Fungi and Bacteria - Singapore Asia Publishers
... mould which has been made into a vaccine to prevent infections or illnesses ...
... mould which has been made into a vaccine to prevent infections or illnesses ...
characterization of procaryotic cells inner structures in bacteria
... All bacterial cells require a constant supply of energy to survive. This energy, typically in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), is derived from the controlled breakdown of various organic substrates (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins). This process of substrate breakdown and conversion into us ...
... All bacterial cells require a constant supply of energy to survive. This energy, typically in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), is derived from the controlled breakdown of various organic substrates (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins). This process of substrate breakdown and conversion into us ...
TGT- Questions
... 14. What are the two ways in which something can be sterilized? Heat or chemicals 15. What is one argument for why viruses are non-living? They cannot reproduce without a host 16. There are two basic structural features to a virus, what are they? A protein coat and a form of genetic information (DNA ...
... 14. What are the two ways in which something can be sterilized? Heat or chemicals 15. What is one argument for why viruses are non-living? They cannot reproduce without a host 16. There are two basic structural features to a virus, what are they? A protein coat and a form of genetic information (DNA ...
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
... SCVs of P. aeruginosa in CF • Slow growing subpopulations (3% of the P. aeruginosa positive sputum specimens) • SCVs exhibit an increased resistance towards a broad spectrum of antimicrobial agents • The recovery of SCV correlates with parameters revealing poor lung function and an inhalative antim ...
... SCVs of P. aeruginosa in CF • Slow growing subpopulations (3% of the P. aeruginosa positive sputum specimens) • SCVs exhibit an increased resistance towards a broad spectrum of antimicrobial agents • The recovery of SCV correlates with parameters revealing poor lung function and an inhalative antim ...
BACTERIA
... Lack a true nucleus; instead, have a region called the ‘nucleoid region‘where DNA congregates ...
... Lack a true nucleus; instead, have a region called the ‘nucleoid region‘where DNA congregates ...
Bacterial colony growth
... two touching/colliding bacteria. The bacterial growth is well characterized, and can be modeled to follow actual experimental observations, which we obtain from the Tans lab (TU Delft / AMOLF). The most basic interaction between two bacteria is repulsive - touching bacteria that grow will repel each ...
... two touching/colliding bacteria. The bacterial growth is well characterized, and can be modeled to follow actual experimental observations, which we obtain from the Tans lab (TU Delft / AMOLF). The most basic interaction between two bacteria is repulsive - touching bacteria that grow will repel each ...
A virus, or virion, is a tiny particle consisting of a DNA or RNA
... A virus, or virion, is a tiny particle consisting of a DNA or RNA genome surrounded by a capsid (protein coat). Viruses are sub-cellular particles that cannot metabolize on their own. In the past, biologists considered them to be nonliving particles; but some now view them as life forms. Viruses may ...
... A virus, or virion, is a tiny particle consisting of a DNA or RNA genome surrounded by a capsid (protein coat). Viruses are sub-cellular particles that cannot metabolize on their own. In the past, biologists considered them to be nonliving particles; but some now view them as life forms. Viruses may ...
Visualizing Bacterial Cell Walls and Biofilms
... in bacterial envelopes are using this approach to reexamine gram-negative bacteria such as E. coli K-12 and P. aeruginosa PAO1 as well as grampositive species such as B. subtilis This diagram shows three regions of the B. subtilis cell wall, 168 and S. aureus D2H (Fig. 6 – 8). determined from images ...
... in bacterial envelopes are using this approach to reexamine gram-negative bacteria such as E. coli K-12 and P. aeruginosa PAO1 as well as grampositive species such as B. subtilis This diagram shows three regions of the B. subtilis cell wall, 168 and S. aureus D2H (Fig. 6 – 8). determined from images ...
Name
... 7. List and describe three ways that ordinary bacteria can get antibiotic-resistant genes from other bacteria, and turn into “superbugs.” 1. Antibiotic-resistant genes are often found on plasmids (circular DNA). Plasmids can transfer from one type of bacteria to a different kind, as long as the germ ...
... 7. List and describe three ways that ordinary bacteria can get antibiotic-resistant genes from other bacteria, and turn into “superbugs.” 1. Antibiotic-resistant genes are often found on plasmids (circular DNA). Plasmids can transfer from one type of bacteria to a different kind, as long as the germ ...
Making sense of the vast Diversity of Life
... Bacteria and bacteria-like Simpler Smaller cell size DNA without nucleus Cell wall & other crude protective layers – Lack organelles ...
... Bacteria and bacteria-like Simpler Smaller cell size DNA without nucleus Cell wall & other crude protective layers – Lack organelles ...
Name - Humble ISD
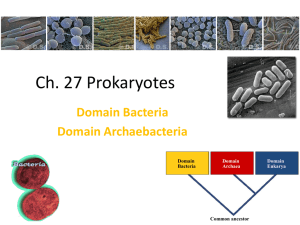
... Prokaryotes, which includes, bacteria are the simplest of all the cells. All prokaryotes have a single, circular chromosome and lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. There are two major groups of prokaryotic organisms --- the Kingdom Eubacteria and the Kingdom Archaebacteria. Eubacteria are ...
... Prokaryotes, which includes, bacteria are the simplest of all the cells. All prokaryotes have a single, circular chromosome and lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. There are two major groups of prokaryotic organisms --- the Kingdom Eubacteria and the Kingdom Archaebacteria. Eubacteria are ...
Biology Warm-Up Jan
... 1. Do a Punnett square to determine the genotypes of the offspring of the following crosses of blood types: a. O, homo.Rh pos. X AB, Rh neg. b.Hetero A, Rh neg. X O, homo. Rh ...
... 1. Do a Punnett square to determine the genotypes of the offspring of the following crosses of blood types: a. O, homo.Rh pos. X AB, Rh neg. b.Hetero A, Rh neg. X O, homo. Rh ...
Author`s post-print - Cardiff Metropolitan University
... reduction was found in biofilm exposed to 50% Medihoney™ for 24 h compared to untreated biofilm. Structural changes in biofilms exposed to Medihoney™ Using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) it was observed that the extent of biofilm bound to coverslips decreased with increasing honey concentration ...
... reduction was found in biofilm exposed to 50% Medihoney™ for 24 h compared to untreated biofilm. Structural changes in biofilms exposed to Medihoney™ Using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) it was observed that the extent of biofilm bound to coverslips decreased with increasing honey concentration ...
Microbial Growth (Ch 6)
... Figure 6.1 Typical growth rates of different types of microorganisms in response to temperature. ...
... Figure 6.1 Typical growth rates of different types of microorganisms in response to temperature. ...
Long-term Monitoring of Bacteria Undergoing Programmed Population Control in a Microchemostat
... population size and is µ the per-genome mutation rate. The time to fixation, on the other hand, is proportional to (2/s)*ln(2N), where s is the selective advantage (S7). Thus the rate at which a mutant with a large selective advantage, once it has appeared, will take over the population is expected ...
... population size and is µ the per-genome mutation rate. The time to fixation, on the other hand, is proportional to (2/s)*ln(2N), where s is the selective advantage (S7). Thus the rate at which a mutant with a large selective advantage, once it has appeared, will take over the population is expected ...
Bacteria - Mrs. Brenner`s Biology
... • Cilia ~ Lots of miniature flagella surround the cell and help to “swim” • Non-motile ~ Sticky cilia-like structures that keep the bacterium from moving ...
... • Cilia ~ Lots of miniature flagella surround the cell and help to “swim” • Non-motile ~ Sticky cilia-like structures that keep the bacterium from moving ...
Combining 2 Powerful Technologies to Enable Further Discovery in
... – Cell wall present on the outside of the cytoplasmic membrane – Consists of peptidoglycan – Essential to survival and the antibiotic penicillin kills the bacteria by inhibiting the synthesis of peptidoglycan ...
... – Cell wall present on the outside of the cytoplasmic membrane – Consists of peptidoglycan – Essential to survival and the antibiotic penicillin kills the bacteria by inhibiting the synthesis of peptidoglycan ...
Combining 2 Powerful Technologies to Enable Further Discovery in
... – Cell wall present on the outside of the cytoplasmic membrane – Consists of peptidoglycan – Essential to survival and the antibiotic penicillin kills the bacteria by inhibiting the synthesis of peptidoglycan ...
... – Cell wall present on the outside of the cytoplasmic membrane – Consists of peptidoglycan – Essential to survival and the antibiotic penicillin kills the bacteria by inhibiting the synthesis of peptidoglycan ...
Bacteria Keywords
... Here is a list of keywords that you will need in your study of bacteria. Match or drag each word to where it is best explained. ...
... Here is a list of keywords that you will need in your study of bacteria. Match or drag each word to where it is best explained. ...
Influence of bacteria on silver dissolution from silver
... dissolution from Ag-Pd surfaces due to the interactions between cell components and the surfaces, and the amount of surface-associated bacteria can improve this effect. This could indicate that in a natural environment Ag-dissolution may be low unless bacteria or activating ions are present. Further ...
... dissolution from Ag-Pd surfaces due to the interactions between cell components and the surfaces, and the amount of surface-associated bacteria can improve this effect. This could indicate that in a natural environment Ag-dissolution may be low unless bacteria or activating ions are present. Further ...
Bacteria Notes
... Some bacteria may have the following structures: Capsule (covering outside of cell wall that protects bacterial cell) Pili (hair-like structures used to transfer genetic material from one bacterium to another) Endospore (Thick covering around DNA; developed under harsh conditions) Plasmid (sma ...
... Some bacteria may have the following structures: Capsule (covering outside of cell wall that protects bacterial cell) Pili (hair-like structures used to transfer genetic material from one bacterium to another) Endospore (Thick covering around DNA; developed under harsh conditions) Plasmid (sma ...
Biofilm

A biofilm is any group of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other on a surface. These adherent cells are frequently embedded within a self-produced matrix of extracellular polymeric substance (EPS). Biofilm extracellular polymeric substance, which is also referred to as slime (although not everything described as slime is a biofilm), is a polymeric conglomeration generally composed of extracellular DNA, proteins, and polysaccharides. Biofilms may form on living or non-living surfaces and can be prevalent in natural, industrial and hospital settings. The microbial cells growing in a biofilm are physiologically distinct from planktonic cells of the same organism, which, by contrast, are single-cells that may float or swim in a liquid medium.Microbes form a biofilm in response to many factors, which may include cellular recognition of specific or non-specific attachment sites on a surface, nutritional cues, or in some cases, by exposure of planktonic cells to sub-inhibitory concentrations of antibiotics. When a cell switches to the biofilm mode of growth, it undergoes a phenotypic shift in behavior in which large suites of genes are differentially regulated.