biochemical composition presentation
... sequence and arrangement of amino acids. • Amino acids are attached to one another by peptide bonds to form polypeptide chains. • Form determines function of a protein. ...
... sequence and arrangement of amino acids. • Amino acids are attached to one another by peptide bonds to form polypeptide chains. • Form determines function of a protein. ...
PowerPoint - Biological Sciences
... • Often stabilizes structure • Difficult to get crystal structure for more than one or two carbohydrate residues ...
... • Often stabilizes structure • Difficult to get crystal structure for more than one or two carbohydrate residues ...
Analytical and Chromatography - Sigma
... Following DNA binding, a transcription factor exerts an influence over gene expression. This is done through interaction with other transcription factors or with the basal transcriptional machinery in order to affect the efficiency of formation or binding of the transcription complex. These associat ...
... Following DNA binding, a transcription factor exerts an influence over gene expression. This is done through interaction with other transcription factors or with the basal transcriptional machinery in order to affect the efficiency of formation or binding of the transcription complex. These associat ...
Protein-protein interactions.
... Go to NCBI Entrez, search for gi461699 Do Blast search against PDB Repeat the same for gi60494508 Compare the results ...
... Go to NCBI Entrez, search for gi461699 Do Blast search against PDB Repeat the same for gi60494508 Compare the results ...
word
... A series of poly-U residues leads to termination of RNA polymerase III RNA processing, regulation of processing, and signal-mediated transport through nuclear pores A. Main steps of RNA processing ...
... A series of poly-U residues leads to termination of RNA polymerase III RNA processing, regulation of processing, and signal-mediated transport through nuclear pores A. Main steps of RNA processing ...
PROTEINS
... an activity of a protein is localized to a small region along its length. For instance, a particular region or regions of a protein may be responsible for its catalytic activity (e.g., a kinase domain) or binding ability (e.g., a DNA-binding domain, a membrane-binding domain). The organization of la ...
... an activity of a protein is localized to a small region along its length. For instance, a particular region or regions of a protein may be responsible for its catalytic activity (e.g., a kinase domain) or binding ability (e.g., a DNA-binding domain, a membrane-binding domain). The organization of la ...
Lh6Ch04aProt
... geometry of the -carbon create a pleated sheetlike structure • Sheet-like arrangement of backbone is held together by hydrogen bonds between the backbone amides in different strands • Side chains protrude from the sheet alternating in up and down direction ...
... geometry of the -carbon create a pleated sheetlike structure • Sheet-like arrangement of backbone is held together by hydrogen bonds between the backbone amides in different strands • Side chains protrude from the sheet alternating in up and down direction ...
Gene Section chromosome 18-like 1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... 396 amino acids, 42990 Da. The SS18L1 protein, similarly to the SS18 protein, exhibits two domains: a SYT N-terminal homology domain found in a wide variety of species ranging from plants to humans and the QPGY domain at the COOH-terminal part, rich in glutamine, proline, glycine, and tyrosine. The ...
... 396 amino acids, 42990 Da. The SS18L1 protein, similarly to the SS18 protein, exhibits two domains: a SYT N-terminal homology domain found in a wide variety of species ranging from plants to humans and the QPGY domain at the COOH-terminal part, rich in glutamine, proline, glycine, and tyrosine. The ...
Slide 1
... 1.5 Construct in both cases sequence logo and frequency plot. Can you identify (regulatory) sequence motifs? ...
... 1.5 Construct in both cases sequence logo and frequency plot. Can you identify (regulatory) sequence motifs? ...
A CAAT–Box Binding Factor Gene That Regulates Seed Development
... •Transcription factors are sequence-specific DNA binding factors proteins. They promote or block transcription by controlling the recruitment of RNA polymerase •Transcription is initiated at regions of DNA called promoters. Specific sequences of nucleotide bases at a promoter are recognized by both ...
... •Transcription factors are sequence-specific DNA binding factors proteins. They promote or block transcription by controlling the recruitment of RNA polymerase •Transcription is initiated at regions of DNA called promoters. Specific sequences of nucleotide bases at a promoter are recognized by both ...
Presentation - Harlem Children Society
... diseases. Structural analysis of the proteins pave our ways to find solutions to certain diseases. In order to analyze proteins which structures haven’t been determine yet, we use homology modeling to model proteins by using appropriate templates. MOE will help us do the homology modeling and be abl ...
... diseases. Structural analysis of the proteins pave our ways to find solutions to certain diseases. In order to analyze proteins which structures haven’t been determine yet, we use homology modeling to model proteins by using appropriate templates. MOE will help us do the homology modeling and be abl ...
Protein degradation in mouse brain slices
... a role for neurotoxic and unusual neuroexitatory amino acids in the aetiology of certain neurodegenerative disordcrs (Spencer er ul., 1987). This has led us to speculate whether those amino acids that are implicated as possible causativc o r contributory agents in these diseases, might also be invol ...
... a role for neurotoxic and unusual neuroexitatory amino acids in the aetiology of certain neurodegenerative disordcrs (Spencer er ul., 1987). This has led us to speculate whether those amino acids that are implicated as possible causativc o r contributory agents in these diseases, might also be invol ...
Prediction of protein disorder - oz
... statistical potentials: Calculated from the frequency of amino acid interactions in globular proteins alone, based on the Boltzmann hypothesis. ...
... statistical potentials: Calculated from the frequency of amino acid interactions in globular proteins alone, based on the Boltzmann hypothesis. ...
Indexed Keywords
... b Department of Biology, Islamic Azad University of Mashhad, Mashhad, Iran c Department of Agronomy and Plant Breeding, College of Agriculture, University of Tehran, Karaj, Iran d Immunology Research Center, Bu-Ali Institute, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, Mashhad, Iran View references (29) ...
... b Department of Biology, Islamic Azad University of Mashhad, Mashhad, Iran c Department of Agronomy and Plant Breeding, College of Agriculture, University of Tehran, Karaj, Iran d Immunology Research Center, Bu-Ali Institute, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, Mashhad, Iran View references (29) ...
Molecules of Life Review Topics
... Active site and substrate – what are they? Modes of enzyme action – lock-and-key, induced fit Conditions that affect enzyme action o Temperature – warm increases rate; hot denatures protein o pH – narrow range for best pH, excess H+ or OH- break 3-D bonds o concentration of enzyme or of substr ...
... Active site and substrate – what are they? Modes of enzyme action – lock-and-key, induced fit Conditions that affect enzyme action o Temperature – warm increases rate; hot denatures protein o pH – narrow range for best pH, excess H+ or OH- break 3-D bonds o concentration of enzyme or of substr ...
How does DNA copy itself?
... • Only known molecule to be able to duplicate itself • Basic: unzips itself, find complementary base pairs ...
... • Only known molecule to be able to duplicate itself • Basic: unzips itself, find complementary base pairs ...
protein_web_notes1
... Essential amino acids cannot be made by your body. You must get them from the foods you eat. Non-essential amino acids are the acids your body can make. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is found in every nucleus of a cell. It has the instructions for how amino acids will be linked to form the proteins in ...
... Essential amino acids cannot be made by your body. You must get them from the foods you eat. Non-essential amino acids are the acids your body can make. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is found in every nucleus of a cell. It has the instructions for how amino acids will be linked to form the proteins in ...
Prep 101
... Elongation : Transcription bubble is formed o Termination: RNA sequences that signal the end of elongation coded by DNA. Terminator sequence stops RNA Polymerase Promoter is essential for transcription. Prokaryotes and eukaryotes have different polymerases Prokaryotes regulate gene transcription via ...
... Elongation : Transcription bubble is formed o Termination: RNA sequences that signal the end of elongation coded by DNA. Terminator sequence stops RNA Polymerase Promoter is essential for transcription. Prokaryotes and eukaryotes have different polymerases Prokaryotes regulate gene transcription via ...
ProteinShop: A tool for protein structure prediction and modeling
... the free energy function of the primary sequence ...
... the free energy function of the primary sequence ...
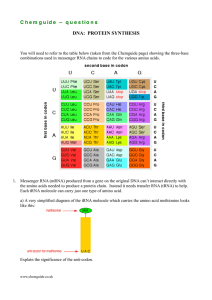
C h e m g u id e –... DNA: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... C h e m g u id e – q u e s t i o n s b) Give the two possible anti-codons for the amino acid tyrosine (Tyr). c) Give the anti-codon for the amino acid tryptophan (Trp). d) Protein synthesis is controlled by a ribosome which comes in two parts – a smaller part and a bigger part. The smaller part is ...
... C h e m g u id e – q u e s t i o n s b) Give the two possible anti-codons for the amino acid tyrosine (Tyr). c) Give the anti-codon for the amino acid tryptophan (Trp). d) Protein synthesis is controlled by a ribosome which comes in two parts – a smaller part and a bigger part. The smaller part is ...
Chapter 1
... Proteins are macromolecules composed of amino acids linked together through peptide bonds. ...
... Proteins are macromolecules composed of amino acids linked together through peptide bonds. ...
Two-hybrid screening
Two-hybrid screening (also known as yeast two-hybrid system or Y2H) is a molecular biology technique used to discover protein–protein interactions (PPIs) and protein–DNA interactions by testing for physical interactions (such as binding) between two proteins or a single protein and a DNA molecule, respectively.The premise behind the test is the activation of downstream reporter gene(s) by the binding of a transcription factor onto an upstream activating sequence (UAS). For two-hybrid screening, the transcription factor is split into two separate fragments, called the binding domain (BD) and activating domain (AD). The BD is the domain responsible for binding to the UAS and the AD is the domain responsible for the activation of transcription. The Y2H is thus a protein-fragment complementation assay.