the Booklet
... space for safety, security, or access. The other meaning is: An agreement between a foreman and the system operator, for permission. When describing new electric services, “clearance” has the first meaning – the distance between two objects. common ground point – The point where the grounding electr ...
... space for safety, security, or access. The other meaning is: An agreement between a foreman and the system operator, for permission. When describing new electric services, “clearance” has the first meaning – the distance between two objects. common ground point – The point where the grounding electr ...
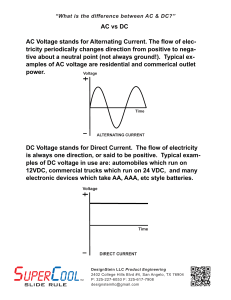
AC vs DC AC Voltage stands for Alternating Current. The flow of elec
... “What is the difference between AC & DC?” ...
... “What is the difference between AC & DC?” ...
95MET-2
... Find the inductance per unit length of a coaxial conductor if inner radius a = 2 mm and the radius of outer conductor, b = 9 mm and = 0. 7. What are the factors on which the speed of a motor depends? Discuss them for series and shunt motors. A shunt motor supplied at 230 V runs at 900 rpm. When t ...
... Find the inductance per unit length of a coaxial conductor if inner radius a = 2 mm and the radius of outer conductor, b = 9 mm and = 0. 7. What are the factors on which the speed of a motor depends? Discuss them for series and shunt motors. A shunt motor supplied at 230 V runs at 900 rpm. When t ...
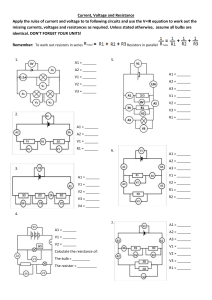
Current, Voltage and Resistance
... Current, Voltage and Resistance Apply the rules of current and voltage to to following circuits and use the V=IR equation to work out the missing currents, voltages and resistances as required. Unless stated otherwise, assume all bulbs are identical. DON’T FORGET YOUR UNITS! Remember: To work out re ...
... Current, Voltage and Resistance Apply the rules of current and voltage to to following circuits and use the V=IR equation to work out the missing currents, voltages and resistances as required. Unless stated otherwise, assume all bulbs are identical. DON’T FORGET YOUR UNITS! Remember: To work out re ...
Current Meter Guard/Ground Connections
... When measuring leakage currents while using a hipot, there are two modes of operation: Guard and Ground. Depending on the objective of the test and the test specimen, one or the other should be chosen. In both cases, the high voltage output from the hipot connects to one end of the load and the othe ...
... When measuring leakage currents while using a hipot, there are two modes of operation: Guard and Ground. Depending on the objective of the test and the test specimen, one or the other should be chosen. In both cases, the high voltage output from the hipot connects to one end of the load and the othe ...
The Electric Circuit
... the other end of the same power supply (closed circuit). Current will only flow when there is a closed circuit. ...
... the other end of the same power supply (closed circuit). Current will only flow when there is a closed circuit. ...
Self Study Unit 1.0 - Tri County Amateur Radio Club WX4TC
... basic unit of resistance is the ohm. The Greek letter omega (Ω) is shorthand for ohm. Conductors are materials that conduct electrical current well, or, in other words, have a low resistance. The copper wires that we use to connect a power supply to a radio are good conductors because copper is a go ...
... basic unit of resistance is the ohm. The Greek letter omega (Ω) is shorthand for ohm. Conductors are materials that conduct electrical current well, or, in other words, have a low resistance. The copper wires that we use to connect a power supply to a radio are good conductors because copper is a go ...
Testing of Low Voltage Installations
... By Separated Extra-Low Voltage (SELV) System – It is extra-low voltage system without connection to earth ...
... By Separated Extra-Low Voltage (SELV) System – It is extra-low voltage system without connection to earth ...
High Voltage Direct Current Test Procedure
... 2. The test shall be performed on each insulated conductor of the circuit and the results recorded and plotted as directed by the Engineer. 3. Conductors shall be tested in the following sequence: a) On the neutral conductor before it is grounded, and b) On the power conductors with the neutral and ...
... 2. The test shall be performed on each insulated conductor of the circuit and the results recorded and plotted as directed by the Engineer. 3. Conductors shall be tested in the following sequence: a) On the neutral conductor before it is grounded, and b) On the power conductors with the neutral and ...
Analysis and Simulation of Bus Loading conditions on Voltage Sag
... In the modern age, telecommunications has typically involved the use of electric means such as the telegraph, thetelephone, and the teletype, the use of fiber optics and their associated electronics, and/or the use of the internet.. ...
... In the modern age, telecommunications has typically involved the use of electric means such as the telegraph, thetelephone, and the teletype, the use of fiber optics and their associated electronics, and/or the use of the internet.. ...
Difference between Bonding, Grounding and
... All electrical/electronic circuits (AC & DC) need a reference potential (zero volts) which is called ground in order to make possible the current flow from generator to load. Ground is May or May not be earthed. In Electrical Power distribution it is either earthed at distribution Point or at Consum ...
... All electrical/electronic circuits (AC & DC) need a reference potential (zero volts) which is called ground in order to make possible the current flow from generator to load. Ground is May or May not be earthed. In Electrical Power distribution it is either earthed at distribution Point or at Consum ...
MWS POWER COMPONENTS
... The MWS T Cable (TC) feeds power to wall mounted or ceiling mounted fixtures and convenience outlets while feeding circuits downstream to another electrical component. ...
... The MWS T Cable (TC) feeds power to wall mounted or ceiling mounted fixtures and convenience outlets while feeding circuits downstream to another electrical component. ...
Download the Quiz
... What kind of hazard might exist in a power supply when it is turned off and disconnected? A. Static electricity could damage the grounding system B. Circulating currents inside the transformer might cause damage C. The fuse might blow if you remove the cover D. You might receive an electric shock fr ...
... What kind of hazard might exist in a power supply when it is turned off and disconnected? A. Static electricity could damage the grounding system B. Circulating currents inside the transformer might cause damage C. The fuse might blow if you remove the cover D. You might receive an electric shock fr ...
electrical engineering department syllabus of paper-i for jnvu
... Matrix Algebra, First order (Linear and Non-Linear) differential equations, Partial differential equations, Laplace Transform. Circuit Theory: Thevenin’s, Norton’s, Superposition, Maximum Power Transfer Theorem and their applications to A.C. & D.C. circuits with dependent and independent sources, Tr ...
... Matrix Algebra, First order (Linear and Non-Linear) differential equations, Partial differential equations, Laplace Transform. Circuit Theory: Thevenin’s, Norton’s, Superposition, Maximum Power Transfer Theorem and their applications to A.C. & D.C. circuits with dependent and independent sources, Tr ...
Electricity and Magnetism Test Review
... What do electric forces between charges depend on? If a neutral metal object is held near an object with a negative charge, how will the neutral object become charged? Batteries produce which type of current? What is the current most in use in your school? What materials allow charges to flow easily ...
... What do electric forces between charges depend on? If a neutral metal object is held near an object with a negative charge, how will the neutral object become charged? Batteries produce which type of current? What is the current most in use in your school? What materials allow charges to flow easily ...
BASIC INDUSTRIAL ELECTRICITY
... introduce the physical laws which govern electricity and how they apply in industry. It will present series and parallel circuits, magnetism and electromagnetism, resistance, capacitance and induction. Relay Logic. The student will learn to use the most common industrial electrical test equipment. ...
... introduce the physical laws which govern electricity and how they apply in industry. It will present series and parallel circuits, magnetism and electromagnetism, resistance, capacitance and induction. Relay Logic. The student will learn to use the most common industrial electrical test equipment. ...
COPPER WIRE APPLIANCE CLASSES Index
... device (fuse or circuit breaker (CB)) or a residual-‐current device (RCD) also named as residual current circuit breaker (RCCB), or ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) or also, residual current ...
... device (fuse or circuit breaker (CB)) or a residual-‐current device (RCD) also named as residual current circuit breaker (RCCB), or ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) or also, residual current ...
FIREFIGHTING AND ELECTRICITY Electric Wires in Houses and Buildings on Fire
... fault condition which may overload the switch at the time of operation. To minimise the problem, do the following: • Stand to one side of the switch • Turn your eyes away while operating the switch The electrical hazards are increased when flooding and wet conditions exist in buildings. Any open wir ...
... fault condition which may overload the switch at the time of operation. To minimise the problem, do the following: • Stand to one side of the switch • Turn your eyes away while operating the switch The electrical hazards are increased when flooding and wet conditions exist in buildings. Any open wir ...
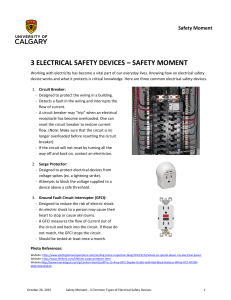
3 ELECTRICAL SAFETY DEVICES – SAFETY MOMENT
... - A circuit breaker may “trip” when an electrical receptacle has become overloaded. One can reset the circuit breaker to restore current flow. (Note: Make sure that the circuit is no longer overloaded before resetting the circuit breaker). - If the circuit will not reset by turning all the way off a ...
... - A circuit breaker may “trip” when an electrical receptacle has become overloaded. One can reset the circuit breaker to restore current flow. (Note: Make sure that the circuit is no longer overloaded before resetting the circuit breaker). - If the circuit will not reset by turning all the way off a ...
Ground Power Supply The external AC ground supply receptacle is
... receptacle. The amber warning Light indicates that the external power is available. The white indicator light indicates that the power supply is not in use. The external power pushbutton switch indicates if the external power is available and if it is in use. A provision is made to support the weigh ...
... receptacle. The amber warning Light indicates that the external power is available. The white indicator light indicates that the power supply is not in use. The external power pushbutton switch indicates if the external power is available and if it is in use. A provision is made to support the weigh ...
Ground (electricity)

In electrical engineering, ground or earth is the reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth.Electrical circuits may be connected to ground (earth) for several reasons. In mains powered equipment, exposed metal parts are connected to ground to prevent user contact with dangerous voltage if electrical insulation fails. Connections to ground limit the build-up of static electricity when handling flammable products or electrostatic-sensitive devices. In some telegraph and power transmission circuits, the earth itself can be used as one conductor of the circuit, saving the cost of installing a separate return conductor (see single-wire earth return).For measurement purposes, the Earth serves as a (reasonably) constant potential reference against which other potentials can be measured. An electrical ground system should have an appropriate current-carrying capability to serve as an adequate zero-voltage reference level. In electronic circuit theory, a ""ground"" is usually idealized as an infinite source or sink for charge, which can absorb an unlimited amount of current without changing its potential. Where a real ground connection has a significant resistance, the approximation of zero potential is no longer valid. Stray voltages or earth potential rise effects will occur, which may create noise in signals or if large enough will produce an electric shock hazard.The use of the term ground (or earth) is so common in electrical and electronics applications that circuits in portable electronic devices such as cell phones and media players as well as circuits in vehicles may be spoken of as having a ""ground"" connection without any actual connection to the Earth, despite ""common"" being a more appropriate term for such a connection. This is usually a large conductor attached to one side of the power supply (such as the ""ground plane"" on a printed circuit board) which serves as the common return path for current from many different components in the circuit.