+9V and -9V from one battery
... pin 5, so it gets a negative voltage equal to the voltage across C1. This charge pumping is a very efficient way to convert voltages. The only power lost is that power dissipated in the resistances of the switches inside the 1044 and the series resistance of the capacitors, as well as the power to r ...
... pin 5, so it gets a negative voltage equal to the voltage across C1. This charge pumping is a very efficient way to convert voltages. The only power lost is that power dissipated in the resistances of the switches inside the 1044 and the series resistance of the capacitors, as well as the power to r ...
Conceptual Questions Chap. 13
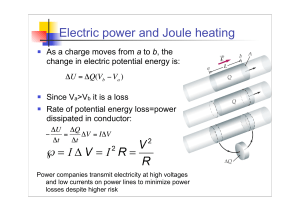
... Resistance is proportional to the length of wire. Thus as the length increases, so does the resistance. It is most efficient to use low current at high voltage. A high current would make P = I2R very large. A lower power loss is obtained for high voltages, since P = (DV)2 / R would not be as large s ...
... Resistance is proportional to the length of wire. Thus as the length increases, so does the resistance. It is most efficient to use low current at high voltage. A high current would make P = I2R very large. A lower power loss is obtained for high voltages, since P = (DV)2 / R would not be as large s ...
Download the Quiz
... Which of the following is good practice for lightning protection grounds? A. They must be bonded to all buried water and gas lines B. Bends in ground wires must be made as close as possible to a right angle C. Lightning grounds must be connected to all ungrounded wiring D. They must be bonded togeth ...
... Which of the following is good practice for lightning protection grounds? A. They must be bonded to all buried water and gas lines B. Bends in ground wires must be made as close as possible to a right angle C. Lightning grounds must be connected to all ungrounded wiring D. They must be bonded togeth ...
Gate
... • A transistor is a device that acts depending on the voltage level of the input signal, either as a conductor or as a resistor of the flow of electricity – Great for logic circuits ...
... • A transistor is a device that acts depending on the voltage level of the input signal, either as a conductor or as a resistor of the flow of electricity – Great for logic circuits ...
AN1681: Grounding Techniques
... Figure 6 shows our best layout. Ground once again forms a plane around the device, but there are 5 slices keeping it from being continuous. Notice that each of the ground planes connects to the others, but only at one place. This is an example of a single-point or star ground. Currents cannot travel ...
... Figure 6 shows our best layout. Ground once again forms a plane around the device, but there are 5 slices keeping it from being continuous. Notice that each of the ground planes connects to the others, but only at one place. This is an example of a single-point or star ground. Currents cannot travel ...
Ground-Fault Protection for
... 1. Detect ground faults in PV arrays mounted on the roofs of dwellings 2. Interrupt the fault current 3. Indicate that a ground fault had occurred 4. Disconnect the faulted part of the PV array 5. Crowbar or short circuit the PV array The original GFPD prototype was developed in two to fires. Fires ...
... 1. Detect ground faults in PV arrays mounted on the roofs of dwellings 2. Interrupt the fault current 3. Indicate that a ground fault had occurred 4. Disconnect the faulted part of the PV array 5. Crowbar or short circuit the PV array The original GFPD prototype was developed in two to fires. Fires ...
Electricity: The flow of electrons through a conductor Electronics
... » Current want to flow to ground. » “True” Ground is literally, the ground. » Floating ground is relative to the circuit it’s a part of... » A reference point from which to measure Voltage » The earth is idealized as an infinite heat-sink for current. It can aborb an unlimited amount without changin ...
... » Current want to flow to ground. » “True” Ground is literally, the ground. » Floating ground is relative to the circuit it’s a part of... » A reference point from which to measure Voltage » The earth is idealized as an infinite heat-sink for current. It can aborb an unlimited amount without changin ...
curriculum template - Bloomfield Public Schools
... The student will understand that: 1. The electrical force is a universal force that exists between any two charged objects. 2. Moving electrical charges produce magnetic forces and moving magnets can produce electrical force. 3. Electrical current can be transformed into light through the excitation ...
... The student will understand that: 1. The electrical force is a universal force that exists between any two charged objects. 2. Moving electrical charges produce magnetic forces and moving magnets can produce electrical force. 3. Electrical current can be transformed into light through the excitation ...
(Anti) Static is Magic! - Simco-Ion
... supply voltage. Anti-static bars, static measuring, static bonding and special products for IML (In mould labelling) will be launched. All products will be managed by the Manager IQ Easy, a controller that will provide distribution of the 24V DC supply voltage to a possible six connected devices. A ...
... supply voltage. Anti-static bars, static measuring, static bonding and special products for IML (In mould labelling) will be launched. All products will be managed by the Manager IQ Easy, a controller that will provide distribution of the 24V DC supply voltage to a possible six connected devices. A ...
Electric power and Joule heating
... tend to have a greater number of low-voltage, step-down transformers located close to customers' premises. For example, in the US a pole-mounted transformer in a suburban setting may supply 1-3 houses, whereas in the UK a typical urban or suburban low-voltage substation might be rated at 2 MW and su ...
... tend to have a greater number of low-voltage, step-down transformers located close to customers' premises. For example, in the US a pole-mounted transformer in a suburban setting may supply 1-3 houses, whereas in the UK a typical urban or suburban low-voltage substation might be rated at 2 MW and su ...
Electricity and Magnetism - Blountstown Middle School
... An open circuit is one in which the pathway of the electrical current is broken. A switch is a device in the circuit in which the circuit can be closed (turned on) or open (turned off). ...
... An open circuit is one in which the pathway of the electrical current is broken. A switch is a device in the circuit in which the circuit can be closed (turned on) or open (turned off). ...
CIRCUITS AND SAFETY
... resistance. You do not want to be that path!!! • You do not want an exposed point of very high voltage (relative to what? relative to ground!)in your home. If a person touched that point, while their feet were touching the ground a large voltage would be across their body, driving a large current an ...
... resistance. You do not want to be that path!!! • You do not want an exposed point of very high voltage (relative to what? relative to ground!)in your home. If a person touched that point, while their feet were touching the ground a large voltage would be across their body, driving a large current an ...
Circuit Protection, Tips, and Troubleshooting
... • Determine part ratings • All components are rated • Capacitors: – If the voltage across the capacitor is going to be 50 [V], should you use a capacitor that is rated to 50 [V]? ...
... • Determine part ratings • All components are rated • Capacitors: – If the voltage across the capacitor is going to be 50 [V], should you use a capacitor that is rated to 50 [V]? ...
File
... In most household wiring, the black wires are at 110 volts relative to ground The white wires are at zero volts because they are connected to ground • If you come into contact with an energized (live) black wire, and you are also in contact with the white grounded wire, current will pass through ...
... In most household wiring, the black wires are at 110 volts relative to ground The white wires are at zero volts because they are connected to ground • If you come into contact with an energized (live) black wire, and you are also in contact with the white grounded wire, current will pass through ...
Electronic Components
... which run underneath the board that connects the component. The metal strips are laid out as shown below: Each strip is a connection. So whichever components connected to a certain strip are connected to each other. The blue strips shown in the illustration are usually used for connecting the batter ...
... which run underneath the board that connects the component. The metal strips are laid out as shown below: Each strip is a connection. So whichever components connected to a certain strip are connected to each other. The blue strips shown in the illustration are usually used for connecting the batter ...
HOW TO USE A VOM
... Ground should ideally be “0”, but is acceptable at less than 1 Volt. The Phase (Hot) to Ground should be the same as the prior AC voltage reading. The Safety Ground should have a DC resistance of .1 ohms or less and .1 or less voltage potential. It is also a good practice to verify that your equipme ...
... Ground should ideally be “0”, but is acceptable at less than 1 Volt. The Phase (Hot) to Ground should be the same as the prior AC voltage reading. The Safety Ground should have a DC resistance of .1 ohms or less and .1 or less voltage potential. It is also a good practice to verify that your equipme ...
Current Transformer Grounding
... risk of redundant ground loops and associated problems. During normal operation more than one ground on a CT circuit is not an obvious problem other than the difficulties it may cause during testing. However during a fault condition, multiple grounds allow a different ground potential rise for each ...
... risk of redundant ground loops and associated problems. During normal operation more than one ground on a CT circuit is not an obvious problem other than the difficulties it may cause during testing. However during a fault condition, multiple grounds allow a different ground potential rise for each ...
Ground (electricity)

In electrical engineering, ground or earth is the reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth.Electrical circuits may be connected to ground (earth) for several reasons. In mains powered equipment, exposed metal parts are connected to ground to prevent user contact with dangerous voltage if electrical insulation fails. Connections to ground limit the build-up of static electricity when handling flammable products or electrostatic-sensitive devices. In some telegraph and power transmission circuits, the earth itself can be used as one conductor of the circuit, saving the cost of installing a separate return conductor (see single-wire earth return).For measurement purposes, the Earth serves as a (reasonably) constant potential reference against which other potentials can be measured. An electrical ground system should have an appropriate current-carrying capability to serve as an adequate zero-voltage reference level. In electronic circuit theory, a ""ground"" is usually idealized as an infinite source or sink for charge, which can absorb an unlimited amount of current without changing its potential. Where a real ground connection has a significant resistance, the approximation of zero potential is no longer valid. Stray voltages or earth potential rise effects will occur, which may create noise in signals or if large enough will produce an electric shock hazard.The use of the term ground (or earth) is so common in electrical and electronics applications that circuits in portable electronic devices such as cell phones and media players as well as circuits in vehicles may be spoken of as having a ""ground"" connection without any actual connection to the Earth, despite ""common"" being a more appropriate term for such a connection. This is usually a large conductor attached to one side of the power supply (such as the ""ground plane"" on a printed circuit board) which serves as the common return path for current from many different components in the circuit.