Grounding and Bonding
... Author’s Comment: Grounding metal parts helps drain off static electricity charges before flashover potential is reached. Static grounding is often used in areas where the discharge (arcing) of the voltage buildup (static) can cause dangerous or undesirable conditions [500.4 Note 3]. DANGER: Because ...
... Author’s Comment: Grounding metal parts helps drain off static electricity charges before flashover potential is reached. Static grounding is often used in areas where the discharge (arcing) of the voltage buildup (static) can cause dangerous or undesirable conditions [500.4 Note 3]. DANGER: Because ...
G / E-Series Motor Protection Relay Product Features Specifications
... requirements may lead to personal injury as well as damage to electrical equipment or other property. NEVER bypass external fusing. NEVER apply the voltages at Program Lock and Auto Reset terminals. Before performing Dielectric or Megger testing on any equipment in which the monitoring device is ins ...
... requirements may lead to personal injury as well as damage to electrical equipment or other property. NEVER bypass external fusing. NEVER apply the voltages at Program Lock and Auto Reset terminals. Before performing Dielectric or Megger testing on any equipment in which the monitoring device is ins ...
Circuits and Current Electricity
... A circuit is a pathway for electricity to flow made up of four basic components. ...
... A circuit is a pathway for electricity to flow made up of four basic components. ...
Static Electricity The Laws of Electrical Charges Current Electricity
... Electrical energy is the energy carried by charged particles. Voltage is a measure of how much electrical energy each charged particle carries. The higher the energy of each charged particle, the greater the potential energy. Also called 'potential difference', the energy delivered by a flow of char ...
... Electrical energy is the energy carried by charged particles. Voltage is a measure of how much electrical energy each charged particle carries. The higher the energy of each charged particle, the greater the potential energy. Also called 'potential difference', the energy delivered by a flow of char ...
Chapter 7 - St. Thomas the Apostle School
... • The parts of a series circuit are wired one after another, so the amount of current is the same through every point. • Open circuit- if any part of a circuit is disconnected. No current flows through the circuit. For example- Christmas lights ...
... • The parts of a series circuit are wired one after another, so the amount of current is the same through every point. • Open circuit- if any part of a circuit is disconnected. No current flows through the circuit. For example- Christmas lights ...
Electricity & Magnetism
... There are 2 types of currents: Current (DC) – Where electrons flow in the same direction in a wire. ...
... There are 2 types of currents: Current (DC) – Where electrons flow in the same direction in a wire. ...
STFE Elite Series - Active Tracking® Filters with Surge
... Power Protection and Conditioning STFE Elite Series - Active Tracking® Filters with Surge Protection The SolaHD STF Elite DIN Rail Mount Series combines Active Tracking® technology with UL Listed surge protection to protect against the full spectrum of voltage transients and surges. It continuously ...
... Power Protection and Conditioning STFE Elite Series - Active Tracking® Filters with Surge Protection The SolaHD STF Elite DIN Rail Mount Series combines Active Tracking® technology with UL Listed surge protection to protect against the full spectrum of voltage transients and surges. It continuously ...
High-Voltage Transmission
... increase electric energy’s pressure (voltage) so it can move long distances over power lines that transmit ...
... increase electric energy’s pressure (voltage) so it can move long distances over power lines that transmit ...
SolarElectricKits - Electrical and Computer Engineering
... 2.a Parallel connection All positives are connected together. All negatives are connected together. ...
... 2.a Parallel connection All positives are connected together. All negatives are connected together. ...
One earth reference on each working circuit – the
... The portion of the earth return current flowing through the soil is the key factor for both EPR and induced voltage hazards ...
... The portion of the earth return current flowing through the soil is the key factor for both EPR and induced voltage hazards ...
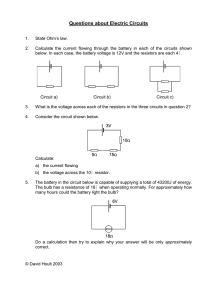
Questions about Electric Circuits
... below. In each case, the battery voltage is 12V and the resistors are each 4Ω. ...
... below. In each case, the battery voltage is 12V and the resistors are each 4Ω. ...
Science 9 Unit 4: Electricity Name:
... Electrical energy is the energy carried by charged particles. Voltage is a measure of how much electrical energy each charged particle carries. The higher the energy of each charged particle, the greater the potential energy. Also called 'potential difference', the energy delivered by a flow of char ...
... Electrical energy is the energy carried by charged particles. Voltage is a measure of how much electrical energy each charged particle carries. The higher the energy of each charged particle, the greater the potential energy. Also called 'potential difference', the energy delivered by a flow of char ...
RF in the SHACK and OTHER GROUNDING MYTHS
... A ground rod is an 8 foot long copper coated road pounded 7 ½ feet into the ground. It should be in a place that is moist from time to time. You cannot put it in dry sand and expect it to work. The ground rod wire, for a power system ground, should be #8 wire or larger. Construction Plans will pro ...
... A ground rod is an 8 foot long copper coated road pounded 7 ½ feet into the ground. It should be in a place that is moist from time to time. You cannot put it in dry sand and expect it to work. The ground rod wire, for a power system ground, should be #8 wire or larger. Construction Plans will pro ...
Grounding and Bonding in Boats and Marinas
... a connection to the water, are connected (bonded) together, then if a ground fault occurs along with a faulty ground path, all these metals will rise in potential together. If you touch 2 objects that are at 120vac, you will not be shocked since there is no potential difference and no current will f ...
... a connection to the water, are connected (bonded) together, then if a ground fault occurs along with a faulty ground path, all these metals will rise in potential together. If you touch 2 objects that are at 120vac, you will not be shocked since there is no potential difference and no current will f ...
Grounding and Bonding in Boats and Marinas
... a connection to the water, are connected (bonded) together, then if a ground fault occurs along with a faulty ground path, all these metals will rise in potential together. If you touch 2 objects that are at 120vac, you will not be shocked since there is no potential difference and no current will f ...
... a connection to the water, are connected (bonded) together, then if a ground fault occurs along with a faulty ground path, all these metals will rise in potential together. If you touch 2 objects that are at 120vac, you will not be shocked since there is no potential difference and no current will f ...
Analysis of a floating vs. grounded output
... Figure 6c: Voltage measurement between neutral and ground with neutral tied to ground reference. Figure 6b illustrates a voltage measurement between line and neutral. The meter indicates the correct output of 120VAC. Figure 6c shows a measurement between neutral and ground while figure 6d indicates ...
... Figure 6c: Voltage measurement between neutral and ground with neutral tied to ground reference. Figure 6b illustrates a voltage measurement between line and neutral. The meter indicates the correct output of 120VAC. Figure 6c shows a measurement between neutral and ground while figure 6d indicates ...
Methods of Personnel Grounding - Techni-Tool
... charge. A continuous connection to ground is required to protect devices. ...
... charge. A continuous connection to ground is required to protect devices. ...
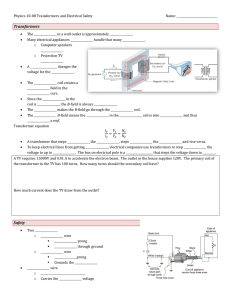
Transformers Safety
... ____________________, but the number of loops are ________________ Normally the induced current is __________ since the two sides ________________ If an ________________ occurs (like current going through a person to the ground), an ________________________ pulls a ________________ ...
... ____________________, but the number of loops are ________________ Normally the induced current is __________ since the two sides ________________ If an ________________ occurs (like current going through a person to the ground), an ________________________ pulls a ________________ ...
Ground (electricity)

In electrical engineering, ground or earth is the reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth.Electrical circuits may be connected to ground (earth) for several reasons. In mains powered equipment, exposed metal parts are connected to ground to prevent user contact with dangerous voltage if electrical insulation fails. Connections to ground limit the build-up of static electricity when handling flammable products or electrostatic-sensitive devices. In some telegraph and power transmission circuits, the earth itself can be used as one conductor of the circuit, saving the cost of installing a separate return conductor (see single-wire earth return).For measurement purposes, the Earth serves as a (reasonably) constant potential reference against which other potentials can be measured. An electrical ground system should have an appropriate current-carrying capability to serve as an adequate zero-voltage reference level. In electronic circuit theory, a ""ground"" is usually idealized as an infinite source or sink for charge, which can absorb an unlimited amount of current without changing its potential. Where a real ground connection has a significant resistance, the approximation of zero potential is no longer valid. Stray voltages or earth potential rise effects will occur, which may create noise in signals or if large enough will produce an electric shock hazard.The use of the term ground (or earth) is so common in electrical and electronics applications that circuits in portable electronic devices such as cell phones and media players as well as circuits in vehicles may be spoken of as having a ""ground"" connection without any actual connection to the Earth, despite ""common"" being a more appropriate term for such a connection. This is usually a large conductor attached to one side of the power supply (such as the ""ground plane"" on a printed circuit board) which serves as the common return path for current from many different components in the circuit.