Electric Circuits
... than one path for the electric current to flow through – current flows through every path, so if one pathway is broken, it may not affect the others – The current in each path can be different depending on the devices connected to the circuit on that path ...
... than one path for the electric current to flow through – current flows through every path, so if one pathway is broken, it may not affect the others – The current in each path can be different depending on the devices connected to the circuit on that path ...
Electrical conduction
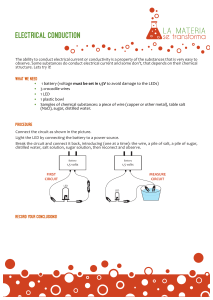
... The ability to conduct electrical current or conductivity is a property of the substances that is very easy to observe. Some substances do conduct electrical current and some don’t, that depends on their chemical structure. Lets try it! ...
... The ability to conduct electrical current or conductivity is a property of the substances that is very easy to observe. Some substances do conduct electrical current and some don’t, that depends on their chemical structure. Lets try it! ...
Ganpat University - UV Patel College of Engineering
... Learning Outcomes: Upon completion of this course, students will acquire knowledge about: ...
... Learning Outcomes: Upon completion of this course, students will acquire knowledge about: ...
Hampehs! What The Hell Is It?
... 8. Unauthorized additions to final circuits resulting in overloaded circuit cables 9. Unprotected or unearthed socket-outlets 10. Appliances with earthing requirements being supplied from two-pin BC adaptors 11. Bell-wire (with extra-low voltage insulation) used to carry mains voltages 12. Use of po ...
... 8. Unauthorized additions to final circuits resulting in overloaded circuit cables 9. Unprotected or unearthed socket-outlets 10. Appliances with earthing requirements being supplied from two-pin BC adaptors 11. Bell-wire (with extra-low voltage insulation) used to carry mains voltages 12. Use of po ...
The EM technician role over the last couple years has led each of
... below. DC POWER DC current is the unidirectional flow of electrical charge. The associated direct voltages are of unchanging polarity. DC current is produced by such sources as batteries, generators, solar power or thermocouples. It is important to note that DC power will usually only shock a person ...
... below. DC POWER DC current is the unidirectional flow of electrical charge. The associated direct voltages are of unchanging polarity. DC current is produced by such sources as batteries, generators, solar power or thermocouples. It is important to note that DC power will usually only shock a person ...
ch 20 21 22
... 3. Charges can act on each other even at a distance, because any charge that is placed in an electric field will be pushed or pulled by the field 4. Electrons move more easily through conductors 5. Electrons do not move easily through insulators, such as plastic, wood, rubber, and glass ...
... 3. Charges can act on each other even at a distance, because any charge that is placed in an electric field will be pushed or pulled by the field 4. Electrons move more easily through conductors 5. Electrons do not move easily through insulators, such as plastic, wood, rubber, and glass ...
Electrical Foreman Oncore Services Inc. is a multi
... Read and interpret drawings, the Canadian Electrical Code and client work package specifications Cut, thread, bend and assemble conduits and other types of electrical raceways and fittings Pull wire and cable through conduits and raceways. Position maintain and install distribution and control equip ...
... Read and interpret drawings, the Canadian Electrical Code and client work package specifications Cut, thread, bend and assemble conduits and other types of electrical raceways and fittings Pull wire and cable through conduits and raceways. Position maintain and install distribution and control equip ...
UFC FlatPakTM SERIES 400 Hz GROUND POWER UNIT 20
... development of reliable, solid-state power systems. Through an innovative design, advanced self-diagnostic systems (BITE) and modular construction, Unitron products assure maximum power availability and minimal repair time. The FlatPakTM Series includes 400 Hz converters specifically designed for in ...
... development of reliable, solid-state power systems. Through an innovative design, advanced self-diagnostic systems (BITE) and modular construction, Unitron products assure maximum power availability and minimal repair time. The FlatPakTM Series includes 400 Hz converters specifically designed for in ...
1. Current which keeps on reversing it`s direction is called
... 30. At distribution stations, 60 kV to 138 kV is lowered to _________kV and transported around cities and towns. 31. Before coming into your home, the voltage is lowered to __________V by a _________________ either located on power poles of on the ground in a metal box. 32. Why are the towers for hi ...
... 30. At distribution stations, 60 kV to 138 kV is lowered to _________kV and transported around cities and towns. 31. Before coming into your home, the voltage is lowered to __________V by a _________________ either located on power poles of on the ground in a metal box. 32. Why are the towers for hi ...
AT-6000 GDS Ground Fault Detection System
... Accumetrics developed the GDS for use with large, turbine-driven synchronous generators. The system detects the occurrence of ground fault leakage current between the generator field circuit and rotor ground, and transmits a good/bad fault determination (based upon a fixed leakage current threshold) ...
... Accumetrics developed the GDS for use with large, turbine-driven synchronous generators. The system detects the occurrence of ground fault leakage current between the generator field circuit and rotor ground, and transmits a good/bad fault determination (based upon a fixed leakage current threshold) ...
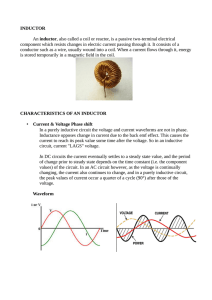
INDUCTOR An inductor, also called a coil or
... INDUCTOR An inductor, also called a coil or reactor, is a passive two-terminal electrical component which resists changes in electric current passing through it. It consists of a conductor such as a wire, usually wound into a coil. When a current flows through it, energy is stored temporarily in a m ...
... INDUCTOR An inductor, also called a coil or reactor, is a passive two-terminal electrical component which resists changes in electric current passing through it. It consists of a conductor such as a wire, usually wound into a coil. When a current flows through it, energy is stored temporarily in a m ...
Alternating Current
... DC motors, single-phase AC motors, three-phase induction motors and universal motors. What is the DC motor used for? Small scale applications and elevators, where continuous and smooth acceleration to a high speed is important. What is the universal motor? It runs on either DC or AC current but vari ...
... DC motors, single-phase AC motors, three-phase induction motors and universal motors. What is the DC motor used for? Small scale applications and elevators, where continuous and smooth acceleration to a high speed is important. What is the universal motor? It runs on either DC or AC current but vari ...
Potential distribution terminals with 16 terminal connections
... picked up without further terminal blocks or wiring. The power contacts are fed through to the next terminal without connecting to the terminal points. The HD EtherCAT Terminals (High Density) with increased packing density feature 16 connection points in the housing of a 12 mm EtherCAT Terminal. Th ...
... picked up without further terminal blocks or wiring. The power contacts are fed through to the next terminal without connecting to the terminal points. The HD EtherCAT Terminals (High Density) with increased packing density feature 16 connection points in the housing of a 12 mm EtherCAT Terminal. Th ...
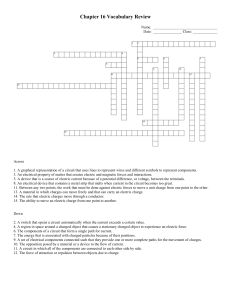
Chapter 16 Vocabulary Review Name: Date: Class: ______ Across
... 1. A graphical representation of a circuit that uses lines to represent wires and different symbols to represent components. 3. An electrical property of matter that creates electric and magnetic forces and interactions. 5. A device that is a source of electric current because of a potential differe ...
... 1. A graphical representation of a circuit that uses lines to represent wires and different symbols to represent components. 3. An electrical property of matter that creates electric and magnetic forces and interactions. 5. A device that is a source of electric current because of a potential differe ...
Solution of Exercise 20 (Electric Circuits)
... 9. Statement (1). When the contact point X touches the metal case and the switch is closed, a large current flows through the metal case to the earth without flowing through the heating element and the fuse will blow because of excessive current. Statement (2). Whent the contact point Y touches the ...
... 9. Statement (1). When the contact point X touches the metal case and the switch is closed, a large current flows through the metal case to the earth without flowing through the heating element and the fuse will blow because of excessive current. Statement (2). Whent the contact point Y touches the ...
Lecture - Montana State University
... and computers will be a part • Practical Troubleshooting—understand the basics of sensors, control systems, and electrical connections ...
... and computers will be a part • Practical Troubleshooting—understand the basics of sensors, control systems, and electrical connections ...
Ground (electricity)

In electrical engineering, ground or earth is the reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth.Electrical circuits may be connected to ground (earth) for several reasons. In mains powered equipment, exposed metal parts are connected to ground to prevent user contact with dangerous voltage if electrical insulation fails. Connections to ground limit the build-up of static electricity when handling flammable products or electrostatic-sensitive devices. In some telegraph and power transmission circuits, the earth itself can be used as one conductor of the circuit, saving the cost of installing a separate return conductor (see single-wire earth return).For measurement purposes, the Earth serves as a (reasonably) constant potential reference against which other potentials can be measured. An electrical ground system should have an appropriate current-carrying capability to serve as an adequate zero-voltage reference level. In electronic circuit theory, a ""ground"" is usually idealized as an infinite source or sink for charge, which can absorb an unlimited amount of current without changing its potential. Where a real ground connection has a significant resistance, the approximation of zero potential is no longer valid. Stray voltages or earth potential rise effects will occur, which may create noise in signals or if large enough will produce an electric shock hazard.The use of the term ground (or earth) is so common in electrical and electronics applications that circuits in portable electronic devices such as cell phones and media players as well as circuits in vehicles may be spoken of as having a ""ground"" connection without any actual connection to the Earth, despite ""common"" being a more appropriate term for such a connection. This is usually a large conductor attached to one side of the power supply (such as the ""ground plane"" on a printed circuit board) which serves as the common return path for current from many different components in the circuit.