Clarity and Conciseness
... In the above example, the noun things is plural; therefore, the verb in the expletive construction must also be the plural form, are. Additionally, revising the sentence to eliminate the expletive construction altogether is often the best move to ensure that your paper is more concise. Example: Ther ...
... In the above example, the noun things is plural; therefore, the verb in the expletive construction must also be the plural form, are. Additionally, revising the sentence to eliminate the expletive construction altogether is often the best move to ensure that your paper is more concise. Example: Ther ...
verb - Images
... • You remember that sometimes a simple predicate can be more than one word. Some sentences have two verbs!! • The main verb shows what the subject does or is. • The helping verb helps the main verb to show an action in the sentence. – By itself, a helping verb cannot show action. ...
... • You remember that sometimes a simple predicate can be more than one word. Some sentences have two verbs!! • The main verb shows what the subject does or is. • The helping verb helps the main verb to show an action in the sentence. – By itself, a helping verb cannot show action. ...
Systemic organization of language
... distinguish dual from plural. Many languages (though not English) have a concept of noun gender, also known as noun class, whereby every noun is designated as, for example, masculine or feminine. ...
... distinguish dual from plural. Many languages (though not English) have a concept of noun gender, also known as noun class, whereby every noun is designated as, for example, masculine or feminine. ...
infinitive
... Example: playing children, running water. The Present participle can be a modifier of verbs. (it describes the condition in which the agent is performing the activity) Example: The children came running. I prefer to eat sitting. The Perfect participle is used when it is necessary to emphasize that t ...
... Example: playing children, running water. The Present participle can be a modifier of verbs. (it describes the condition in which the agent is performing the activity) Example: The children came running. I prefer to eat sitting. The Perfect participle is used when it is necessary to emphasize that t ...
Adjectives and Adverbs with Transitive and Intransitive Verbs
... Adjectives modify nouns and pronouns, specifying such things as how many, what kind, and which one. A predicate adjective usually follows a linking verb. He is strange. I am slow. The response was quick. She feels bad. We are poor. Linking verbs are used to show a “state of being” of the subject, no ...
... Adjectives modify nouns and pronouns, specifying such things as how many, what kind, and which one. A predicate adjective usually follows a linking verb. He is strange. I am slow. The response was quick. She feels bad. We are poor. Linking verbs are used to show a “state of being” of the subject, no ...
Fragments,Verbs,Pronouns
... Chapt 9 Subject Verb Agreement To be verbs: The verb agrees with the subject and not the predicate nominative The only fruit now [is/are] peaches Peaches [are/is] the only fruit now. ...
... Chapt 9 Subject Verb Agreement To be verbs: The verb agrees with the subject and not the predicate nominative The only fruit now [is/are] peaches Peaches [are/is] the only fruit now. ...
201-210 - Epic Charter Schools
... · Differentiate between similar common and proper nouns · Classes, schools · Compass directions: when they are correctly and incorrectly capitalized · Ships · Identify proper nouns New Vocabulary: closing, book title, paragraph Grammar Usage Use Basic Sentence Patterns · Sentences have more complex ...
... · Differentiate between similar common and proper nouns · Classes, schools · Compass directions: when they are correctly and incorrectly capitalized · Ships · Identify proper nouns New Vocabulary: closing, book title, paragraph Grammar Usage Use Basic Sentence Patterns · Sentences have more complex ...
WGNet++summary
... {ed} directly to the word’s ‘base’, but this turned out to be logically inconsistent. The solution we adopted was to add the suffix to a new form which has the same realisation (i.e. the same pronunciation) as the base, rather than to the base itself. This rule effectively defines a class of forms ( ...
... {ed} directly to the word’s ‘base’, but this turned out to be logically inconsistent. The solution we adopted was to add the suffix to a new form which has the same realisation (i.e. the same pronunciation) as the base, rather than to the base itself. This rule effectively defines a class of forms ( ...
Grammar Terms You Should Know
... Note: Present participles can be used without helpers to serve as nouns that label or name activities: The closing of the store. These types of nouns are called ―gerunds.‖ (See 1g.) Notice the difference between a gerund and a participial modifier: The ending day (here ―ending‖ is a modifier could ...
... Note: Present participles can be used without helpers to serve as nouns that label or name activities: The closing of the store. These types of nouns are called ―gerunds.‖ (See 1g.) Notice the difference between a gerund and a participial modifier: The ending day (here ―ending‖ is a modifier could ...
Study Guide - Effingham County Schools
... Punctuating Titles & Capitalizing Words in Titles- Underline the titles of books, movies, plays, and television programs and the names of newspapers and magazines. When titles of works appear in print, italics takes the place of underlining. Use quotation marks around the titles of stories, magazine ...
... Punctuating Titles & Capitalizing Words in Titles- Underline the titles of books, movies, plays, and television programs and the names of newspapers and magazines. When titles of works appear in print, italics takes the place of underlining. Use quotation marks around the titles of stories, magazine ...
Syllabus - Florida International University
... generating and imparting knowledge through excellent teaching and research, the rigorous and respectful exchange of ideas, and community service. All students should respect the right of others to have an equitable opportunity to learn and honestly to demonstrate the quality of their learning. There ...
... generating and imparting knowledge through excellent teaching and research, the rigorous and respectful exchange of ideas, and community service. All students should respect the right of others to have an equitable opportunity to learn and honestly to demonstrate the quality of their learning. There ...
Morphology is the study of the internal structure of
... An adverb is a part of speech. It is any word that modifies any part of language other than a noun (modifiers of nouns are primarily adjectives and determiners). Adverbs can modify verbs, adjectives (including numbers), clauses, sentences and other adverbs. In English, they often end in -ly. This fu ...
... An adverb is a part of speech. It is any word that modifies any part of language other than a noun (modifiers of nouns are primarily adjectives and determiners). Adverbs can modify verbs, adjectives (including numbers), clauses, sentences and other adverbs. In English, they often end in -ly. This fu ...
Transitive and Intransitive Verbs
... • A linking verb connects/links the subject with a word that— describes or identifies the subject. (predicate adjective) ...
... • A linking verb connects/links the subject with a word that— describes or identifies the subject. (predicate adjective) ...
chapter 5 modified
... 1. Between the Determiner and the Noun Ex:- the beautiful rose 2. The Third Slot in Pattern 2 Ex:- These girls are young. 3. The Position after the Noun. This position accepts adjectives, adverbs, verbs (in the participle forms), and word groups. Ex:- The player, old and weary, could not finish the ...
... 1. Between the Determiner and the Noun Ex:- the beautiful rose 2. The Third Slot in Pattern 2 Ex:- These girls are young. 3. The Position after the Noun. This position accepts adjectives, adverbs, verbs (in the participle forms), and word groups. Ex:- The player, old and weary, could not finish the ...
Year 6 - South Marston C of E Primary
... The ‘i before e except after c’ rule applies to words where the sound spelt by ei is /i:/. ...
... The ‘i before e except after c’ rule applies to words where the sound spelt by ei is /i:/. ...
Year 5
... The ‘i before e except after c’ rule applies to words where the sound spelt by ei is /i:/. ...
... The ‘i before e except after c’ rule applies to words where the sound spelt by ei is /i:/. ...
Writing Clinic – Session 1
... complex sentence you form a compound complex sentence. This sentence must have two or more independent clauses and at least one subordinate clause. Americans often use the term “tyrant” when they discuss King George III, but he and most British subjects did not believe the colonies were being tr ...
... complex sentence you form a compound complex sentence. This sentence must have two or more independent clauses and at least one subordinate clause. Americans often use the term “tyrant” when they discuss King George III, but he and most British subjects did not believe the colonies were being tr ...
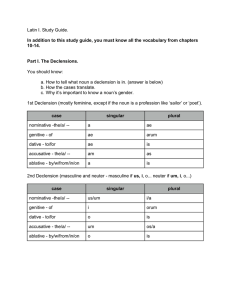
singular - Washington Latin Grade 8
... You need to know that when you look up a verb in your book like ‘colo, colere’ that: ‘colo’ is referred to as the 1st principal part. This is the first person, singular of the verb (I worship). You also need to know that the second word ‘colere’ is known as the second principal part or ‘the infiniti ...
... You need to know that when you look up a verb in your book like ‘colo, colere’ that: ‘colo’ is referred to as the 1st principal part. This is the first person, singular of the verb (I worship). You also need to know that the second word ‘colere’ is known as the second principal part or ‘the infiniti ...
Diapositiva 1
... • They are placed after the simple tenses of the verb To Be and before the simple tenses of verbs different than the verb To Be. • They are placed after the first auxiliary with verbal tenses that have more than one verb. • Adverbs of frequency are often placed before the auxiliary when they are use ...
... • They are placed after the simple tenses of the verb To Be and before the simple tenses of verbs different than the verb To Be. • They are placed after the first auxiliary with verbal tenses that have more than one verb. • Adverbs of frequency are often placed before the auxiliary when they are use ...
AAC Language Lab Lesson Plan Summary
... usage of infinitive complements (adding to + verb to complete a sentence, for example "I want to play.") ...
... usage of infinitive complements (adding to + verb to complete a sentence, for example "I want to play.") ...
RECOGNIZE A VERB WHEN YOU SEE ONE.
... My grumpy old English teacher smiled at the plate of cold meatloaf. My grumpy old English teacher = stalled subject; smiled = verb. The daredevil cockroach splashed into Sara's soup. The daredevil cockroach = stalled subject; splashed = verb. Theo's overworked computer exploded in a spray of sparks. ...
... My grumpy old English teacher smiled at the plate of cold meatloaf. My grumpy old English teacher = stalled subject; smiled = verb. The daredevil cockroach splashed into Sara's soup. The daredevil cockroach = stalled subject; splashed = verb. Theo's overworked computer exploded in a spray of sparks. ...
SCHEMAS - SFU.ca
... Example: /-s/ marks the inflectional categories ‘third person, singular, present tense’ in He walk-s. Dimensions: Categories: Example: walk-er is the derived noun, formed by adding the derivational suffix /-er/. CONSTRUCTING PARADIGMS Assumption: inflectional paradigms represent dimensions as column ...
... Example: /-s/ marks the inflectional categories ‘third person, singular, present tense’ in He walk-s. Dimensions: Categories: Example: walk-er is the derived noun, formed by adding the derivational suffix /-er/. CONSTRUCTING PARADIGMS Assumption: inflectional paradigms represent dimensions as column ...