Why teach a course in bioinformatics?
... • An ORF is a sequence of codons in DNA that starts with a Start codon, ends with a Stop codon, and has no other Stop codons ...
... • An ORF is a sequence of codons in DNA that starts with a Start codon, ends with a Stop codon, and has no other Stop codons ...
Coarse-Graining of Macromolecules
... Genomic libraries constructed by chopping up DNA of interest with restriction enzymes and then gluing these fragments into the phage genome and then infecting cells with the modified phage. The phage DNA circularizes within E. coli and is then propagated from one generation of E. coli to the next an ...
... Genomic libraries constructed by chopping up DNA of interest with restriction enzymes and then gluing these fragments into the phage genome and then infecting cells with the modified phage. The phage DNA circularizes within E. coli and is then propagated from one generation of E. coli to the next an ...
Protein Synthesis PPT
... 3. Enzymes used for digestion and other chemical reactions are proteins (Enzymes speed up the rate of a reaction) 4. Component of all cell membranes ...
... 3. Enzymes used for digestion and other chemical reactions are proteins (Enzymes speed up the rate of a reaction) 4. Component of all cell membranes ...
Lesson
... * Stages involved with formation of proteins * Primary, secondary, tertiary & quaternary structures ...
... * Stages involved with formation of proteins * Primary, secondary, tertiary & quaternary structures ...
Protein and Amino Acid
... Proteins are complex molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. All proteins also contain approximately 16% nitrogen. This nitrogen consistency is the basis for the nitrogen balance test which is used to estimate an animal’s body protein status. Amino acids are the basis units of proteins a ...
... Proteins are complex molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. All proteins also contain approximately 16% nitrogen. This nitrogen consistency is the basis for the nitrogen balance test which is used to estimate an animal’s body protein status. Amino acids are the basis units of proteins a ...
protein/power point
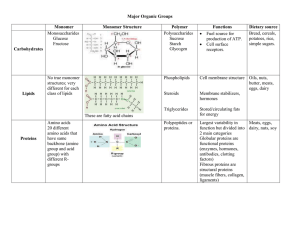
... compounds found in living things are: • Carbohydrates • Lipids • Nucleic acids • Proteins ...
... compounds found in living things are: • Carbohydrates • Lipids • Nucleic acids • Proteins ...
Complete Protein - Kelloggs Nutrition
... blood stream. Amino acids, of which there are 20, are the building blocks of protein. Various combinations and formations of these amino acids make up different proteins, and each one serves a different function. The body can produce about half of these amino acids on its own. The rest, however, mus ...
... blood stream. Amino acids, of which there are 20, are the building blocks of protein. Various combinations and formations of these amino acids make up different proteins, and each one serves a different function. The body can produce about half of these amino acids on its own. The rest, however, mus ...
Principles of sorting and assembly of peroxisomal alcohol
... the cytosol to its target organelle is generally present within the primary amino acid sequence of the protein. This information (for instance a short sequence of a few amino acids) is recognized by a receptor that brings the protein to the correct target organelle. Sorting of proteins to organelles ...
... the cytosol to its target organelle is generally present within the primary amino acid sequence of the protein. This information (for instance a short sequence of a few amino acids) is recognized by a receptor that brings the protein to the correct target organelle. Sorting of proteins to organelles ...
Syllabus: Biochem 104b
... Biochem 104b deals with a topic that is a very active area of research. Many of the fundamental driving forces that shape macromolecules are only partially understood. In addition, biological macromolecules are very large and complex systems and so might evade rigorous quantitative analysis even if ...
... Biochem 104b deals with a topic that is a very active area of research. Many of the fundamental driving forces that shape macromolecules are only partially understood. In addition, biological macromolecules are very large and complex systems and so might evade rigorous quantitative analysis even if ...
Teaching DNA, Proteins, and Protein Synthesis
... Learn about amino acid side chains and construct primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary protein structures with the LEGO amino acids. ...
... Learn about amino acid side chains and construct primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary protein structures with the LEGO amino acids. ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... insulin, which has 51 amino acids, to huge molecules such as the muscle protein titin, with 34,350 amino acids. ...
... insulin, which has 51 amino acids, to huge molecules such as the muscle protein titin, with 34,350 amino acids. ...
Computational (Structural) Biology
... to fresh buds, and these if vigorous, branch out and overtop on all sides many a feebler branch, so by generation I believe it has been with the great Tree of Life, which fills with its dead and broken branches the crust of the earth, and covers the surface with its ever branching and beautiful rami ...
... to fresh buds, and these if vigorous, branch out and overtop on all sides many a feebler branch, so by generation I believe it has been with the great Tree of Life, which fills with its dead and broken branches the crust of the earth, and covers the surface with its ever branching and beautiful rami ...
Protein Structure:
... The transcription factor AP1 is a heterodimer formed from the proto-oncogenes c-fos (shown in red) and c-jun (shown in blue). In order to bind to DNA, and activate transcription, the two subunits associate by virtue of hydrophobic interactions, involving a structural motif known as a leucine zipper ...
... The transcription factor AP1 is a heterodimer formed from the proto-oncogenes c-fos (shown in red) and c-jun (shown in blue). In order to bind to DNA, and activate transcription, the two subunits associate by virtue of hydrophobic interactions, involving a structural motif known as a leucine zipper ...
The four types of nucleotides in DNA are Adenine, Thymine
... What is the genetic code? A synonym for DNA The sequence of nucleotides that a protein is composed of The information carried by mRNA The set of rules determining which codons code for which amino acids ...
... What is the genetic code? A synonym for DNA The sequence of nucleotides that a protein is composed of The information carried by mRNA The set of rules determining which codons code for which amino acids ...
Biological Chemistry II: Problem Set 1
... (c) Although β-hairpin structures are often unstable in solution, incorporation of D-ProXaa sequences has been found to promote autonomous hairpin formation in aqueous solution. The corresponding L-Pro-containing sequences are completely disordered. Why? ...
... (c) Although β-hairpin structures are often unstable in solution, incorporation of D-ProXaa sequences has been found to promote autonomous hairpin formation in aqueous solution. The corresponding L-Pro-containing sequences are completely disordered. Why? ...
Efficient Sampling Methods for Protein Structure Refinement
... In protein folding, scientists are interested in the prediction of the three-dimensional structure, based on the amino acid sequence. Initial structures of new proteins are often built by finding templates from databases of proteins with known structure; this procedure is called homology modeling in ...
... In protein folding, scientists are interested in the prediction of the three-dimensional structure, based on the amino acid sequence. Initial structures of new proteins are often built by finding templates from databases of proteins with known structure; this procedure is called homology modeling in ...
Folding in the cell Cytosolic proteins
... denaturants such as high concentrations of urea and guanidinium chloride, but they will spontaneously refold on returning conditions to normal. This refolding takes place in two phases. First a very rapid formation of secondary structure such as a-helices and b-sheets, and folding of these to form a ...
... denaturants such as high concentrations of urea and guanidinium chloride, but they will spontaneously refold on returning conditions to normal. This refolding takes place in two phases. First a very rapid formation of secondary structure such as a-helices and b-sheets, and folding of these to form a ...
Product: Cat. No.: Lot No.: Synonyms: Size: Storage: Usage: Product
... growth factor (HGF), platelet derived growth factor (PDGF), and c-Kit receptors. Also known as Ruk (regulator of ubiquitous kinase) and SETA (SH3 domain-containing gene expressed in tumorigenic astrocytes), CIN85 is an ubiquitously expressed adaptor protein with three SH3 domains. It interacts with ...
... growth factor (HGF), platelet derived growth factor (PDGF), and c-Kit receptors. Also known as Ruk (regulator of ubiquitous kinase) and SETA (SH3 domain-containing gene expressed in tumorigenic astrocytes), CIN85 is an ubiquitously expressed adaptor protein with three SH3 domains. It interacts with ...
Vocabulary “Inside the Cell”, Chapters 1 and 2
... nucleus to ribosomes either in the cytoplasm or on the endoplasmic reticulum where mRNA is used as instructions to make proteins. ...
... nucleus to ribosomes either in the cytoplasm or on the endoplasmic reticulum where mRNA is used as instructions to make proteins. ...
Slide 1 - helmricht
... solubility –allowing them to travel through blood and other body fluids to sites where activity is needed ...
... solubility –allowing them to travel through blood and other body fluids to sites where activity is needed ...
Proteins*
... Defense – antibodies in bloodstream Storage – albumin in egg whites Signaling – growth hormones in bloodstream ...
... Defense – antibodies in bloodstream Storage – albumin in egg whites Signaling – growth hormones in bloodstream ...
Buffers
... b) A decrease in [CO2], causing an increase in [H+] and decrease in pH. c) An increase in [CO2], causing an increase in [H+] and decrease in pH. d) A decrease in [CO2], causing an increase in [H+] and increase in pH. e) An increase in [CO2], causing a decrease in [H+] and increase in pH. ...
... b) A decrease in [CO2], causing an increase in [H+] and decrease in pH. c) An increase in [CO2], causing an increase in [H+] and decrease in pH. d) A decrease in [CO2], causing an increase in [H+] and increase in pH. e) An increase in [CO2], causing a decrease in [H+] and increase in pH. ...
Two-hybrid screening
Two-hybrid screening (also known as yeast two-hybrid system or Y2H) is a molecular biology technique used to discover protein–protein interactions (PPIs) and protein–DNA interactions by testing for physical interactions (such as binding) between two proteins or a single protein and a DNA molecule, respectively.The premise behind the test is the activation of downstream reporter gene(s) by the binding of a transcription factor onto an upstream activating sequence (UAS). For two-hybrid screening, the transcription factor is split into two separate fragments, called the binding domain (BD) and activating domain (AD). The BD is the domain responsible for binding to the UAS and the AD is the domain responsible for the activation of transcription. The Y2H is thus a protein-fragment complementation assay.