Voltage in Electrical Systems
... • Electrons and ions are separated in a cell creating a voltage. • Voltage depends on the chemicals used (Table ...
... • Electrons and ions are separated in a cell creating a voltage. • Voltage depends on the chemicals used (Table ...
Safety Example Using Low
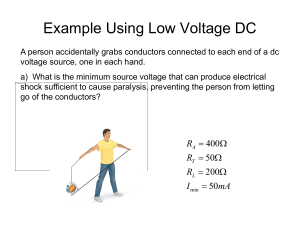
... Example Using Low Voltage DC A person accidentally grabs conductors connected to each end of a dc voltage source, one in each hand. a) What is the minimum source voltage that can produce electrical shock sufficient to cause paralysis, preventing the person from letting go of the conductors? ...
... Example Using Low Voltage DC A person accidentally grabs conductors connected to each end of a dc voltage source, one in each hand. a) What is the minimum source voltage that can produce electrical shock sufficient to cause paralysis, preventing the person from letting go of the conductors? ...
12.1 Electricity at Home (Pages 485
... A doorbell is connected to a 110 V supply, but it operates on only about 12 to 14 V. What kind of transformer does it have? • A step-down transformer allows electricity to be distributed in lower voltages Advantages of supplying alternating current to homes and businesses? • Transmitting electrical ...
... A doorbell is connected to a 110 V supply, but it operates on only about 12 to 14 V. What kind of transformer does it have? • A step-down transformer allows electricity to be distributed in lower voltages Advantages of supplying alternating current to homes and businesses? • Transmitting electrical ...
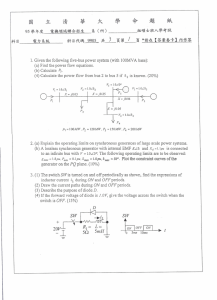
1. Given the following five-bus power system (with lOOMVA base): (b)
... 5. The percentage differential relay and the overvoltage relay are to be applied to the protection of generator windings. (15 %) (a) Sketch the developed three-phase or single-phase wiring diagram (which depicts the CT or PT connections) for both the percentage differential and the overvoltage relay ...
... 5. The percentage differential relay and the overvoltage relay are to be applied to the protection of generator windings. (15 %) (a) Sketch the developed three-phase or single-phase wiring diagram (which depicts the CT or PT connections) for both the percentage differential and the overvoltage relay ...
Oct - Directorate General of Shipping
... (c) Explain the procedure you, as Chief Engineer, would adopt in order to locate and rectify a general fault in the UMS system. ...
... (c) Explain the procedure you, as Chief Engineer, would adopt in order to locate and rectify a general fault in the UMS system. ...
Understanding the Differences Between Bonding, Grounding, and
... problems, such as rebooting, data errors, and intermittent shutdowns. This decrease is due to the reduced amount of voltage transients or "noise" on the ground rod, as compared to a common building grounding system. Because of the reduction in data errors attributed to the ground rod, some manufactu ...
... problems, such as rebooting, data errors, and intermittent shutdowns. This decrease is due to the reduced amount of voltage transients or "noise" on the ground rod, as compared to a common building grounding system. Because of the reduction in data errors attributed to the ground rod, some manufactu ...
View as Printable PDF
... Electrical energy is the energy carried by charged particles. Voltage is a measure of how much electrical energy each charged particle carries. The higher the energy of each charged particle, the greater the potential energy. Also called 'potential difference', the energy delivered by a flow of char ...
... Electrical energy is the energy carried by charged particles. Voltage is a measure of how much electrical energy each charged particle carries. The higher the energy of each charged particle, the greater the potential energy. Also called 'potential difference', the energy delivered by a flow of char ...
MARIA VAN BOMMEL PRESS RELEASE
... Queen’s Park – Lambton-Kent-Middlesex MPP Maria Van Bommel today proudly rose in the Legislature to move 2nd reading of her Private Member’s Bill 143, An Act Respecting Ground Current Pollution in Ontario. The bill received unanimous approval from all 3 parties and was referred to the Standing Commi ...
... Queen’s Park – Lambton-Kent-Middlesex MPP Maria Van Bommel today proudly rose in the Legislature to move 2nd reading of her Private Member’s Bill 143, An Act Respecting Ground Current Pollution in Ontario. The bill received unanimous approval from all 3 parties and was referred to the Standing Commi ...
Document
... conductor. Copper is used in electrical wiring. □ Insulator: A material that makes a poor path for electricity. □ Electromagnet: Created when an electric current passes through a coil of wire. You can make a simple electromagnet by wrapping a wire 9 or more times around a nail, then connecting both ...
... conductor. Copper is used in electrical wiring. □ Insulator: A material that makes a poor path for electricity. □ Electromagnet: Created when an electric current passes through a coil of wire. You can make a simple electromagnet by wrapping a wire 9 or more times around a nail, then connecting both ...
Do You Know Where Your Fault Currents are Flowing?
... In 1986, Mr. Fuhr established PowerStudies, Inc., a consulting firm that specializes in power systems studies, power quality services, and commissioning services. He also teaches classes in protective relaying, electrical systems, safety, power factor correction, harmonics and filter design. Mr. Fuh ...
... In 1986, Mr. Fuhr established PowerStudies, Inc., a consulting firm that specializes in power systems studies, power quality services, and commissioning services. He also teaches classes in protective relaying, electrical systems, safety, power factor correction, harmonics and filter design. Mr. Fuh ...
Electricity notes - Lesmahagow High School
... 7. STAYING SAFE WITH ELECTRICITY Passing a current in a wire causes it to heat up. If the current in a wire gets too high, ...
... 7. STAYING SAFE WITH ELECTRICITY Passing a current in a wire causes it to heat up. If the current in a wire gets too high, ...
Highport Marina - Boat Slips Lake Front Restaurant Service boat
... surrounding water will not allow the passage of sufficient current to blow a fuse or trip a circuit breaker. (If the total resistance of the path through the water is above 10 ohms, for example, this will limit the current flow from a 120-volt circuit to 12 amps, which is not enough to trip a typica ...
... surrounding water will not allow the passage of sufficient current to blow a fuse or trip a circuit breaker. (If the total resistance of the path through the water is above 10 ohms, for example, this will limit the current flow from a 120-volt circuit to 12 amps, which is not enough to trip a typica ...
Sc9 - D 2.3 (teacher notes)
... A Series Circuit has only one path to ground, so electrons must go through each component to get back to ground. All loads are placed in series. Therefore: 1. An open in the circuit will disable the entire circuit. 2. The voltage divides (shared) between the loads. 3. The current flow is the same th ...
... A Series Circuit has only one path to ground, so electrons must go through each component to get back to ground. All loads are placed in series. Therefore: 1. An open in the circuit will disable the entire circuit. 2. The voltage divides (shared) between the loads. 3. The current flow is the same th ...
2) it seems that I have no ground loop in my set up
... source between floating GND and earth there will never be any voltage between DGND and earth, Or, more precisely (since DGND is connected to earth in your pc and on the same potential), there will be no compensation current flowing into (or out of) the DGND terminal. ...
... source between floating GND and earth there will never be any voltage between DGND and earth, Or, more precisely (since DGND is connected to earth in your pc and on the same potential), there will be no compensation current flowing into (or out of) the DGND terminal. ...
スライド 1 - Indico
... • The decision about the development will be based on prospects of such the transformers, where the demand for the transformers in a high energy physics is not considered so much as we expect. ...
... • The decision about the development will be based on prospects of such the transformers, where the demand for the transformers in a high energy physics is not considered so much as we expect. ...
unit_6_electricity_and_power
... 5. Power supplies on a computer are both transformers and rectifiers. They change current from AC to DC and volts from 110 to +/- 12, 5, & 3.3 volts C. Hot, Neutral, and Ground 1. Electricity flows from the power plant to the home appliance through the hot wire and is returned to the power plant thr ...
... 5. Power supplies on a computer are both transformers and rectifiers. They change current from AC to DC and volts from 110 to +/- 12, 5, & 3.3 volts C. Hot, Neutral, and Ground 1. Electricity flows from the power plant to the home appliance through the hot wire and is returned to the power plant thr ...
Ground (electricity)

In electrical engineering, ground or earth is the reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth.Electrical circuits may be connected to ground (earth) for several reasons. In mains powered equipment, exposed metal parts are connected to ground to prevent user contact with dangerous voltage if electrical insulation fails. Connections to ground limit the build-up of static electricity when handling flammable products or electrostatic-sensitive devices. In some telegraph and power transmission circuits, the earth itself can be used as one conductor of the circuit, saving the cost of installing a separate return conductor (see single-wire earth return).For measurement purposes, the Earth serves as a (reasonably) constant potential reference against which other potentials can be measured. An electrical ground system should have an appropriate current-carrying capability to serve as an adequate zero-voltage reference level. In electronic circuit theory, a ""ground"" is usually idealized as an infinite source or sink for charge, which can absorb an unlimited amount of current without changing its potential. Where a real ground connection has a significant resistance, the approximation of zero potential is no longer valid. Stray voltages or earth potential rise effects will occur, which may create noise in signals or if large enough will produce an electric shock hazard.The use of the term ground (or earth) is so common in electrical and electronics applications that circuits in portable electronic devices such as cell phones and media players as well as circuits in vehicles may be spoken of as having a ""ground"" connection without any actual connection to the Earth, despite ""common"" being a more appropriate term for such a connection. This is usually a large conductor attached to one side of the power supply (such as the ""ground plane"" on a printed circuit board) which serves as the common return path for current from many different components in the circuit.