chapter7-Section6
... automatically disconnect a circuit if the current is large enough to cause excessive ohmic heating. • At extremely low temperatures, many materials become superconductors—they have zero resistance. ...
... automatically disconnect a circuit if the current is large enough to cause excessive ohmic heating. • At extremely low temperatures, many materials become superconductors—they have zero resistance. ...
ch 28 sol
... wire is heated to 30.0°C while the 9.0V potential difference is maintained, what is the resulting current in the wire? Resistivity of Cu =1.72x10-8 Ω·m at 20 C0, temperature coefficient: α =3.93 x10-3 C-1 ...
... wire is heated to 30.0°C while the 9.0V potential difference is maintained, what is the resulting current in the wire? Resistivity of Cu =1.72x10-8 Ω·m at 20 C0, temperature coefficient: α =3.93 x10-3 C-1 ...
Powder Coating System Grounding
... Refer to Figure 1. All electrical circuits need a complete path for current to make its way back to the source (circle=circuit). Electrostatic spray guns emit current (ions) and therefore require a complete circuit. Some of the current emitted by the spray gun is attracted to the spray booth, but mo ...
... Refer to Figure 1. All electrical circuits need a complete path for current to make its way back to the source (circle=circuit). Electrostatic spray guns emit current (ions) and therefore require a complete circuit. Some of the current emitted by the spray gun is attracted to the spray booth, but mo ...
Electric Power Distribution
... 1. A generator at a power station produces AC electricity at V = 25,000 volts, flowing at 8,000 A. 2. A step-up transformer raises V 16x to 400,000 volts (decreases current by 16x to 500 A) ...
... 1. A generator at a power station produces AC electricity at V = 25,000 volts, flowing at 8,000 A. 2. A step-up transformer raises V 16x to 400,000 volts (decreases current by 16x to 500 A) ...
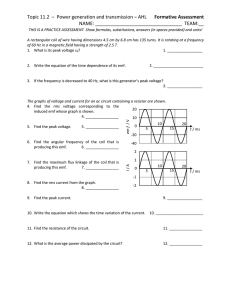
this is a practice assessment
... A power transmission cable having a diameter of 4.75 cm is made of aluminum which has a resistivity of 5.1810 -8 m. 17. Find the cross-sectional area of the cable in m2. 17. ________________ ...
... A power transmission cable having a diameter of 4.75 cm is made of aluminum which has a resistivity of 5.1810 -8 m. 17. Find the cross-sectional area of the cable in m2. 17. ________________ ...
Basic Electrical Circuits
... Current is a flow of electricity that is not constant. In fact the direction of current flow periodically switches direction. Examples of AC are: ...
... Current is a flow of electricity that is not constant. In fact the direction of current flow periodically switches direction. Examples of AC are: ...
Series & Parallel Circuits
... • In an electric circuit, the increase in voltage provided by the energy source (battery), Vsource, is equal to the sum of the voltage drop across the devices • Vsource=VA+VB+… ...
... • In an electric circuit, the increase in voltage provided by the energy source (battery), Vsource, is equal to the sum of the voltage drop across the devices • Vsource=VA+VB+… ...
DC Islands in AC Smart Grids Abstract
... higher quality supply and easier reconfigurability of the system .This piece presents the idea of introducing some DC islands interconnected with the AC distribution network. This will make it easier to connect storage systems, electrical drives, power converters, and renewable sources (i.e., photov ...
... higher quality supply and easier reconfigurability of the system .This piece presents the idea of introducing some DC islands interconnected with the AC distribution network. This will make it easier to connect storage systems, electrical drives, power converters, and renewable sources (i.e., photov ...
Science Part B Chapter –4- Electrical Energy Lesson –1
... Circuit breakers and fuses prevent too much current from flowing through a circuit. GFCI outlets (ground fault circuit interrupters) are special outlets with a safety switch that instantly switches off in some dangerous situations to help prevent a shock. The volt is a unit used to measure how stron ...
... Circuit breakers and fuses prevent too much current from flowing through a circuit. GFCI outlets (ground fault circuit interrupters) are special outlets with a safety switch that instantly switches off in some dangerous situations to help prevent a shock. The volt is a unit used to measure how stron ...
346N_No19_Elect_Design2
... • Review conductor and conduit selection • Learn about protection systems (basic rules) • Learn to design Residential Electrical Systems ...
... • Review conductor and conduit selection • Learn about protection systems (basic rules) • Learn to design Residential Electrical Systems ...
TIA-968-A leakage question - Telecommunications Industry
... A telephone connection, auxiliary lead, or E&M lead that has an intentional dc conducting path to earth ground for protection purposes at the leakage current test voltages (such as through a surge suppressor), may have the component providing the conducting path removed from the equipment for the le ...
... A telephone connection, auxiliary lead, or E&M lead that has an intentional dc conducting path to earth ground for protection purposes at the leakage current test voltages (such as through a surge suppressor), may have the component providing the conducting path removed from the equipment for the le ...
Physics 4700 Experiment 2 R-L-C Circuits
... Measure the frequency response (i.e. voltage gain and output voltage phase shift relative to the input voltage) of the filter you built in part 1) to a sine wave. Make measurements over the frequency range 10 Hz-100 kHz (or as high as you can go). Plot the measurements with the theoretical expectati ...
... Measure the frequency response (i.e. voltage gain and output voltage phase shift relative to the input voltage) of the filter you built in part 1) to a sine wave. Make measurements over the frequency range 10 Hz-100 kHz (or as high as you can go). Plot the measurements with the theoretical expectati ...
DFB Mains supply considerations
... a standard UK mains plug fitted with a 13 Amp fuse. You may get away with more connected for a while, but sooner or later the fuse will require replacement. Similarly for trouble free operation on a supply protected by breakers, we do not recommend using more fittings than the numeric current rating ...
... a standard UK mains plug fitted with a 13 Amp fuse. You may get away with more connected for a while, but sooner or later the fuse will require replacement. Similarly for trouble free operation on a supply protected by breakers, we do not recommend using more fittings than the numeric current rating ...
Positive Negative
... Since the war, plastic insulation has been used extensively, and because of this the leakage current no longer prevails. As there is no leakage to bother about, it does not matter which battery terminal is earthed from a corrosion point of view. Sparking plugs still operate more effectively with a p ...
... Since the war, plastic insulation has been used extensively, and because of this the leakage current no longer prevails. As there is no leakage to bother about, it does not matter which battery terminal is earthed from a corrosion point of view. Sparking plugs still operate more effectively with a p ...
SONDERKOLLOQUIUM der TF am 14.02.2014 Herr Prof. Costas D. Vournas
... Load tap changers (LTC) are used traditionally to control the distribution side voltage, while capacitor banks are switched on and off to correct power factor during load variations. The problem with this practice is that LTC tap adjustment is contributing to load recovery after a contingency and th ...
... Load tap changers (LTC) are used traditionally to control the distribution side voltage, while capacitor banks are switched on and off to correct power factor during load variations. The problem with this practice is that LTC tap adjustment is contributing to load recovery after a contingency and th ...
Basic Vehicle Electric circuits
... tested for short circuits and/or damage to the wiring. Use a DMM to check the resistance through the wiring and components from the power supply source through to ground reference. It is also vital to check for short circuits between these reference points. For example, where two cables have fused t ...
... tested for short circuits and/or damage to the wiring. Use a DMM to check the resistance through the wiring and components from the power supply source through to ground reference. It is also vital to check for short circuits between these reference points. For example, where two cables have fused t ...
Ground (electricity)

In electrical engineering, ground or earth is the reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth.Electrical circuits may be connected to ground (earth) for several reasons. In mains powered equipment, exposed metal parts are connected to ground to prevent user contact with dangerous voltage if electrical insulation fails. Connections to ground limit the build-up of static electricity when handling flammable products or electrostatic-sensitive devices. In some telegraph and power transmission circuits, the earth itself can be used as one conductor of the circuit, saving the cost of installing a separate return conductor (see single-wire earth return).For measurement purposes, the Earth serves as a (reasonably) constant potential reference against which other potentials can be measured. An electrical ground system should have an appropriate current-carrying capability to serve as an adequate zero-voltage reference level. In electronic circuit theory, a ""ground"" is usually idealized as an infinite source or sink for charge, which can absorb an unlimited amount of current without changing its potential. Where a real ground connection has a significant resistance, the approximation of zero potential is no longer valid. Stray voltages or earth potential rise effects will occur, which may create noise in signals or if large enough will produce an electric shock hazard.The use of the term ground (or earth) is so common in electrical and electronics applications that circuits in portable electronic devices such as cell phones and media players as well as circuits in vehicles may be spoken of as having a ""ground"" connection without any actual connection to the Earth, despite ""common"" being a more appropriate term for such a connection. This is usually a large conductor attached to one side of the power supply (such as the ""ground plane"" on a printed circuit board) which serves as the common return path for current from many different components in the circuit.