Nominative Form of Pronouns
... The profit was split between Andy and myself. (myself does not refer to another word in the sentence) ...
... The profit was split between Andy and myself. (myself does not refer to another word in the sentence) ...
DAYMUNC Resolution Writing Guide
... clause ends in semicolons except for the final one ending in a period). Independent verb clauses do not include a subject; however, each one begins with a present tense singular verb (generally, the ones that end in the letter "s" such as decides, notes, appoints, etc). The verb (and any modifiers) ...
... clause ends in semicolons except for the final one ending in a period). Independent verb clauses do not include a subject; however, each one begins with a present tense singular verb (generally, the ones that end in the letter "s" such as decides, notes, appoints, etc). The verb (and any modifiers) ...
CAP Writing and Editing Guide
... it. (As a rule of thumb, if it looks right with a comma before it, it should be a “which.”) Examples: “Of all the available CAPs, I chose the one that showed the most best practice.” “The CAR CAP, which was led by a former CAP Section Chief, showed some good practice.” Who/whom: “Who” (subject) or “ ...
... it. (As a rule of thumb, if it looks right with a comma before it, it should be a “which.”) Examples: “Of all the available CAPs, I chose the one that showed the most best practice.” “The CAR CAP, which was led by a former CAP Section Chief, showed some good practice.” Who/whom: “Who” (subject) or “ ...
Document
... into a gerundive phrase, by (1) putting the noun into the necessary case (so, if you have means, put noun into the ablative. If you are using causā, put noun into genitive), then (2) change the gerund to a gerundive to agree in case, number & gender with the noun Gerundives (aka, Future Passive Part ...
... into a gerundive phrase, by (1) putting the noun into the necessary case (so, if you have means, put noun into the ablative. If you are using causā, put noun into genitive), then (2) change the gerund to a gerundive to agree in case, number & gender with the noun Gerundives (aka, Future Passive Part ...
Subject Complements Linking Verbs—such as be, appear, become
... Predicate nouns rename, identify, or refer to the subject of the sentence. They are either predicate nouns or predicate pronouns. Those people are tourists. (predicate noun) This magazine is mine. (predicate pronoun) Predicate adjectives modify the subject of a sentence. The food is spicy. (predicat ...
... Predicate nouns rename, identify, or refer to the subject of the sentence. They are either predicate nouns or predicate pronouns. Those people are tourists. (predicate noun) This magazine is mine. (predicate pronoun) Predicate adjectives modify the subject of a sentence. The food is spicy. (predicat ...
WHO 1 SS
... TASK 2. Use any of the three ways to correct comma splices and run-ons in these sentences. 1. There are several ways to prepare for a hurricane, here is one of them. ______________________________________________________________________________. 2. My father hates music, my mother enjoys it. ______ ...
... TASK 2. Use any of the three ways to correct comma splices and run-ons in these sentences. 1. There are several ways to prepare for a hurricane, here is one of them. ______________________________________________________________________________. 2. My father hates music, my mother enjoys it. ______ ...
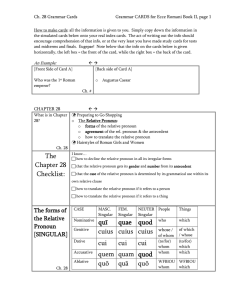
Nominative quī quae quod who cuius cuius cuius whose / cui cui cui
... “who” as follows… o “who” is one of the few words that inflects or declines in English: Pronoun o the word “who” can only be the subject of a verb in English o the possessive form in English is “whose” o the object is always “whom”: “whom” (direct object), “(to/for) whom” (indirect object), “with/fr ...
... “who” as follows… o “who” is one of the few words that inflects or declines in English: Pronoun o the word “who” can only be the subject of a verb in English o the possessive form in English is “whose” o the object is always “whom”: “whom” (direct object), “(to/for) whom” (indirect object), “with/fr ...
English Grammar - Barnes church of Christ
... future perfect verb “shall have been bound” a better rendering than the simple future “shall be bound” in Matt. 16:19? Who can say without first knowing the difference in the two verb tenses! In any language, the rules of grammar mean as much or more to a sentence than the definitions of the individ ...
... future perfect verb “shall have been bound” a better rendering than the simple future “shall be bound” in Matt. 16:19? Who can say without first knowing the difference in the two verb tenses! In any language, the rules of grammar mean as much or more to a sentence than the definitions of the individ ...
Paragraphs: complete units of organized and rational thoughts and
... Personal pronouns: I, my, mine, me, you, your, yours, he, his, him, she, her, hers, it, its, we, Pronouns: take the our, ours, us, you, your, yours, they, their, theirs, them place of a Relative pronouns: who, whom, whose, which, that previously Interrogative pronouns (used in questions): Who…? Whos ...
... Personal pronouns: I, my, mine, me, you, your, yours, he, his, him, she, her, hers, it, its, we, Pronouns: take the our, ours, us, you, your, yours, they, their, theirs, them place of a Relative pronouns: who, whom, whose, which, that previously Interrogative pronouns (used in questions): Who…? Whos ...
Spanish Phonetics and Phonology Diphthongs, syllable structure
... (1) Verb-endings: -é, -ó (Preterite), -é, etc. (Future), -ía, etc. (Conditional and Imperfect). (2) Words ending in -n and -s which are not respectively plural forms of verbs and nouns, e.g. nación, francés. (3) Stress patterns which vary consistently with morphological category, e.g. ánimo (Noun), ...
... (1) Verb-endings: -é, -ó (Preterite), -é, etc. (Future), -ía, etc. (Conditional and Imperfect). (2) Words ending in -n and -s which are not respectively plural forms of verbs and nouns, e.g. nación, francés. (3) Stress patterns which vary consistently with morphological category, e.g. ánimo (Noun), ...
Absolute Adjective
... The minor word classes include FORMULAIC EXPRESSIONS, INTERJECTIONS, PARTICLES, EXISTENTIAL THERE and special cases of the personal pronoun it, dummy it, prop it, anticipatory it and cleft it. Most, though not all, of these are also closed-class items See also ...
... The minor word classes include FORMULAIC EXPRESSIONS, INTERJECTIONS, PARTICLES, EXISTENTIAL THERE and special cases of the personal pronoun it, dummy it, prop it, anticipatory it and cleft it. Most, though not all, of these are also closed-class items See also ...
fjcl state latin forum 2007
... Reason: a, c, and d are all in the locative case; b is dative or ablative case Analysis: a, b, and d: The locative case is used to indicate “place where” and is found primarily with the names of cities, towns and small islands (islands small enough that the one city on it IS the island). The forms f ...
... Reason: a, c, and d are all in the locative case; b is dative or ablative case Analysis: a, b, and d: The locative case is used to indicate “place where” and is found primarily with the names of cities, towns and small islands (islands small enough that the one city on it IS the island). The forms f ...
Chapter 4: Modifiers - St. John the Beloved School
... Adverbs describe verbs, adjectives or other adverbs – I ran quickly. (Quickly describes the verb “run” – The bright, red, marker (“Bright” describes the adjective red) ...
... Adverbs describe verbs, adjectives or other adverbs – I ran quickly. (Quickly describes the verb “run” – The bright, red, marker (“Bright” describes the adjective red) ...
Lesson 15: Derived forms of the verb
... patterns – different combinations of how you alter the word exactly to produce the new word). However only the first 9 are common enough to study at this point. Most roots (meaning basic 3 letters) can be modified to include most of the various pattern derivations, although there are some which can ...
... patterns – different combinations of how you alter the word exactly to produce the new word). However only the first 9 are common enough to study at this point. Most roots (meaning basic 3 letters) can be modified to include most of the various pattern derivations, although there are some which can ...
Expanded - UK Linguistics Olympiad
... shared property of the things the nouns refer to. We have seen that Mokilese has a classifer for animals. Similarly, Japanese has a classifier for mechanical things, while Chinese has a classifier for lamps and electric lights. So classifiers can be used for very general categories and for very spec ...
... shared property of the things the nouns refer to. We have seen that Mokilese has a classifer for animals. Similarly, Japanese has a classifier for mechanical things, while Chinese has a classifier for lamps and electric lights. So classifiers can be used for very general categories and for very spec ...
Dogs - English 9
... Direct objects follow the verb on the horizontal line; they are separated from the verb by a vertical line that does not go through the horizontal line. Direct objects follow action verbs and answer who or what is receiving the action?: Dogs chase cats. ...
... Direct objects follow the verb on the horizontal line; they are separated from the verb by a vertical line that does not go through the horizontal line. Direct objects follow action verbs and answer who or what is receiving the action?: Dogs chase cats. ...
Pronouns
... These are the times that try men’s souls. We have nothing to fear but fear itself. In the first example, she is a personal pronoun standing in for an unnamed person (perhaps the writer is being discreet). Although English doesn’t really care about the case or gender of nouns, these do matter when ch ...
... These are the times that try men’s souls. We have nothing to fear but fear itself. In the first example, she is a personal pronoun standing in for an unnamed person (perhaps the writer is being discreet). Although English doesn’t really care about the case or gender of nouns, these do matter when ch ...
ACT English - Dawn Weathersbee
... Indefinite pronouns refer to persons or things that have not been specified. These can be tricky because some indefinite pronouns that seem plural are in fact singular. Indefinite pronouns are popular with ACT writers, so you’d be wise to memorize a few of these. ...
... Indefinite pronouns refer to persons or things that have not been specified. These can be tricky because some indefinite pronouns that seem plural are in fact singular. Indefinite pronouns are popular with ACT writers, so you’d be wise to memorize a few of these. ...
Writing Review
... • Use before singular and plural nouns when the noun is specific and/or definite. Example: The penguin over there is cute. Example: The classes I’m taking are difficult. • Use when referring to a particular member of a group. Example: The leader of Congress has a challenging role. • Use with noncoun ...
... • Use before singular and plural nouns when the noun is specific and/or definite. Example: The penguin over there is cute. Example: The classes I’m taking are difficult. • Use when referring to a particular member of a group. Example: The leader of Congress has a challenging role. • Use with noncoun ...
Latin Primer 2
... H. Label the parts of each sentence: V for main verbs, S for subjects, DO for direct object, PA for predicate adjectives, and PN for predicate nouns. Then translate the sentence into English. ...
... H. Label the parts of each sentence: V for main verbs, S for subjects, DO for direct object, PA for predicate adjectives, and PN for predicate nouns. Then translate the sentence into English. ...
Infinitives
... passive sentence. There is no indirect object between the verb and the infinitive. The teacher allowed her students to eat in class. Her students were allowed to eat in class. ...
... passive sentence. There is no indirect object between the verb and the infinitive. The teacher allowed her students to eat in class. Her students were allowed to eat in class. ...
Active and Passive Voice
... Tells to what or to whom or for what or for whom an action is done Action verbs that have an indirect object will always have a direct object Not every sentence has an indirect object ...
... Tells to what or to whom or for what or for whom an action is done Action verbs that have an indirect object will always have a direct object Not every sentence has an indirect object ...
Pronunciation of the Regular Past Tense Endings
... “Use” refers to how each structure is used in real life. For example, one way we use the past forms of verbs (“went”, “saw”, “ate”, etc.) is to tell a story. One way we use the word “could” is to ask a favor: “Could you open the door?” Another way we use the word “could” is to talk things we wer ...
... “Use” refers to how each structure is used in real life. For example, one way we use the past forms of verbs (“went”, “saw”, “ate”, etc.) is to tell a story. One way we use the word “could” is to ask a favor: “Could you open the door?” Another way we use the word “could” is to talk things we wer ...