Circuit notes
... And, if you want a circuit you ALWAYS need two things: a power supply and a conductor. • Most circuits also have an electrical device and a switch. ...
... And, if you want a circuit you ALWAYS need two things: a power supply and a conductor. • Most circuits also have an electrical device and a switch. ...
1 Alternating Current (AC) Current that constantly and rapidly
... A device for changing an alternating voltage from one value to another which by the principle of electromagnetic induction. An alternating current in the primary coil creates an alternating magnetic field, which induces an alternating current in the secondary coil. The ratio of the voltage in the se ...
... A device for changing an alternating voltage from one value to another which by the principle of electromagnetic induction. An alternating current in the primary coil creates an alternating magnetic field, which induces an alternating current in the secondary coil. The ratio of the voltage in the se ...
Wire free Door Guard
... contacts remain closed so that the reset pin of IC HEF 4060 will be high. This inhibits its oscillation and it remains standby. When an intruder opens the door, magnet and reed switch move away taking the reset pin of IC to ground potential. IC starts oscillating using the components C1 and R3.Blink ...
... contacts remain closed so that the reset pin of IC HEF 4060 will be high. This inhibits its oscillation and it remains standby. When an intruder opens the door, magnet and reed switch move away taking the reset pin of IC to ground potential. IC starts oscillating using the components C1 and R3.Blink ...
curriculum vitae
... storage tank which is located at top of the building. By using pressure of flow of water of the turbine is rotated which is directly coupled to dynamo and electrically is produced. This generated electrical power is in DC form. This further converted into AC form. This electrical power can be utiliz ...
... storage tank which is located at top of the building. By using pressure of flow of water of the turbine is rotated which is directly coupled to dynamo and electrically is produced. This generated electrical power is in DC form. This further converted into AC form. This electrical power can be utiliz ...
Chapter 36 Summary – Magnetism
... Directions: circle the word that would correctly complete the sentence. Static electricity is when (charges, circuits) accumulate on the (inside, surface) of an object which gains or loses (electrons, branches) which move more easily on a (conductor, insulator) than they do on a (conductor, insulato ...
... Directions: circle the word that would correctly complete the sentence. Static electricity is when (charges, circuits) accumulate on the (inside, surface) of an object which gains or loses (electrons, branches) which move more easily on a (conductor, insulator) than they do on a (conductor, insulato ...
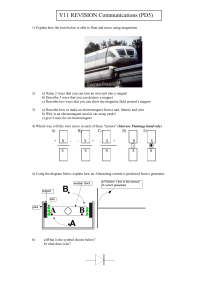
Comms Revision Questions
... b) Why is an electromagnet used in car scrap yards? c) give 6 uses for an electromagnet ...
... b) Why is an electromagnet used in car scrap yards? c) give 6 uses for an electromagnet ...
“Switch-On” Electronics - Cleveland State University
... • One amp of current means a flow of one Coulomb (6.241 × 1018 electrons) per second Amps = Coulombs / second ...
... • One amp of current means a flow of one Coulomb (6.241 × 1018 electrons) per second Amps = Coulombs / second ...
Appalachian Power Safety Policy No. 22
... To protect workers under this condition, additional measures must be taken to prevent injury from these voltages. An equipotential zone created by ensuring that an existing, partial or newly installed pole ground is in contact with the pole and properly bonded to the neutral has been shown to provid ...
... To protect workers under this condition, additional measures must be taken to prevent injury from these voltages. An equipotential zone created by ensuring that an existing, partial or newly installed pole ground is in contact with the pole and properly bonded to the neutral has been shown to provid ...
Lightning and Power Surges
... to high, rapid heating of water vapor in the surrounding air, which explains why windows are frequently blown out. Lightning can create electromagnetic fields that induce voltage and current surges in electric and communications lines causing damage to equipment, especially solid-state electronics. ...
... to high, rapid heating of water vapor in the surrounding air, which explains why windows are frequently blown out. Lightning can create electromagnetic fields that induce voltage and current surges in electric and communications lines causing damage to equipment, especially solid-state electronics. ...
02461-05.8 Physical Properties of Elect Circuits
... To effectively and safely use electricity, it is important to understand some of its basic principles. Electrical devices used for agricultural purposes require current, the flow of electrons along a conductor. Current electricity flows to devices through a complete circuit. These circuits commonly ...
... To effectively and safely use electricity, it is important to understand some of its basic principles. Electrical devices used for agricultural purposes require current, the flow of electrons along a conductor. Current electricity flows to devices through a complete circuit. These circuits commonly ...
TR41.9.2-05-02-007 - Telecommunications Industry Association
... contribution; and at TIA's sole discretion to permit others to reproduce in whole or in part such contribution or the resulting TIA Publication. This contributor will also be willing to grant licenses under such copyrights to third parties on reasonable, non-discriminatory terms and conditions for p ...
... contribution; and at TIA's sole discretion to permit others to reproduce in whole or in part such contribution or the resulting TIA Publication. This contributor will also be willing to grant licenses under such copyrights to third parties on reasonable, non-discriminatory terms and conditions for p ...
Electronics & Signals
... level Excessive collisions can slow the network down or bring it to a halt. ...
... level Excessive collisions can slow the network down or bring it to a halt. ...
Here we have some circuits with voltage sources.
... Here we have some circuits with voltage sources. We will determine whether these are valid circuits. The first circuit is 1 V applied across a resistor, which is valid. The second circuit is two series voltage sources, and the voltage simply add together to produce a net voltage of -1 V across the r ...
... Here we have some circuits with voltage sources. We will determine whether these are valid circuits. The first circuit is 1 V applied across a resistor, which is valid. The second circuit is two series voltage sources, and the voltage simply add together to produce a net voltage of -1 V across the r ...
Ultra Fast Acting Electronic Circuit Breaker
... compared against the preset voltage proportional to the current by a level comparator to generate an output for the load to trip. The concept of electronic circuit breaker came into focus realizing that conventional circuit breakers such as MCBs take longer time to trip. Therefore, for sensitive loa ...
... compared against the preset voltage proportional to the current by a level comparator to generate an output for the load to trip. The concept of electronic circuit breaker came into focus realizing that conventional circuit breakers such as MCBs take longer time to trip. Therefore, for sensitive loa ...
Electrical safety of LHC quench heater circuits in case of
... As expected fuse blows and protects the equipment Maximum observed voltage: U_max = 22 V, t < 0.1 ms ...
... As expected fuse blows and protects the equipment Maximum observed voltage: U_max = 22 V, t < 0.1 ms ...
Making an Earth Battery - United Scientific Supplies
... zinc (anode) and copper (cathode) in the ground about one meter (3.2 feet) apart producing an output voltage of approximately 1 volt. Have students create earth electrodes out of two dissimilar metals. Ask them to hypothesize what soil conditions are best for creating an earth battery. (Suggestions ...
... zinc (anode) and copper (cathode) in the ground about one meter (3.2 feet) apart producing an output voltage of approximately 1 volt. Have students create earth electrodes out of two dissimilar metals. Ask them to hypothesize what soil conditions are best for creating an earth battery. (Suggestions ...
Ground (electricity)

In electrical engineering, ground or earth is the reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth.Electrical circuits may be connected to ground (earth) for several reasons. In mains powered equipment, exposed metal parts are connected to ground to prevent user contact with dangerous voltage if electrical insulation fails. Connections to ground limit the build-up of static electricity when handling flammable products or electrostatic-sensitive devices. In some telegraph and power transmission circuits, the earth itself can be used as one conductor of the circuit, saving the cost of installing a separate return conductor (see single-wire earth return).For measurement purposes, the Earth serves as a (reasonably) constant potential reference against which other potentials can be measured. An electrical ground system should have an appropriate current-carrying capability to serve as an adequate zero-voltage reference level. In electronic circuit theory, a ""ground"" is usually idealized as an infinite source or sink for charge, which can absorb an unlimited amount of current without changing its potential. Where a real ground connection has a significant resistance, the approximation of zero potential is no longer valid. Stray voltages or earth potential rise effects will occur, which may create noise in signals or if large enough will produce an electric shock hazard.The use of the term ground (or earth) is so common in electrical and electronics applications that circuits in portable electronic devices such as cell phones and media players as well as circuits in vehicles may be spoken of as having a ""ground"" connection without any actual connection to the Earth, despite ""common"" being a more appropriate term for such a connection. This is usually a large conductor attached to one side of the power supply (such as the ""ground plane"" on a printed circuit board) which serves as the common return path for current from many different components in the circuit.