* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What`s on an Electric Power Pole?
War of the currents wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Transformer types wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Overhead power line wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Single-wire earth return wikipedia , lookup
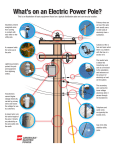
What’s on an Electric Power Pole? This is an illustration of basic equipment found on a typical distribution pole and can vary by location. Insulators prevent energized wires from coming in contact with each other or the utility pole. Primary wires are on top of the pole and usually carry from 1,000 to 46,000 volts of electricity from a substation. A crossarm holds the wires up on the pole and provides the required clearances for high voltage conductors. “Cutouts” act like a fuse and open when there is a problem with the line or a section of it. Surge protectors protect the equipment from lightning strikes or other electrical surges. The neutral wire is below the transformer and helps complete the circuit. The secondary wire carries the lower voltage electricity after it passes though the transformer. Transformers convert higher voltage electricity carried by primary wires and lower the voltage for use by customers. A ground wire runs the entire length of the pole. It directs any electricity on the pole safely into the earth. Communication wires such as telephone and cable tv are typically the lowest wires. Guy wires help stabilize utility poles.