Bioinformatic analysis of diverse protein superfamilies to
... mutation pattern can be described as subfamily-dependent conservation – conserved within functional subfamilies but different between them. To describe these positions a term “subfamily-specific position(s)” or SSP(s) can be used to outline that distribution of amino acid types in a column is specif ...
... mutation pattern can be described as subfamily-dependent conservation – conserved within functional subfamilies but different between them. To describe these positions a term “subfamily-specific position(s)” or SSP(s) can be used to outline that distribution of amino acid types in a column is specif ...
Importance of Protein sorting Cell organization depend on sorting
... 3. Genetic approach to identify essential players ...
... 3. Genetic approach to identify essential players ...
1 Protein structure Protein folding
... Nitrogenase has an unusual set of cofactors: – Iron, sulfur and a molybdenum ion – Thought to perform the nitrogen-fixing reaction, although precise details are still unknown: structure helps, but need more chemistry, too. – Electrons fed to Mo/Fe cluster which is stabilized with homocitrate ...
... Nitrogenase has an unusual set of cofactors: – Iron, sulfur and a molybdenum ion – Thought to perform the nitrogen-fixing reaction, although precise details are still unknown: structure helps, but need more chemistry, too. – Electrons fed to Mo/Fe cluster which is stabilized with homocitrate ...
Slide 1
... – Side chains may have different pKas • pKa affected by charges on amino/carboxyl groups • pKa may be affected by interactions with other side chains in the larger molecule ...
... – Side chains may have different pKas • pKa affected by charges on amino/carboxyl groups • pKa may be affected by interactions with other side chains in the larger molecule ...
The Biochemistry of Life
... Proteins with covalently linked carbohydrate are called glycoproteins The function of a protein is determined by its shape. The shape of a protein is determined by its primary structure (sequence of amino acids). The sequence of amino acids in a protein is determined by the sequence of nucleotides i ...
... Proteins with covalently linked carbohydrate are called glycoproteins The function of a protein is determined by its shape. The shape of a protein is determined by its primary structure (sequence of amino acids). The sequence of amino acids in a protein is determined by the sequence of nucleotides i ...
Macromolecules
... can avoid freezing by increasing the number of unsaturated fatty acids in its cell membranes… ...
... can avoid freezing by increasing the number of unsaturated fatty acids in its cell membranes… ...
4NucleicAcidsProteins - San Elijo Elementary School
... Nucleic Acids • Consists of C, H, N, O, P • 3 types: DNA – Deoxyribonucleic Acid RNA – Ribonucleic Acid ATP – Adenosine Triphosphate • Different functions – DNA: hereditary information – RNA: production of proteins – ATP: energy molecule ...
... Nucleic Acids • Consists of C, H, N, O, P • 3 types: DNA – Deoxyribonucleic Acid RNA – Ribonucleic Acid ATP – Adenosine Triphosphate • Different functions – DNA: hereditary information – RNA: production of proteins – ATP: energy molecule ...
Proteiinien rakenne ja laskostuminen
... gives information about the global conformation of a molecule rms distance from each atom of the molecule to their centroid ...
... gives information about the global conformation of a molecule rms distance from each atom of the molecule to their centroid ...
Exploratorium Presentation
... What is bacterial transformation? Transformation is the alteration of cells by the incorporation of foreign DNA into the cell ...
... What is bacterial transformation? Transformation is the alteration of cells by the incorporation of foreign DNA into the cell ...
Proteins - Downtown Magnets High School
... such a way that it creates a 1 An unfolded polyhydrophilic environment for peptide enters the the folding of the polypeptide. cylinder from one end. ...
... such a way that it creates a 1 An unfolded polyhydrophilic environment for peptide enters the the folding of the polypeptide. cylinder from one end. ...
Les 6b RNA Transcription and Translation
... http://www.biologycorner.com/bio4/notes/gene-expression.php ...
... http://www.biologycorner.com/bio4/notes/gene-expression.php ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS STEP 1: Transcription
... If the protein needs to have a specific sequence of amino acids, then how does the tRNA know which amino acid to bring to the ribosome? ● There are only 20 different amino acids. ● There are four different bases (A, U, C, G). ● Each codon is made of 3 bases (letters). ● That means there are ...
... If the protein needs to have a specific sequence of amino acids, then how does the tRNA know which amino acid to bring to the ribosome? ● There are only 20 different amino acids. ● There are four different bases (A, U, C, G). ● Each codon is made of 3 bases (letters). ● That means there are ...
SSE – secondary structure element (ex. helices, sheets)
... max(match(a,b)^PdbIdb=P)( WArea(a,b) X WARatio(a,b) X WOrdinal(a,b) ) ] WFMCount is to compensate the effect that the large proteins being matched and scored more frequently than the small ones. WTerm is to add more weight to the query index terms that rarely occur in the database. ...
... max(match(a,b)^PdbIdb=P)( WArea(a,b) X WARatio(a,b) X WOrdinal(a,b) ) ] WFMCount is to compensate the effect that the large proteins being matched and scored more frequently than the small ones. WTerm is to add more weight to the query index terms that rarely occur in the database. ...
Major components of cells
... Peripheral membrane proteins • They are proteins that dissociate from the membrane following treatments with polar reagents (solutions of extreme pH or high salt concentration) that do not disrupt the phospholipid bilayer. • Once dissociated, they are soluble in aqueous buffers. • They are indirect ...
... Peripheral membrane proteins • They are proteins that dissociate from the membrane following treatments with polar reagents (solutions of extreme pH or high salt concentration) that do not disrupt the phospholipid bilayer. • Once dissociated, they are soluble in aqueous buffers. • They are indirect ...
ucla1 - WEHI Bioinformatics
... The information content of various species in terms of the number of nucleotides in the genome. The complete genome sequences were determined in the years as designated. The increase of the GenBank nucleotide sequence database is also shown together with the release dates. (Bit s) ...
... The information content of various species in terms of the number of nucleotides in the genome. The complete genome sequences were determined in the years as designated. The increase of the GenBank nucleotide sequence database is also shown together with the release dates. (Bit s) ...
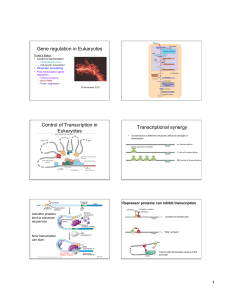
Gene Expression - Biology Department | Western Washington
... Gene Expression …the processes by which information contained in genes and genomes is decoded by cells, ...in order to produce molecules that determine the phenotypes observed in organisms, – transcription (post-transcriptional modifications), – translation (post-translational modifications. ...
... Gene Expression …the processes by which information contained in genes and genomes is decoded by cells, ...in order to produce molecules that determine the phenotypes observed in organisms, – transcription (post-transcriptional modifications), – translation (post-translational modifications. ...
Proteins in body fluids
... Aspartate formed in mitochondria by transamination between oxaloacetate and glutamate can be transported to cytosol, where it serves as nitrogen donor in the urea cycle reaction catalyzed by argininosuccinate synthetase. These reactions , making up the aspartateargininosuccinate shunt ...
... Aspartate formed in mitochondria by transamination between oxaloacetate and glutamate can be transported to cytosol, where it serves as nitrogen donor in the urea cycle reaction catalyzed by argininosuccinate synthetase. These reactions , making up the aspartateargininosuccinate shunt ...
The Body`s Essential Building Blocks, Article by Gloria Gilbère, N.D.
... proper pH balance in the gastrointestinal tract and body tissues. Scientific research confirms that proAUTHORS NOTE biotics are a vital necessity in the supThose that follow my work and writings know port of overall human health, that I credit goat-milk products for a major role in my specifically d ...
... proper pH balance in the gastrointestinal tract and body tissues. Scientific research confirms that proAUTHORS NOTE biotics are a vital necessity in the supThose that follow my work and writings know port of overall human health, that I credit goat-milk products for a major role in my specifically d ...
Protein Synthesis
... The mRNA is single stranded. The mRNA uses U instead of T. (A,U,G,C) The DNA zips back together. ...
... The mRNA is single stranded. The mRNA uses U instead of T. (A,U,G,C) The DNA zips back together. ...
13.3 RNA and Gene Expression
... The DNA strand has a code for “start,” the RNA Polymerase is triggered to start reading the code at this spot. RNA Polymerase unzips the DNA to make a copy of one section of it. The RNA nucleotides line up to make a copy of the DNA. ...
... The DNA strand has a code for “start,” the RNA Polymerase is triggered to start reading the code at this spot. RNA Polymerase unzips the DNA to make a copy of one section of it. The RNA nucleotides line up to make a copy of the DNA. ...
Two-hybrid screening
Two-hybrid screening (also known as yeast two-hybrid system or Y2H) is a molecular biology technique used to discover protein–protein interactions (PPIs) and protein–DNA interactions by testing for physical interactions (such as binding) between two proteins or a single protein and a DNA molecule, respectively.The premise behind the test is the activation of downstream reporter gene(s) by the binding of a transcription factor onto an upstream activating sequence (UAS). For two-hybrid screening, the transcription factor is split into two separate fragments, called the binding domain (BD) and activating domain (AD). The BD is the domain responsible for binding to the UAS and the AD is the domain responsible for the activation of transcription. The Y2H is thus a protein-fragment complementation assay.