of more sequences and this observation has led to numerous ‘focused sequencing’ projects which seek to obtain sequence for a smal ...
... evolutionary history of species and in identifying functional regions in genomes. The possibilities for identifying regions under selection are enhanced with the addition of more sequences and this observation has led to numerous ‘focused sequencing’ projects which seek to obtain sequence for a smal ...
16S rRNA Sequence Analysis of Bacteria Present in Foaming Activated Sludge Introduction
... reclassified from Rhodococcus maris by RAINEY et al. (1995). D. maris has been isolated as a dominant microbe from activated sludge foam (SEZGIN et al. 1988). In Group 2 clones 14 and 17 grouped with Nostocoida limicola II often associated with foaming activated sludge (SEVIOUR and BLACKALL, 1999). ...
... reclassified from Rhodococcus maris by RAINEY et al. (1995). D. maris has been isolated as a dominant microbe from activated sludge foam (SEZGIN et al. 1988). In Group 2 clones 14 and 17 grouped with Nostocoida limicola II often associated with foaming activated sludge (SEVIOUR and BLACKALL, 1999). ...
Human genome

The human genome is the complete set of nucleic acid sequence for humans (Homo sapiens), encoded as DNA within the 23 chromosome pairs in cell nuclei and in a small DNA molecule found within individual mitochondria. Human genomes include both protein-coding DNA genes and noncoding DNA. Haploid human genomes, which are contained in germ cells (the egg and sperm gamete cells created in the meiosis phase of sexual reproduction before fertilization creates a zygote) consist of three billion DNA base pairs, while diploid genomes (found in somatic cells) have twice the DNA content. While there are significant differences among the genomes of human individuals (on the order of 0.1%), these are considerably smaller than the differences between humans and their closest living relatives, the chimpanzees (approximately 4%) and bonobos. Humans share 50% of their DNA with bananas.The Human Genome Project produced the first complete sequences of individual human genomes, with the first draft sequence and initial analysis being published on February 12, 2001. The human genome was the first of all vertebrates to be completely sequenced. As of 2012, thousands of human genomes have been completely sequenced, and many more have been mapped at lower levels of resolution. The resulting data are used worldwide in biomedical science, anthropology, forensics and other branches of science. There is a widely held expectation that genomic studies will lead to advances in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases, and to new insights in many fields of biology, including human evolution.Although the sequence of the human genome has been (almost) completely determined by DNA sequencing, it is not yet fully understood. Most (though probably not all) genes have been identified by a combination of high throughput experimental and bioinformatics approaches, yet much work still needs to be done to further elucidate the biological functions of their protein and RNA products. Recent results suggest that most of the vast quantities of noncoding DNA within the genome have associated biochemical activities, including regulation of gene expression, organization of chromosome architecture, and signals controlling epigenetic inheritance.There are an estimated 20,000-25,000 human protein-coding genes. The estimate of the number of human genes has been repeatedly revised down from initial predictions of 100,000 or more as genome sequence quality and gene finding methods have improved, and could continue to drop further. Protein-coding sequences account for only a very small fraction of the genome (approximately 1.5%), and the rest is associated with non-coding RNA molecules, regulatory DNA sequences, LINEs, SINEs, introns, and sequences for which as yet no function has been elucidated.