Genomic imprinting of a placental lactogen gene in Peromyscus
... the parental alleles of a gene based on parent-of-origin (Bartolomei and Tilghman 1997). By rendering all imprinted loci functionally hemizygous, the evolution of imprinting in mammals imposes a survival cost to the organism. For this reason there has been intense debate about the function of imprin ...
... the parental alleles of a gene based on parent-of-origin (Bartolomei and Tilghman 1997). By rendering all imprinted loci functionally hemizygous, the evolution of imprinting in mammals imposes a survival cost to the organism. For this reason there has been intense debate about the function of imprin ...
Chapter 27 Phage Strategies
... • cascade – A sequence of events, each of which is stimulated by the previous one. – Transcriptional regulation is divided into stages, and at each stage one of the genes that is expressed encodes a regulator needed to express the genes of the next stage. FIGURE 03: Lytic development is a regulatory ...
... • cascade – A sequence of events, each of which is stimulated by the previous one. – Transcriptional regulation is divided into stages, and at each stage one of the genes that is expressed encodes a regulator needed to express the genes of the next stage. FIGURE 03: Lytic development is a regulatory ...
University of Birmingham Immunolabelling of human metaphase
... It remains uncertain whether the patterns of histone modification that define individual chromosome bands are a simple reflection of gene richness and/or ongoing transcription, or whether they play a determining role in chromatin packaging and intra-nuclear location at the Mb level. In this respect, ...
... It remains uncertain whether the patterns of histone modification that define individual chromosome bands are a simple reflection of gene richness and/or ongoing transcription, or whether they play a determining role in chromatin packaging and intra-nuclear location at the Mb level. In this respect, ...
genetic testing - NYU School of Medicine
... that encode the hemoglobin protein. The most commonly used genetic tests only provide information about those genes or chromosomes that doctors know are associated with disease. Whole Genome Sequencing The genome is the entire set of genetic instructions found in a cell. In humans, the genome consis ...
... that encode the hemoglobin protein. The most commonly used genetic tests only provide information about those genes or chromosomes that doctors know are associated with disease. Whole Genome Sequencing The genome is the entire set of genetic instructions found in a cell. In humans, the genome consis ...
publication
... the shuffling of exons during protein evolution. Allied with this hypothesis was the notion that exons encoded structural and/or functional domains of proteins. Although several notable examples of the latter have been demonstrated, and indeed the presence of introns in such cases could reasonably m ...
... the shuffling of exons during protein evolution. Allied with this hypothesis was the notion that exons encoded structural and/or functional domains of proteins. Although several notable examples of the latter have been demonstrated, and indeed the presence of introns in such cases could reasonably m ...
Tracking the evolution of 3D gene organization demonstrates its
... (6,7,11) and TF binding sites (8,12). In addition, genes encoding interacting proteins, that form protein complexes and genes along the same pathway have been shown to be co-localized in 3D in human (10). Chromosomes’ 3D conformation has been shown to be related to tissue-specific regulation (13,14) ...
... (6,7,11) and TF binding sites (8,12). In addition, genes encoding interacting proteins, that form protein complexes and genes along the same pathway have been shown to be co-localized in 3D in human (10). Chromosomes’ 3D conformation has been shown to be related to tissue-specific regulation (13,14) ...
Specialized adaptation of a lactic acid bacterium to the milk
... multiple lactic acid bacteria genomes sequencing project and comparative analysis [10]. The LMD-9 genome is comprised of a single circular chromosome (1,856,368 bp; 39.1% G + C) and two cryptic plasmids, pSTER_A (4,449 bp; 37.0% G + C) and pSTER_B (3,361 bp; 35.1% G + C) (Figure 1). Collectively, th ...
... multiple lactic acid bacteria genomes sequencing project and comparative analysis [10]. The LMD-9 genome is comprised of a single circular chromosome (1,856,368 bp; 39.1% G + C) and two cryptic plasmids, pSTER_A (4,449 bp; 37.0% G + C) and pSTER_B (3,361 bp; 35.1% G + C) (Figure 1). Collectively, th ...
Chromosomal Abnormalities
... 4. Find a partner to marry. Be sure this person has used two different colors for the parents. You will have one child with this person, sharing your chromosomes to create the next generation. Each of you will have to toss a coin to determine which of your parental chro-mosomes will be passed down i ...
... 4. Find a partner to marry. Be sure this person has used two different colors for the parents. You will have one child with this person, sharing your chromosomes to create the next generation. Each of you will have to toss a coin to determine which of your parental chro-mosomes will be passed down i ...
Significant enhancement of fatty acid composition in seeds of the
... was confirmed by DNA sequencing. Sequence analyses of DNA from leaf and seed samples (Data Set S2) confirmed multiple mutations over multiple generations at each of the three target sites in each of the three different FAD2 gene types present, respectively, in the A, B and C subgenomes of the allohe ...
... was confirmed by DNA sequencing. Sequence analyses of DNA from leaf and seed samples (Data Set S2) confirmed multiple mutations over multiple generations at each of the three target sites in each of the three different FAD2 gene types present, respectively, in the A, B and C subgenomes of the allohe ...
Genetics
... Download K2.4_2.0a Authored by Liz Lakin and Keith Ross, University of Gloucestershire. accessed from ...
... Download K2.4_2.0a Authored by Liz Lakin and Keith Ross, University of Gloucestershire. accessed from ...
univERsity oF copEnhAGEn
... reflect the expected relationship between human and primates (figure 8). ...
... reflect the expected relationship between human and primates (figure 8). ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... the functioning of several newly discovered genetic elements. As an increasing number of bacterial genomes become sequenced and new genetic elements get discovered, it is apparent that the lines between plasmid, bacteriophage, and transposon are becoming blurred when describing these new elements. T ...
... the functioning of several newly discovered genetic elements. As an increasing number of bacterial genomes become sequenced and new genetic elements get discovered, it is apparent that the lines between plasmid, bacteriophage, and transposon are becoming blurred when describing these new elements. T ...
BIOLOGY SUPPORT MATERIAL
... Ans: Specialized cells in diploid organism, i.e., gamete mother cell which undergo meiosis. 2- Name the kind of reproduction in bees by which drones are produced? Ans: Parthenogenesis. 3- What is special in flowering bamboo? Ans: Bamboo species flower only once in their life-times generally after 50 ...
... Ans: Specialized cells in diploid organism, i.e., gamete mother cell which undergo meiosis. 2- Name the kind of reproduction in bees by which drones are produced? Ans: Parthenogenesis. 3- What is special in flowering bamboo? Ans: Bamboo species flower only once in their life-times generally after 50 ...
Genetic Issues for Perinatal Nurses, 3 rd Edition
... DNA Structure and Replication • DNA provides the codes for proteins. It is a double helix made of two strands held together with chemical bonds. • DNA replicates by undoing the bonds and creating a complementary strand. • As the strands separate, one serves as a template for messenger RNA (mRNA), t ...
... DNA Structure and Replication • DNA provides the codes for proteins. It is a double helix made of two strands held together with chemical bonds. • DNA replicates by undoing the bonds and creating a complementary strand. • As the strands separate, one serves as a template for messenger RNA (mRNA), t ...
Heredity and the Environment
... The questions Daniel and Teri face cut to the very core of child development research. How much does a child's personality, intellectual functioning, and other characteristics depend on genes inherited from the child's biological parents? How much are these characteristics learned or modified from ...
... The questions Daniel and Teri face cut to the very core of child development research. How much does a child's personality, intellectual functioning, and other characteristics depend on genes inherited from the child's biological parents? How much are these characteristics learned or modified from ...
Isolation of DNA from A Single Helminth Using New Developed Kit
... tion by agarose gel electrophoresis may be more reliable. The amount of the extracted DNA was low, when the worms were used for the DNA extraction promptly after removing from 70% ethanol solution. The important critical point for the DNA extraction is to ensure that the worm is well disrupted, homo ...
... tion by agarose gel electrophoresis may be more reliable. The amount of the extracted DNA was low, when the worms were used for the DNA extraction promptly after removing from 70% ethanol solution. The important critical point for the DNA extraction is to ensure that the worm is well disrupted, homo ...
Genetic Control of Meat Quality Traits
... These are major welfare problems as well as threatening productivity. In addition, the inadvertent selection for genetic defects linked to desirable production characteristics is a potential risk, especially when selection programes focus on a limited number of breeding individuals. The traits that ...
... These are major welfare problems as well as threatening productivity. In addition, the inadvertent selection for genetic defects linked to desirable production characteristics is a potential risk, especially when selection programes focus on a limited number of breeding individuals. The traits that ...
MAK, a computational tool kit for automated MITE
... elements and the anchored elements. In the automated anchor finding process, a BLASTN is carried out at very low stringency (with high E_value, lowest word size, high hitlist_size, low gapcosts and a specified organism) for shortest hits possible. All HSPs that match either end of the query sequence ...
... elements and the anchored elements. In the automated anchor finding process, a BLASTN is carried out at very low stringency (with high E_value, lowest word size, high hitlist_size, low gapcosts and a specified organism) for shortest hits possible. All HSPs that match either end of the query sequence ...
Why Mitochondrial Genes are Most Often Found in Nuclei
... 1998). More to the point, an experimental system to study and quantify the transfer of sequences between mitochondrial and nuclear genomes in the yeast S. cerevisiae has been developed by Thorsness and Fox (1990, 1993). Thorsness and his collaborators have used this system to study a number of mutan ...
... 1998). More to the point, an experimental system to study and quantify the transfer of sequences between mitochondrial and nuclear genomes in the yeast S. cerevisiae has been developed by Thorsness and Fox (1990, 1993). Thorsness and his collaborators have used this system to study a number of mutan ...
Gene - Representing Genes
... fact that most mutations are recessive in the heterozygote. Hence, if an offspring derives a mutant allele of one gene from one parent and a mutant allele of another gene from the other parent, it should also receive a mutation-free, functional copy of each gene from the other parent and appear phen ...
... fact that most mutations are recessive in the heterozygote. Hence, if an offspring derives a mutant allele of one gene from one parent and a mutant allele of another gene from the other parent, it should also receive a mutation-free, functional copy of each gene from the other parent and appear phen ...
From Genetics to DNA
... of guanosine, as well as double-strand breaks. It has been estimated that in each human cell, about 500 bases suffer oxidative damage per day. Of these oxidative lesions, the most dangerous are double-strand breaks, as these lesions are difficult to repair and can produce point mutations, insertions ...
... of guanosine, as well as double-strand breaks. It has been estimated that in each human cell, about 500 bases suffer oxidative damage per day. Of these oxidative lesions, the most dangerous are double-strand breaks, as these lesions are difficult to repair and can produce point mutations, insertions ...
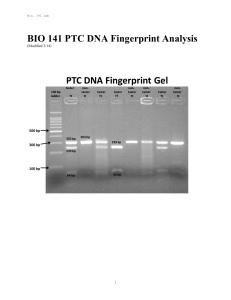
BIO 141 PTC DNA Fingerprint Analysis
... DNA’s structure resembles a twisted ladder called the double helix. DNA in all organisms consists of four bases called guanine, adenine, thymine, and cytosine. The unique order or sequence of these bases in an individual’s cells serves as the blueprint for that individual. Of the approximately 3.3 b ...
... DNA’s structure resembles a twisted ladder called the double helix. DNA in all organisms consists of four bases called guanine, adenine, thymine, and cytosine. The unique order or sequence of these bases in an individual’s cells serves as the blueprint for that individual. Of the approximately 3.3 b ...
Semiconservative Replication in the Quasispecies Model
... The formulation of the quasispecies equations given above are inadequate to describe evolution with doublestranded, semiconservatively replicated genomes. There are two reasons for this: First of all, because DNA is double-stranded, there is no well-defined Hamming distance between two DNA molecules ...
... The formulation of the quasispecies equations given above are inadequate to describe evolution with doublestranded, semiconservatively replicated genomes. There are two reasons for this: First of all, because DNA is double-stranded, there is no well-defined Hamming distance between two DNA molecules ...
How many genes in Arabidopsis come from cyanobacteria? An
... Chloroplasts are descendants of freeliving cyanobacteria, but they have highly reduced genomes. Higher plant chloroplast genomes encode about 80 proteins, the more diverse plastids among algae encode anywhere between 60 and 200 proteins, and nonphotosynthetic plastids encode as few as 23 proteins1. ...
... Chloroplasts are descendants of freeliving cyanobacteria, but they have highly reduced genomes. Higher plant chloroplast genomes encode about 80 proteins, the more diverse plastids among algae encode anywhere between 60 and 200 proteins, and nonphotosynthetic plastids encode as few as 23 proteins1. ...
Human genome

The human genome is the complete set of nucleic acid sequence for humans (Homo sapiens), encoded as DNA within the 23 chromosome pairs in cell nuclei and in a small DNA molecule found within individual mitochondria. Human genomes include both protein-coding DNA genes and noncoding DNA. Haploid human genomes, which are contained in germ cells (the egg and sperm gamete cells created in the meiosis phase of sexual reproduction before fertilization creates a zygote) consist of three billion DNA base pairs, while diploid genomes (found in somatic cells) have twice the DNA content. While there are significant differences among the genomes of human individuals (on the order of 0.1%), these are considerably smaller than the differences between humans and their closest living relatives, the chimpanzees (approximately 4%) and bonobos. Humans share 50% of their DNA with bananas.The Human Genome Project produced the first complete sequences of individual human genomes, with the first draft sequence and initial analysis being published on February 12, 2001. The human genome was the first of all vertebrates to be completely sequenced. As of 2012, thousands of human genomes have been completely sequenced, and many more have been mapped at lower levels of resolution. The resulting data are used worldwide in biomedical science, anthropology, forensics and other branches of science. There is a widely held expectation that genomic studies will lead to advances in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases, and to new insights in many fields of biology, including human evolution.Although the sequence of the human genome has been (almost) completely determined by DNA sequencing, it is not yet fully understood. Most (though probably not all) genes have been identified by a combination of high throughput experimental and bioinformatics approaches, yet much work still needs to be done to further elucidate the biological functions of their protein and RNA products. Recent results suggest that most of the vast quantities of noncoding DNA within the genome have associated biochemical activities, including regulation of gene expression, organization of chromosome architecture, and signals controlling epigenetic inheritance.There are an estimated 20,000-25,000 human protein-coding genes. The estimate of the number of human genes has been repeatedly revised down from initial predictions of 100,000 or more as genome sequence quality and gene finding methods have improved, and could continue to drop further. Protein-coding sequences account for only a very small fraction of the genome (approximately 1.5%), and the rest is associated with non-coding RNA molecules, regulatory DNA sequences, LINEs, SINEs, introns, and sequences for which as yet no function has been elucidated.