Data Sheet
... The only controlled copy of this Data Sheet is the electronic read-only version located on the Cooper Bussmann Network Drive. All other copies of this document are by definition uncontrolled. This bulletin is intended to clearly present comprehensive product data and provide technical information th ...
... The only controlled copy of this Data Sheet is the electronic read-only version located on the Cooper Bussmann Network Drive. All other copies of this document are by definition uncontrolled. This bulletin is intended to clearly present comprehensive product data and provide technical information th ...
electrical circuits
... An electric current is a flow of microscopic particles called electrons flowing through wires and ...
... An electric current is a flow of microscopic particles called electrons flowing through wires and ...
Rating of Ground Bus in Metal-Enclosed
... All metal-enclosed switchgear built to ANSI standards is required to include a ground bus to connect together all items in the switchgear that are required to be grounded. This includes such things as the enclosures, circuit breaker frames, CT and VT secondary circuits, relay and instrument cases, e ...
... All metal-enclosed switchgear built to ANSI standards is required to include a ground bus to connect together all items in the switchgear that are required to be grounded. This includes such things as the enclosures, circuit breaker frames, CT and VT secondary circuits, relay and instrument cases, e ...
AC Current and Voltage
... current. • An a.c. current is so-called as it continuously changes size and direction. • A voltage that produces such a current is called an a.c. voltage. • When working with a.c. currents and voltages we often need to use a kind of average value. ...
... current. • An a.c. current is so-called as it continuously changes size and direction. • A voltage that produces such a current is called an a.c. voltage. • When working with a.c. currents and voltages we often need to use a kind of average value. ...
Unitron, LP
... and hazardous waste, increasing operational efficiency, reducing costs and increasing worker safety, Unitron has developed a product line to support the SFLEDS program. The standard UFC Series SFLEDS includes 400Hz converters, power distribution units (PDUs), 400Hz aircraft power cables and obstruct ...
... and hazardous waste, increasing operational efficiency, reducing costs and increasing worker safety, Unitron has developed a product line to support the SFLEDS program. The standard UFC Series SFLEDS includes 400Hz converters, power distribution units (PDUs), 400Hz aircraft power cables and obstruct ...
Unitron, LP
... hazardous waste, increasing operational efficiency, reducing costs and increasing worker safety, Unitron has developed a product line to support the SFLEDS program. The 270VDC UDC Series SFLEDS includes 270VDC converters, power distribution units (PDUs), 270VDC aircraft power cables and obstruction ...
... hazardous waste, increasing operational efficiency, reducing costs and increasing worker safety, Unitron has developed a product line to support the SFLEDS program. The 270VDC UDC Series SFLEDS includes 270VDC converters, power distribution units (PDUs), 270VDC aircraft power cables and obstruction ...
POWER SYSTEMS TECH – PWRT
... ABCWUA Position Description POWER SYSTEMS TECHNICIAN Status APPROVED ...
... ABCWUA Position Description POWER SYSTEMS TECHNICIAN Status APPROVED ...
Circuit Analysis
... A. the power should remain off until the circuit is completed. B. the voltage output should be set to 0.0 V C. the current output should be set to ½ maximum Ground +V When the circuit is complete, then A. turn the power on B. slowly increase the voltage to the desired setting C. turn the power off i ...
... A. the power should remain off until the circuit is completed. B. the voltage output should be set to 0.0 V C. the current output should be set to ½ maximum Ground +V When the circuit is complete, then A. turn the power on B. slowly increase the voltage to the desired setting C. turn the power off i ...
Basic wiring configuration for branch circuits in homes and
... ("neutral") should be the wide blade and the electrical potential should be near zero potential. In the U.S. the black wire ("hot") is 120 volts RMS (root-mean-square) sinusoid, 60 Hz repetition frequency, with peaks ±170 volts respect to the neutral. Keep in mind that the colors are purely customar ...
... ("neutral") should be the wide blade and the electrical potential should be near zero potential. In the U.S. the black wire ("hot") is 120 volts RMS (root-mean-square) sinusoid, 60 Hz repetition frequency, with peaks ±170 volts respect to the neutral. Keep in mind that the colors are purely customar ...
CMGT 235 Quiz #8 Show all calculations! Name
... 13. What’s the power loss in watts for two conductors that carry 12A and have a voltage drop of 3.60V? ...
... 13. What’s the power loss in watts for two conductors that carry 12A and have a voltage drop of 3.60V? ...
3A1981
... 1. This Surge Protective Device (SPD) is intended for ordinary indoor use on communication loop circuits that are isolated from the Public Switched Telephone Network. 2. The SPD module shall be secured to the compatible base before applying power to the communication loop. 3. The base shall be secur ...
... 1. This Surge Protective Device (SPD) is intended for ordinary indoor use on communication loop circuits that are isolated from the Public Switched Telephone Network. 2. The SPD module shall be secured to the compatible base before applying power to the communication loop. 3. The base shall be secur ...
ITS_1_Unit 1 Summative Test
... periodically reverse their direction of movement. Alternating Current 2. In electricity, __________ is an electric current flowing in one direction only and substantially constant in value. Direct Current ...
... periodically reverse their direction of movement. Alternating Current 2. In electricity, __________ is an electric current flowing in one direction only and substantially constant in value. Direct Current ...
In this task you will build upon your knowledge of electricity to
... paste them in the space provided (say which country they’re from). 32. Why are household circuits wired in parallel and not in series? ...
... paste them in the space provided (say which country they’re from). 32. Why are household circuits wired in parallel and not in series? ...
snix quik-snix super snix
... 4.04 The SNIX and QUIK-SNIX will limit longitudinal AC voltages-to-ground up to 30 volts AC. The Super SNIX will suppress up to 50 volts AC. Voltages above these values may cause the SNIXs to saturate, which can increase the AC voltage or generate noise on the circuit. 4.05 All SNIXs and Super SNIXs ...
... 4.04 The SNIX and QUIK-SNIX will limit longitudinal AC voltages-to-ground up to 30 volts AC. The Super SNIX will suppress up to 50 volts AC. Voltages above these values may cause the SNIXs to saturate, which can increase the AC voltage or generate noise on the circuit. 4.05 All SNIXs and Super SNIXs ...
Instrumentation and Measurement Techniques
... is a device that converts ac electrical energy at one voltage level to ac electrical energy at another voltage level, but with the same frequency. In general, transformers operate on the same principles as generators and motors, and are usually studied together with generators and motors. These 3 ty ...
... is a device that converts ac electrical energy at one voltage level to ac electrical energy at another voltage level, but with the same frequency. In general, transformers operate on the same principles as generators and motors, and are usually studied together with generators and motors. These 3 ty ...
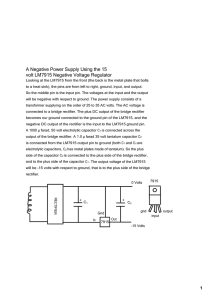
A Negative Power Supply Using the 15 volt LM7915 Negative
... A Negative Power Supply Using the 15 volt LM7915 Negative Voltage Regulator Looking at the LM7915 from the front ﴾the back is the metal plate that bolts ...
... A Negative Power Supply Using the 15 volt LM7915 Negative Voltage Regulator Looking at the LM7915 from the front ﴾the back is the metal plate that bolts ...
Ground (electricity)

In electrical engineering, ground or earth is the reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth.Electrical circuits may be connected to ground (earth) for several reasons. In mains powered equipment, exposed metal parts are connected to ground to prevent user contact with dangerous voltage if electrical insulation fails. Connections to ground limit the build-up of static electricity when handling flammable products or electrostatic-sensitive devices. In some telegraph and power transmission circuits, the earth itself can be used as one conductor of the circuit, saving the cost of installing a separate return conductor (see single-wire earth return).For measurement purposes, the Earth serves as a (reasonably) constant potential reference against which other potentials can be measured. An electrical ground system should have an appropriate current-carrying capability to serve as an adequate zero-voltage reference level. In electronic circuit theory, a ""ground"" is usually idealized as an infinite source or sink for charge, which can absorb an unlimited amount of current without changing its potential. Where a real ground connection has a significant resistance, the approximation of zero potential is no longer valid. Stray voltages or earth potential rise effects will occur, which may create noise in signals or if large enough will produce an electric shock hazard.The use of the term ground (or earth) is so common in electrical and electronics applications that circuits in portable electronic devices such as cell phones and media players as well as circuits in vehicles may be spoken of as having a ""ground"" connection without any actual connection to the Earth, despite ""common"" being a more appropriate term for such a connection. This is usually a large conductor attached to one side of the power supply (such as the ""ground plane"" on a printed circuit board) which serves as the common return path for current from many different components in the circuit.