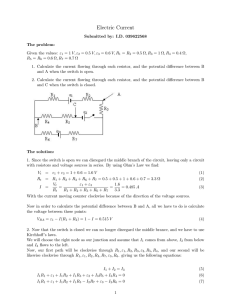
March
... (c) Controller (d) Desired value. 2. (a) State why front switch boards are required for A.C system having voltage to earth greater than 55V (b) Explain how section of an electrical system aboard ship can be isolated for maintenance work (c) Describe, with reference to electrical connections, the pro ...
... (c) Controller (d) Desired value. 2. (a) State why front switch boards are required for A.C system having voltage to earth greater than 55V (b) Explain how section of an electrical system aboard ship can be isolated for maintenance work (c) Describe, with reference to electrical connections, the pro ...
3. Measuring Electricity
... Resistance – is the ability to hold back the flow of electrons in a conductor. The molecules found in every type of conductor resists the flow of electrons to some extent. Resistors – are electrical devices that are used in circuits that are designed to resist the flow of electricity. The symbol fo ...
... Resistance – is the ability to hold back the flow of electrons in a conductor. The molecules found in every type of conductor resists the flow of electrons to some extent. Resistors – are electrical devices that are used in circuits that are designed to resist the flow of electricity. The symbol fo ...
Panel Installation guide - Al Sabir Electrical Services
... A relay is used to isolate one electrical circuit from another. It allows a low current control circuit to make or break an electrically isolated high current circuit path. Normally-open (NO) contacts connect the circuit when the relay is activated; the circuit is disconnected when the relay is inac ...
... A relay is used to isolate one electrical circuit from another. It allows a low current control circuit to make or break an electrically isolated high current circuit path. Normally-open (NO) contacts connect the circuit when the relay is activated; the circuit is disconnected when the relay is inac ...
SI99-01 - Semtech
... Guard traces may be used in situations where a long (> 30cm) interconnected signal trace cannot be avoided (Figure 5). An even better solution is to place a ground plane opposite the signal line. The signal line should be within 13 mm of the guard trace or ground plane. Transpose long sections (> 30 ...
... Guard traces may be used in situations where a long (> 30cm) interconnected signal trace cannot be avoided (Figure 5). An even better solution is to place a ground plane opposite the signal line. The signal line should be within 13 mm of the guard trace or ground plane. Transpose long sections (> 30 ...
Basic Electrical
... AC generators (large electromagnets) can be built with much larger and powerful voltage ratings than DC Less expensive than DC to produce due to the simplicity of the winding and brushes Voltages can be stepped down or up efficiently by the use of simple transformers (induction principle) ...
... AC generators (large electromagnets) can be built with much larger and powerful voltage ratings than DC Less expensive than DC to produce due to the simplicity of the winding and brushes Voltages can be stepped down or up efficiently by the use of simple transformers (induction principle) ...
Alternating Current - School
... P2 – Physics - Fuses Fuses are _______ devices. If there is a fault in an appliance which causes the ____ and neutral (or earth) wire to cross then a ______ current will flow through the _____ and cause it to _____. This will break the _______ and protect the appliance and ...
... P2 – Physics - Fuses Fuses are _______ devices. If there is a fault in an appliance which causes the ____ and neutral (or earth) wire to cross then a ______ current will flow through the _____ and cause it to _____. This will break the _______ and protect the appliance and ...
Photovoltaic Terminology
... Isc(stc), Short-circuit current short-circuit current of a PV module, PV string, PV array or PV generator under standard test conditions Isolation A function intended to cut off for reasons of safety the supply from all, or a discrete section, of the installation by separating the installation or se ...
... Isc(stc), Short-circuit current short-circuit current of a PV module, PV string, PV array or PV generator under standard test conditions Isolation A function intended to cut off for reasons of safety the supply from all, or a discrete section, of the installation by separating the installation or se ...
Electric Current
... The pressure of the water flowing through the pipes on the last slide compare to the voltage (electric potential) flowing through the wires of the circuit. The unit used to measure voltage is volts (V). The flow of charges in a circuit is called current. Current (I) is measured in Amperes (A). Cur ...
... The pressure of the water flowing through the pipes on the last slide compare to the voltage (electric potential) flowing through the wires of the circuit. The unit used to measure voltage is volts (V). The flow of charges in a circuit is called current. Current (I) is measured in Amperes (A). Cur ...
Advance Matlab - Ascent Softech
... Single pulse rectifier consisting of a Diode, an RL load and an AC Voltage source.Single pulse thyristor rectifier is used to feed an RL load.Ideal Switch to switch an RLC circuit on an AC source. Use of the MOSFET in a zero-current quasi-resonant switch converter ...
... Single pulse rectifier consisting of a Diode, an RL load and an AC Voltage source.Single pulse thyristor rectifier is used to feed an RL load.Ideal Switch to switch an RLC circuit on an AC source. Use of the MOSFET in a zero-current quasi-resonant switch converter ...
P5 – Electrical Circuits
... • This is calculated as their voltage x the current they use: – Power (W) = Voltage (V) x Current (A) ...
... • This is calculated as their voltage x the current they use: – Power (W) = Voltage (V) x Current (A) ...
Summary 1. About electrical drives
... In the wide field of technical legislation, the electricity sector is particularly complex because of the strong interdependence between the rules adopted in relation to different products: electrical equipment, for example, often consists of a set of electrical devices each of which can be consider ...
... In the wide field of technical legislation, the electricity sector is particularly complex because of the strong interdependence between the rules adopted in relation to different products: electrical equipment, for example, often consists of a set of electrical devices each of which can be consider ...
Chapter 17 Section 1 1. Describe how an object is charged by
... cannot determine the type of charge (positive or negative) the object has. Explain why not. a. Like charges repel, but repulsion does not indicate what charge is involved. Therefore, the electroscope will behave the same, regardless of an object’s charge. 1. What is static electricity? Give an examp ...
... cannot determine the type of charge (positive or negative) the object has. Explain why not. a. Like charges repel, but repulsion does not indicate what charge is involved. Therefore, the electroscope will behave the same, regardless of an object’s charge. 1. What is static electricity? Give an examp ...
Presentation - cloudfront.net
... • Brushed alternators use little pieces of carbon/graphite to pass electricity across a spinning gap - this often creates little sparks (which can cause radio interference). Brushed alternators are cheaper to produce, but the brushes do wear out over time and require replacement. • Brushless alterna ...
... • Brushed alternators use little pieces of carbon/graphite to pass electricity across a spinning gap - this often creates little sparks (which can cause radio interference). Brushed alternators are cheaper to produce, but the brushes do wear out over time and require replacement. • Brushless alterna ...
Telecommunications Earthing Training
... Carry out soil resistivity testing of the soil available. From this calculate the expected resistance on one rod. Then install one rod and measure its resistance to ground to verify the calculated result. Calculate resistance of multiple rods. Install these multiple rods and measure the resistance t ...
... Carry out soil resistivity testing of the soil available. From this calculate the expected resistance on one rod. Then install one rod and measure its resistance to ground to verify the calculated result. Calculate resistance of multiple rods. Install these multiple rods and measure the resistance t ...
Ground (electricity)

In electrical engineering, ground or earth is the reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth.Electrical circuits may be connected to ground (earth) for several reasons. In mains powered equipment, exposed metal parts are connected to ground to prevent user contact with dangerous voltage if electrical insulation fails. Connections to ground limit the build-up of static electricity when handling flammable products or electrostatic-sensitive devices. In some telegraph and power transmission circuits, the earth itself can be used as one conductor of the circuit, saving the cost of installing a separate return conductor (see single-wire earth return).For measurement purposes, the Earth serves as a (reasonably) constant potential reference against which other potentials can be measured. An electrical ground system should have an appropriate current-carrying capability to serve as an adequate zero-voltage reference level. In electronic circuit theory, a ""ground"" is usually idealized as an infinite source or sink for charge, which can absorb an unlimited amount of current without changing its potential. Where a real ground connection has a significant resistance, the approximation of zero potential is no longer valid. Stray voltages or earth potential rise effects will occur, which may create noise in signals or if large enough will produce an electric shock hazard.The use of the term ground (or earth) is so common in electrical and electronics applications that circuits in portable electronic devices such as cell phones and media players as well as circuits in vehicles may be spoken of as having a ""ground"" connection without any actual connection to the Earth, despite ""common"" being a more appropriate term for such a connection. This is usually a large conductor attached to one side of the power supply (such as the ""ground plane"" on a printed circuit board) which serves as the common return path for current from many different components in the circuit.