MORPHOLOGY I
... a piece of cake a slice of bread a roast of meat a bowl of soup a pint of beer a pint of butter team of players a bunch of flowers a crew of helpers a splash of bread a pair of shoes a gang of thieves a blade of grass a pile of rubbish a speck of dust a load of hay a foot of water a yard of cloth a ...
... a piece of cake a slice of bread a roast of meat a bowl of soup a pint of beer a pint of butter team of players a bunch of flowers a crew of helpers a splash of bread a pair of shoes a gang of thieves a blade of grass a pile of rubbish a speck of dust a load of hay a foot of water a yard of cloth a ...
prepositional phrase
... Prepositions answer the question (?) where, when, to whom, etc…. Remember….ASK YOURSELF ?’s !!!!!! A prepositional phrase is made up of the: preposition, its’ object & any other modifiers. o I went to the football game. The prepositional phrase is: to the football game. Answers the (?) whe ...
... Prepositions answer the question (?) where, when, to whom, etc…. Remember….ASK YOURSELF ?’s !!!!!! A prepositional phrase is made up of the: preposition, its’ object & any other modifiers. o I went to the football game. The prepositional phrase is: to the football game. Answers the (?) whe ...
Eksamensoppgave i ENG1101 Engelsk språkvitenskap (7,5
... better chance of survival are passed on from generation to generation. Darwin called this process ‘natural selection’. Darwin found wildlife and fossils fascinating from an early age. While he was studying in Cambridge and in Edinburgh, he had a rather unusual hobby: beetle collecting. While he was ...
... better chance of survival are passed on from generation to generation. Darwin called this process ‘natural selection’. Darwin found wildlife and fossils fascinating from an early age. While he was studying in Cambridge and in Edinburgh, he had a rather unusual hobby: beetle collecting. While he was ...
Ablative Absolute
... b. Future Less Vivid present subjunctive Si id faciat, sapiens sit. If he should do it, he would be wise. - III. Contrary to Fact a. Present- imperf. subj. Si id faceret, sapiens esset. If he were doing it, he would be wise. (But in reality, he’s not doing it, so he’s not wise.) b. Past- plupf. subj ...
... b. Future Less Vivid present subjunctive Si id faciat, sapiens sit. If he should do it, he would be wise. - III. Contrary to Fact a. Present- imperf. subj. Si id faceret, sapiens esset. If he were doing it, he would be wise. (But in reality, he’s not doing it, so he’s not wise.) b. Past- plupf. subj ...
LIFEPAC 9th Grade Language Arts Unit 10 - HomeSchool
... Study these words to enhance your learning success in this section. abstract noun (ab’ strakt noun). A common noun that refers to a quality, state of being, idea, or action rather than to a thing that can be seen, smelled, felt, or touched, such as love. Aryan (ãr’ ē un). The prehistoric language fr ...
... Study these words to enhance your learning success in this section. abstract noun (ab’ strakt noun). A common noun that refers to a quality, state of being, idea, or action rather than to a thing that can be seen, smelled, felt, or touched, such as love. Aryan (ãr’ ē un). The prehistoric language fr ...
Section 5: Language Mechanics and Word Usage
... Nouns may be plural and name more than one person, place, thing, or idea. Possessive nouns show ownership. An apostrophe (‘) is used to show the possessive case. Example-Jennifer’s bicycle ...
... Nouns may be plural and name more than one person, place, thing, or idea. Possessive nouns show ownership. An apostrophe (‘) is used to show the possessive case. Example-Jennifer’s bicycle ...
Gerunds and Infinitives
... Running regularly will make you feel better. Studying requires most of my time during the day. The -ing form can also be called a present participle; however, the function is that of a verb when used in the present or past progressive: Example : The teacher is speaking to her students. If a gerund i ...
... Running regularly will make you feel better. Studying requires most of my time during the day. The -ing form can also be called a present participle; however, the function is that of a verb when used in the present or past progressive: Example : The teacher is speaking to her students. If a gerund i ...
Grammar 101
... Pair test—helpful in distinguishing adverbs from adjectives That absolutely, dreadful old man That man X Absolutely man Dreadful man Old man Adjectives can be subdivided into two main classes: determiners and descriptive adjectives Determiners Articles: the (definite); a and an (indefinite) Demonstr ...
... Pair test—helpful in distinguishing adverbs from adjectives That absolutely, dreadful old man That man X Absolutely man Dreadful man Old man Adjectives can be subdivided into two main classes: determiners and descriptive adjectives Determiners Articles: the (definite); a and an (indefinite) Demonstr ...
Target Vocabulary and Glossary of Terms
... information, tape scripts, supporting materials and other downloads. In part 1, we will look at the three main learning objectives of this section: the grammar focus is on asking questions; the target vocabulary is everyday objects, and the pronunciation focus is on speaking clearly and the use of t ...
... information, tape scripts, supporting materials and other downloads. In part 1, we will look at the three main learning objectives of this section: the grammar focus is on asking questions; the target vocabulary is everyday objects, and the pronunciation focus is on speaking clearly and the use of t ...
Sentence Clarity - St. Lawrence College
... Introduce your readers to the "big picture" first by giving them information they already know. Then they can link what's familiar to the new information you give them. As that new information becomes familiar, it too becomes old information that can link to newer information. The following example ...
... Introduce your readers to the "big picture" first by giving them information they already know. Then they can link what's familiar to the new information you give them. As that new information becomes familiar, it too becomes old information that can link to newer information. The following example ...
Latin I Concept Building TRANSPARENCY
... Is there an indirect object in these sentences? If so, what is it? He asks many questions for his friend. The general ordered the men to seize the wide fields. Sing me a song, please. For the time being, we stayed at home. BUT IN LATIN: Again, word order matters less than the endings of the words. I ...
... Is there an indirect object in these sentences? If so, what is it? He asks many questions for his friend. The general ordered the men to seize the wide fields. Sing me a song, please. For the time being, we stayed at home. BUT IN LATIN: Again, word order matters less than the endings of the words. I ...
packet for today and tomorrow - Hatboro
... 2) A singular pronoun is used to refer to two or more singular antecedents joined by or or nor. A plural pronoun is used with two or more plural antecedents joined by or or nor. Ben or Tom will give his presentation today. Either the juniors or the seniors are singing their class song. 3) When a sin ...
... 2) A singular pronoun is used to refer to two or more singular antecedents joined by or or nor. A plural pronoun is used with two or more plural antecedents joined by or or nor. Ben or Tom will give his presentation today. Either the juniors or the seniors are singing their class song. 3) When a sin ...
Parts of Speech for the Helpless Soul
... every word is a noun. Nouns are everywhere! • Don’t get mixed up with all the different types of parts in sentences. Subjects are nouns, objects of the prepositional phrase are nouns, direct objects are nouns…there are so many nouns that we use in speaking and writing! • Nouns can be common or prope ...
... every word is a noun. Nouns are everywhere! • Don’t get mixed up with all the different types of parts in sentences. Subjects are nouns, objects of the prepositional phrase are nouns, direct objects are nouns…there are so many nouns that we use in speaking and writing! • Nouns can be common or prope ...
Lesson 1 (Word Document)
... A pronoun is in Englisc naman spellend, that is, “representing a noun”. The noun it represents depends on how you use it. The modern third person pronoun “he” can represent any single male except the speaker and the person spoken to. It’s unchanged from Englisc, but Englisc could use it for things a ...
... A pronoun is in Englisc naman spellend, that is, “representing a noun”. The noun it represents depends on how you use it. The modern third person pronoun “he” can represent any single male except the speaker and the person spoken to. It’s unchanged from Englisc, but Englisc could use it for things a ...
Glossary of Writing Terms
... about, above, across, after, against, around, at, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, besides, between, beyond, by, down, during, except, for, from, in, inside, into, like, near, of, off, on, out, outside, over, since, through, throughout, till, to, toward, under, until, up, upon, with, without, ...
... about, above, across, after, against, around, at, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, besides, between, beyond, by, down, during, except, for, from, in, inside, into, like, near, of, off, on, out, outside, over, since, through, throughout, till, to, toward, under, until, up, upon, with, without, ...
Verb Tenses: The Future Perfect Continuous
... followed by the subject. – Will I have been negotiating a cease fire for two ...
... followed by the subject. – Will I have been negotiating a cease fire for two ...
What is a phrase - Spokane Public Schools
... What is a phrase? A group of words WITHOUT a subject and its predicate that acts like a single part of speech. How do I know how a phrase is functioning? Phrases ...
... What is a phrase? A group of words WITHOUT a subject and its predicate that acts like a single part of speech. How do I know how a phrase is functioning? Phrases ...
WORKSHEET 1--PARTS OF SPEECH
... 2. __________________________ are words that tell what someone or something is doing. 3. Action verbs can show ____________________ or _______________________ action. 4. An antecedent is a word that is replaced by a ________________________. 5. ___________________________ pronouns refer to a specifi ...
... 2. __________________________ are words that tell what someone or something is doing. 3. Action verbs can show ____________________ or _______________________ action. 4. An antecedent is a word that is replaced by a ________________________. 5. ___________________________ pronouns refer to a specifi ...
Key Stage 2 PaG Progression - St Nicolas and St Mary CE Primary
... Expressing time, place and cause using conjunctions [for example, when, before, after, while, so, because], adverbs [for example, then, next, soon, therefore], or prepositions [for example, before, after, during, in, because of] ...
... Expressing time, place and cause using conjunctions [for example, when, before, after, while, so, because], adverbs [for example, then, next, soon, therefore], or prepositions [for example, before, after, during, in, because of] ...
HS4 – LOS USOS DIFERENTES DEL PRONOMBRE “SE” Perhaps
... Use Five: Accidental/Unplanned Occurrences – the “se” is used to express an accidental or unplanned occurrence. Many times it is used to remove the element of blame from the person who did the action so that (s)he does not have to claim responsibility. An indirect object pronoun will be used to refe ...
... Use Five: Accidental/Unplanned Occurrences – the “se” is used to express an accidental or unplanned occurrence. Many times it is used to remove the element of blame from the person who did the action so that (s)he does not have to claim responsibility. An indirect object pronoun will be used to refe ...
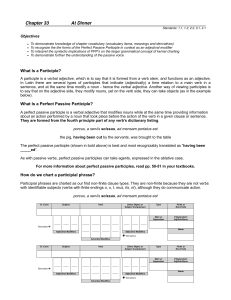
CH33 Objectives
... To interpret the syntactic implications of PPP’s on the larger grammatical concept of kernel charting To demonstrate further the understanding of the passive voice ...
... To interpret the syntactic implications of PPP’s on the larger grammatical concept of kernel charting To demonstrate further the understanding of the passive voice ...
PRESENT TENSE and FOOD QUIZ Study:
... -Your “Verb Changer” sheet. Know how “-ar”, “-er”, and “-ir” verbs change. -Your Food Vocabulary. Know this vocabulary and how to categorize them. ...
... -Your “Verb Changer” sheet. Know how “-ar”, “-er”, and “-ir” verbs change. -Your Food Vocabulary. Know this vocabulary and how to categorize them. ...
spanish and french
... from the language and English now use either helping verbs (may, might, would etc.) or past tenses to show that something is unreal. For verbs with infinitives ending in –er or –ir, the endings of the present subjunctive is formed by taking off the –o ending on the `I’ form of the ordinary present t ...
... from the language and English now use either helping verbs (may, might, would etc.) or past tenses to show that something is unreal. For verbs with infinitives ending in –er or –ir, the endings of the present subjunctive is formed by taking off the –o ending on the `I’ form of the ordinary present t ...