linear integrated-circuit voltage
... 4. Plot the theoretical frequencies on the same graph. (It is convenient to use Excel for this. Plot the theoretical values as a continuous line and the measured data as discrete points.) ...
... 4. Plot the theoretical frequencies on the same graph. (It is convenient to use Excel for this. Plot the theoretical values as a continuous line and the measured data as discrete points.) ...
Model 855 Specification 1.4 - Berkeley Nucleonics Corporation
... generator with a frequency range from 10 MHz to 6.2, 12.5 or 20.0 GHz and is ideally suited for a wide range of application, where good signal quality accurate and wide output power range is required. Excellent phase noise is combined with spurious and harmonic rejection. A high-stability OCXO refer ...
... generator with a frequency range from 10 MHz to 6.2, 12.5 or 20.0 GHz and is ideally suited for a wide range of application, where good signal quality accurate and wide output power range is required. Excellent phase noise is combined with spurious and harmonic rejection. A high-stability OCXO refer ...
Subcircuits
... Between t3 and t4 additional charge is transferred to C1 from the channel capacitance of M2. ...
... Between t3 and t4 additional charge is transferred to C1 from the channel capacitance of M2. ...
IC Technology and Device Models
... etc., from a computer or other digital instrument. Frequency Synthesizer: It is a device that generates sine waves whose frequencies can be set precisely. The frequency is set digitally, often to eight significant figures or more and is internally synthesized from a precise standard (a quartz crysta ...
... etc., from a computer or other digital instrument. Frequency Synthesizer: It is a device that generates sine waves whose frequencies can be set precisely. The frequency is set digitally, often to eight significant figures or more and is internally synthesized from a precise standard (a quartz crysta ...
BH1417F Stereo PLL FM Transmitter Design Guide Introduction
... oscillator can operate will directly depend on the maximum and minimum values of the varactor. In BH1417 data sheet, This Colpitts voltage-controlled oscillator is employed as a VCO for phased-lock loop circuit which is a frequency synthesizer and is capable of producing very accurate, high quality ...
... oscillator can operate will directly depend on the maximum and minimum values of the varactor. In BH1417 data sheet, This Colpitts voltage-controlled oscillator is employed as a VCO for phased-lock loop circuit which is a frequency synthesizer and is capable of producing very accurate, high quality ...
Digital to Analog Converters (DAC)
... Time required for the output signal to settle within +/- ½ LSB of its final value after a given change in input scale Limited by slew rate of output amplifier Ideally, an instantaneous change in analog voltage would occur when a new binary word enters into DAC ...
... Time required for the output signal to settle within +/- ½ LSB of its final value after a given change in input scale Limited by slew rate of output amplifier Ideally, an instantaneous change in analog voltage would occur when a new binary word enters into DAC ...
Transmitter Architectures
... multipliers, implemented as 4-FET switches data edges are aligned with the 12-MHz system clock and a logic circuit produces complementary clock signals to drive the 4-FET switches analog Gaussian low-pass filter following the modulator ...
... multipliers, implemented as 4-FET switches data edges are aligned with the 12-MHz system clock and a logic circuit produces complementary clock signals to drive the 4-FET switches analog Gaussian low-pass filter following the modulator ...
IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Processing (IOSR-JVSP)
... Steady miniaturization of transistors with each new generation of bulk CMOS technology has yielded continual improvement in the performance of digital circuits.In the case of non portable devices, power consumption is also very important because of the increased in packaging density and cooling cost ...
... Steady miniaturization of transistors with each new generation of bulk CMOS technology has yielded continual improvement in the performance of digital circuits.In the case of non portable devices, power consumption is also very important because of the increased in packaging density and cooling cost ...
MAE511 FinalReport ASavas ARousing BReimold
... gain and DC offset (see Figure 21 in Chapter C of the Appendix). The operational amplifiers (op-amps) used in this stage are railed to ˘15 V, meaning that the oscilloscope can sample signals within that range (otherwise the sampled signals will be railed). The ability to offset the incoming signal b ...
... gain and DC offset (see Figure 21 in Chapter C of the Appendix). The operational amplifiers (op-amps) used in this stage are railed to ˘15 V, meaning that the oscilloscope can sample signals within that range (otherwise the sampled signals will be railed). The ability to offset the incoming signal b ...
Oscillator Notes 2
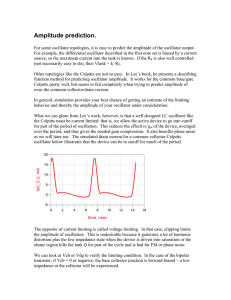
... the Colpitts must be current limited: that is, we allow the active device to go into cutoff for part of the period of oscillation. This reduces the effective gm of the device, averaged over the period, and thus gives the needed gain compression. It also benefits phase noise as we will later see. The ...
... the Colpitts must be current limited: that is, we allow the active device to go into cutoff for part of the period of oscillation. This reduces the effective gm of the device, averaged over the period, and thus gives the needed gain compression. It also benefits phase noise as we will later see. The ...
Fundamentals of Linear Electronics Integrated & Discrete
... to maintain a pure sine wave. If the gain is left too high, the sinewave amplitude will increase until it hits the rails and is clipped. • The cure is to include a means for the circuit to lower its gain a bit once it starts oscillating. This is a type of negative feedback based on amplitude. ...
... to maintain a pure sine wave. If the gain is left too high, the sinewave amplitude will increase until it hits the rails and is clipped. • The cure is to include a means for the circuit to lower its gain a bit once it starts oscillating. This is a type of negative feedback based on amplitude. ...
PCM1744 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... Important Information and Disclaimer:The information provided on this page represents TI's knowledge and belief as of the date that it is provided. TI bases its knowledge and belief on information provided by third parties, and makes no representation or warranty as to the accuracy of such informati ...
... Important Information and Disclaimer:The information provided on this page represents TI's knowledge and belief as of the date that it is provided. TI bases its knowledge and belief on information provided by third parties, and makes no representation or warranty as to the accuracy of such informati ...
Telly the Teaching Time Clock #4528 USER`S
... bell will sound and the user will be greeted by Telly saying “Hello how are you I am Telly the Teaching Time Clock”. Telly has two modes of operation to chose from, Teaching Time or Quiz Game. After Telly is turned ON you can select the mode of your choice using the indicating controls on Telly. 5. ...
... bell will sound and the user will be greeted by Telly saying “Hello how are you I am Telly the Teaching Time Clock”. Telly has two modes of operation to chose from, Teaching Time or Quiz Game. After Telly is turned ON you can select the mode of your choice using the indicating controls on Telly. 5. ...
Time-to-digital converter

In electronic instrumentation and signal processing, a time to digital converter (abbreviated TDC) is a device for recognizing events and providing a digital representation of the time they occurred. For example, a TDC might output the time of arrival for each incoming pulse. Some applications wish to measure the time interval between two events rather than some notion of an absolute time.In electronics time-to-digital converters (TDCs) or time digitizers are devices commonly used to measure a time interval and convert it into digital (binary) output. In some cases interpolating TDCs are also called time counters (TCs).TDCs are used in many different applications, where the time interval between two signal pulses (start and stop pulse) should be determined. Measurement is started and stopped, when either the rising or the falling edge of a signal pulse crosses a set threshold. These requirements are fulfilled in many physical experiments, like time-of-flight and lifetime measurements in atomic and high energy physics, experiments that involve laser ranging and electronic research involving the testing of integrated circuits and high-speed data transfer.