Diachronic and Typological Properties of Morphology and
... affixation; all words consist of single morphemes. An example of such a language, referred to as analytic or isolating, is Mandarin Chinese. In Mandarin, most words are monomorphemic, although compounds do exist, and a few suffix-like morphemes are developing from compounds in the way described ...
... affixation; all words consist of single morphemes. An example of such a language, referred to as analytic or isolating, is Mandarin Chinese. In Mandarin, most words are monomorphemic, although compounds do exist, and a few suffix-like morphemes are developing from compounds in the way described ...
Document
... In Spanish, several verbs have irregular yo forms in the present tense. You have already seen three verbs with the -go ending in the yo form: decir digo, tener tengo, and venir vengo. ...
... In Spanish, several verbs have irregular yo forms in the present tense. You have already seen three verbs with the -go ending in the yo form: decir digo, tener tengo, and venir vengo. ...
The Acquisition of English Locative Constructions by Native
... consistent verb semantics-syntax correspondences, and knowing these regularities can help an L2 learner assign correct syntactic structures to verbs. For example, if a learner understands that mental verbs such as “think,” “know,” and “hope” take a sentential argument, then he or she can use this me ...
... consistent verb semantics-syntax correspondences, and knowing these regularities can help an L2 learner assign correct syntactic structures to verbs. For example, if a learner understands that mental verbs such as “think,” “know,” and “hope” take a sentential argument, then he or she can use this me ...
Creole English
... give bena, wena, and dida with a meaning corresponding to the English past progressive (16). Ben also combines with de to give bende, highly stigmatized as a basilectal and rural PROG marker (17). ...
... give bena, wena, and dida with a meaning corresponding to the English past progressive (16). Ben also combines with de to give bende, highly stigmatized as a basilectal and rural PROG marker (17). ...
12 Editing for Grammar Conventions
... In a democracy, we are all equal before the law. In a dictatorship, we are all equal before the police. What make the following sentences parallel? 1. The fruit is both tasty and fresh. 2. He either loves you or hates you. 3. Yvette not only plays golf but also swims like a pro. 4. I would rather ...
... In a democracy, we are all equal before the law. In a dictatorship, we are all equal before the police. What make the following sentences parallel? 1. The fruit is both tasty and fresh. 2. He either loves you or hates you. 3. Yvette not only plays golf but also swims like a pro. 4. I would rather ...
Formalizing Langacker`s Notions of Nouns and Verbs
... Figure 1: The Into construction and related schemas. Langacker describes a preposition as an atemporal relation between the participants in an utterance. Within these atemporal relations, there is an asymmetrical relationship between these participants in that the focused entity’s position (the traj ...
... Figure 1: The Into construction and related schemas. Langacker describes a preposition as an atemporal relation between the participants in an utterance. Within these atemporal relations, there is an asymmetrical relationship between these participants in that the focused entity’s position (the traj ...
Unit 4 Week 2 PP
... Object pronouns (e.g. me, you, her, him, us, them) are objects of verbs or prepositions. Kenya went to town with her. Reflexive pronouns (e.g. myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself) match the subject. ...
... Object pronouns (e.g. me, you, her, him, us, them) are objects of verbs or prepositions. Kenya went to town with her. Reflexive pronouns (e.g. myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself) match the subject. ...
16 Subject-Verb Agreement 16.1
... Number can be singular or plural. Singular words indicate one; plural words indicate more than one. A singular subject takes a singular verb. A plural subject takes a plural verb. With most verbs, the only change in form to indicate agreement in person occurs in the present tense. An -s (or -es) is ...
... Number can be singular or plural. Singular words indicate one; plural words indicate more than one. A singular subject takes a singular verb. A plural subject takes a plural verb. With most verbs, the only change in form to indicate agreement in person occurs in the present tense. An -s (or -es) is ...
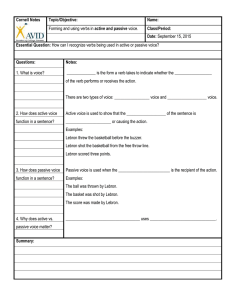
Active and Passive Voice Cornell Notes
... ______________________ or causing the action. Examples: Lebron threw the basketball before the buzzer. Lebron shot the basketball from the free throw line. Lebron scored three points. ...
... ______________________ or causing the action. Examples: Lebron threw the basketball before the buzzer. Lebron shot the basketball from the free throw line. Lebron scored three points. ...
Moods
... 1 Mood is the grammatical category which correlates with the degree or kind of reality assigned by the speaker to what s/he is saying. 1.1 the indicative/declarative mood (utterance presented as a fact), 1.2 the imperative mood (utterance presented as a command), 1.3 the subjunctive mood 1.3.1 the o ...
... 1 Mood is the grammatical category which correlates with the degree or kind of reality assigned by the speaker to what s/he is saying. 1.1 the indicative/declarative mood (utterance presented as a fact), 1.2 the imperative mood (utterance presented as a command), 1.3 the subjunctive mood 1.3.1 the o ...
Grammar essentials - Branson Public Schools
... Rule #2: Use an apostrophe and s to form the possessive of a plural noun that does not end in s. Examples: men’s, women’s, oxen’s, geese’s Rule #3: Use an apostrophe alone to form the possessive of a plural noun that ends in s. Examples: boys’, babies’, Thompsons’ ...
... Rule #2: Use an apostrophe and s to form the possessive of a plural noun that does not end in s. Examples: men’s, women’s, oxen’s, geese’s Rule #3: Use an apostrophe alone to form the possessive of a plural noun that ends in s. Examples: boys’, babies’, Thompsons’ ...
Page 1of 27 011700 ENGLISH FOR EDUCATIONAL
... Because the subject is being "acted upon" (or is passive), such sentences are said to be in the passive voice. NOTE: Colorful parrots live in the rainforests cannot be changed to passive voice because the sentence does not have a direct object. To change a sentence from active to passive voice, do t ...
... Because the subject is being "acted upon" (or is passive), such sentences are said to be in the passive voice. NOTE: Colorful parrots live in the rainforests cannot be changed to passive voice because the sentence does not have a direct object. To change a sentence from active to passive voice, do t ...
Punctuation guidelines
... it shows the grammatical structure of the text, its meaning, and often the relationship between words or clauses. - With the exception of the cases described below, the rules concerning punctuation, especially commas, are not as hard and fast in English as in some other languages. Some writers use f ...
... it shows the grammatical structure of the text, its meaning, and often the relationship between words or clauses. - With the exception of the cases described below, the rules concerning punctuation, especially commas, are not as hard and fast in English as in some other languages. Some writers use f ...
W04-0102 - Association for Computational Linguistics
... class. Neologisms and foreign loan words all fall into it. The second conjugation has far fewer members (17%), which are for the most part irregular (around 95%). The third conjugation is the smallest class (10%). It is mostly regular (around 10% of its verbs are irregular) and only partially produc ...
... class. Neologisms and foreign loan words all fall into it. The second conjugation has far fewer members (17%), which are for the most part irregular (around 95%). The third conjugation is the smallest class (10%). It is mostly regular (around 10% of its verbs are irregular) and only partially produc ...
adverbs - iVyucovani.cz
... B) Mary was sick, but now she is well. WELL = an adjective meaning HEALTHY, NOT SICK. It follows the verb BE and describes the subject SHE. ...
... B) Mary was sick, but now she is well. WELL = an adjective meaning HEALTHY, NOT SICK. It follows the verb BE and describes the subject SHE. ...
The Rise of Realism - Kentucky Department of Education
... Use commas to separate items in a series. The camp counselor distributed baseballs, bats, volleyballs, tennis rackets, and bandages. [words in a series] We have a government of the people, by the people, and for the people. [phrases in a series] I know I will pass the test if I take good notes, ...
... Use commas to separate items in a series. The camp counselor distributed baseballs, bats, volleyballs, tennis rackets, and bandages. [words in a series] We have a government of the people, by the people, and for the people. [phrases in a series] I know I will pass the test if I take good notes, ...
glossary of grammatical terminology
... I will look through these papers, while you look through those. (These in these papers is a demonstrative adjective.) Dependent clause A clause, sometimes called a subordinate clause, that cannot stand alone but must work together with an independent clause to complete its meaning and form a complet ...
... I will look through these papers, while you look through those. (These in these papers is a demonstrative adjective.) Dependent clause A clause, sometimes called a subordinate clause, that cannot stand alone but must work together with an independent clause to complete its meaning and form a complet ...
Correlative Conjunctions (Paired Coordinators)
... I will be neither happy nor healthy if you don’t let me go. (4) a contradictory or additional choice (not only...but also): He not only works as a teacher but also performs at the theater. Correlative conjunctions can precede nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositional phrases, infinitives, par ...
... I will be neither happy nor healthy if you don’t let me go. (4) a contradictory or additional choice (not only...but also): He not only works as a teacher but also performs at the theater. Correlative conjunctions can precede nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositional phrases, infinitives, par ...
Glossary of Terms Used in Spelling, Punctuation and Grammar
... A sentence where the exact words spoken are represented, and shown in speech marks (also known as inverted commas). (“Tidy your room, please,” said Mum). Three dots which are used to show missing words or to create a pause for effect. For example, ‘So…tell me what happened’. A clause used in the mid ...
... A sentence where the exact words spoken are represented, and shown in speech marks (also known as inverted commas). (“Tidy your room, please,” said Mum). Three dots which are used to show missing words or to create a pause for effect. For example, ‘So…tell me what happened’. A clause used in the mid ...
Some Differences Between Arabic and English: A Step Towards an
... There should be agreement between verb and agent. Depending on the agent, the morphological state of the verb may be put in dual or plural form, or be feminine, or stay singular. For each of these cases, there are rules to decide which form to use. Sentences may be affirmative or negative. There are ...
... There should be agreement between verb and agent. Depending on the agent, the morphological state of the verb may be put in dual or plural form, or be feminine, or stay singular. For each of these cases, there are rules to decide which form to use. Sentences may be affirmative or negative. There are ...
Sentence variety exercise 1
... I will be neither happy nor healthy if you don’t let me go. (4) a contradictory or additional choice (not only...but also): He not only works as a teacher but also performs at the theater. Correlative conjunctions can precede nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositional phrases, infinitives, par ...
... I will be neither happy nor healthy if you don’t let me go. (4) a contradictory or additional choice (not only...but also): He not only works as a teacher but also performs at the theater. Correlative conjunctions can precede nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositional phrases, infinitives, par ...
Pyramids - WordPress.com
... Adverb clauses modify verbs, and they are sometimes called dependent clauses or even, because they begin with subordinating conjunctions, subordinate clauses. Sometimes people call them “adverbial clauses” as well. (Unfortunately, you will need to learn all of these terms because a future English in ...
... Adverb clauses modify verbs, and they are sometimes called dependent clauses or even, because they begin with subordinating conjunctions, subordinate clauses. Sometimes people call them “adverbial clauses” as well. (Unfortunately, you will need to learn all of these terms because a future English in ...
`Modal verbs in English and Irish`, in: Esa Penttilä and Heli Paulasto
... forms of the English language. Modals are a subset of verbs which carry out specific functions in grammar (Palmer 1986, Depraetere and Reed 2006, Depraetere and Verhulst 2006; Leech 2003) and whose forms reflect an older state of the language which is fragmentary and incomplete today and has been fo ...
... forms of the English language. Modals are a subset of verbs which carry out specific functions in grammar (Palmer 1986, Depraetere and Reed 2006, Depraetere and Verhulst 2006; Leech 2003) and whose forms reflect an older state of the language which is fragmentary and incomplete today and has been fo ...
little handy words - Ormiston Denes Academy
... carefully. Don‟t switch off in the long pauses, or you might miss the beginning of the next ...
... carefully. Don‟t switch off in the long pauses, or you might miss the beginning of the next ...
Systemic polyfunctionality and morphology
... of the Samoyedic language Tundra Nenets. We will refer to this as systemic polyfunctionality in the sense that the phenomenon becomes explicable only by consideration of the nature of organization observed in the Tundra Nenets grammar system: it cannot be understood by simply analyzing each differen ...
... of the Samoyedic language Tundra Nenets. We will refer to this as systemic polyfunctionality in the sense that the phenomenon becomes explicable only by consideration of the nature of organization observed in the Tundra Nenets grammar system: it cannot be understood by simply analyzing each differen ...