Gerunds, Infinitives, and Participles. Oh my!
... working as the direct object of the verb wanted. • I have no desire to see that movie. I have no desire to see that movie. Is it working as a noun, adjective, or adverb? An adjective! It describes desire. • We are studying gerunds, participles, and infinitives to improve our writing. We are studying ...
... working as the direct object of the verb wanted. • I have no desire to see that movie. I have no desire to see that movie. Is it working as a noun, adjective, or adverb? An adjective! It describes desire. • We are studying gerunds, participles, and infinitives to improve our writing. We are studying ...
Parts of speech overview
... Adverbs • Modify a verb, an adjective, or another adverb • Tells how, when, where, or to what extent (how much, how long, or how often) • Some of the most frequently used adverbs end in – ly, but not all words ending in –ly are adverbs Noun + ly = adjective Love + ly = lovely ...
... Adverbs • Modify a verb, an adjective, or another adverb • Tells how, when, where, or to what extent (how much, how long, or how often) • Some of the most frequently used adverbs end in – ly, but not all words ending in –ly are adverbs Noun + ly = adjective Love + ly = lovely ...
CH33 Objectives
... to say that on the adjective side, they modify nouns, yet on the verb side, they can take objects (as in the example below). ...
... to say that on the adjective side, they modify nouns, yet on the verb side, they can take objects (as in the example below). ...
Daily Grammar Practice (DGP) Notes
... 2. 1st person=___, 2nd person=___, 3rd person=___ 3. Define and give an example of the following types of pronouns: subjective objective possessive reflexive relative 4. Brady and Jill walked with _____ _____. (one another/each other) ...
... 2. 1st person=___, 2nd person=___, 3rd person=___ 3. Define and give an example of the following types of pronouns: subjective objective possessive reflexive relative 4. Brady and Jill walked with _____ _____. (one another/each other) ...
objects! - Cobb Learning
... the verb – the exception would be in a question Not all action verbs have DO’s – these are called intransitive verbs Linking Verbs NEVER have DO’s!! ...
... the verb – the exception would be in a question Not all action verbs have DO’s – these are called intransitive verbs Linking Verbs NEVER have DO’s!! ...
basics - La Salle University
... Some parts of speech, sentences we need. We will point those out as needed, but often know it’s right without exact terminology. verbs nouns pronouns: [know nominative/subjective vs. objective, e.g. she/her, I/me, who/whom] adjectives modify nouns, pronouns adverbs (many –ly) modify verbs, ...
... Some parts of speech, sentences we need. We will point those out as needed, but often know it’s right without exact terminology. verbs nouns pronouns: [know nominative/subjective vs. objective, e.g. she/her, I/me, who/whom] adjectives modify nouns, pronouns adverbs (many –ly) modify verbs, ...
English 1 for Management (1EA)
... Possessive pronouns are NOT followed immediately by a noun. They stand alone. Example: That shirt is mine. Those are yours over there. ...
... Possessive pronouns are NOT followed immediately by a noun. They stand alone. Example: That shirt is mine. Those are yours over there. ...
Lecture 3. Phrases
... May contain one or more postmodifiers, which provide more information on the head, such as (see UGE [p. 60] for a more comprehensive list): ...
... May contain one or more postmodifiers, which provide more information on the head, such as (see UGE [p. 60] for a more comprehensive list): ...
Magnetic Story - Cincinnati Zoo
... antelope this summer. Verb – action or state of being. Example: She saw a cheetah chasing an antelope. Adjective – modifies or describes a noun or pronoun. Example: She saw a young cheetah chase after an injured antelope. Pronoun – word that takes the place of a noun. Example: She saw a cheetah chas ...
... antelope this summer. Verb – action or state of being. Example: She saw a cheetah chasing an antelope. Adjective – modifies or describes a noun or pronoun. Example: She saw a young cheetah chase after an injured antelope. Pronoun – word that takes the place of a noun. Example: She saw a cheetah chas ...
Phrase Toolbox
... Swimming for his life, John crossed the English Channel. Gerund phrase A gerund is an “-ing” verb form that functions as a noun. The phrase is the gerund plus its complements and modifiers. Walking in the moonlight is a romantic way to end a date. (subject of the sentence) He particularly enjoyed wa ...
... Swimming for his life, John crossed the English Channel. Gerund phrase A gerund is an “-ing” verb form that functions as a noun. The phrase is the gerund plus its complements and modifiers. Walking in the moonlight is a romantic way to end a date. (subject of the sentence) He particularly enjoyed wa ...
File
... 1. Sonia and Aaron (get, gets) a free dessert. 2. (Have, Has) you seen today’s news? 3. That dog (howl, howls) every night. 4. Juan (work, works) at the local coffee shop. 5. I (walk, walks) to work every day. 6. They (write, writes) stories in English class. Exercise 6: ...
... 1. Sonia and Aaron (get, gets) a free dessert. 2. (Have, Has) you seen today’s news? 3. That dog (howl, howls) every night. 4. Juan (work, works) at the local coffee shop. 5. I (walk, walks) to work every day. 6. They (write, writes) stories in English class. Exercise 6: ...
Grammar - InRisk - University of British Columbia
... o A conjunction joins words, phrases, or clauses o Examples: and, but, or, nor, for, as, since, so, because Preposition o A preposition connects a noun, pronoun, or phrase to some other parts of a sentence o Examples: in, on, at, between, by, for, of, to, from, through, with Interjection o Interject ...
... o A conjunction joins words, phrases, or clauses o Examples: and, but, or, nor, for, as, since, so, because Preposition o A preposition connects a noun, pronoun, or phrase to some other parts of a sentence o Examples: in, on, at, between, by, for, of, to, from, through, with Interjection o Interject ...
Parent Workshop ~ Year 6 28/09/16
... The term “noun phrase” can refer to just one word, eg Tom, she, but more generally to a group of words, eg a lot of money, the best team in the world, that functions in the same way as a noun in the sentence. A noun phrase can include a determiner, eg these hats, a baby; an adjective, eg sad face, w ...
... The term “noun phrase” can refer to just one word, eg Tom, she, but more generally to a group of words, eg a lot of money, the best team in the world, that functions in the same way as a noun in the sentence. A noun phrase can include a determiner, eg these hats, a baby; an adjective, eg sad face, w ...
The Writing Skills Workshop -
... Nouns name persons, places, or things. Verbs show action or existence. Pronouns serve as noun substitutes. Adjectives describe nouns and pronouns. Adverbs describe verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs. Conjunctions join words or groups of words. Prepositions form phrases with nouns and pronouns. ...
... Nouns name persons, places, or things. Verbs show action or existence. Pronouns serve as noun substitutes. Adjectives describe nouns and pronouns. Adverbs describe verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs. Conjunctions join words or groups of words. Prepositions form phrases with nouns and pronouns. ...
Verb Errors
... of students don’t understand verbs change. They also don’t know how to make the right variation in verbs. But we can see there are some kinds of changes in it, such as the tense we should know how to use the regular or irregular verbs. But for the beginners, they will use one rule in any kinds of si ...
... of students don’t understand verbs change. They also don’t know how to make the right variation in verbs. But we can see there are some kinds of changes in it, such as the tense we should know how to use the regular or irregular verbs. But for the beginners, they will use one rule in any kinds of si ...
Document
... personal pronoun possessive pronoun adverb adverb, comparative adverb, superlative particle to interjection verb, base form verb, past tense verb, gerund/present participle verb, past participle verb, sing. present, non-3d verb, 3rd person sing. present wh-determiner wh-pronoun possessive wh-pronoun ...
... personal pronoun possessive pronoun adverb adverb, comparative adverb, superlative particle to interjection verb, base form verb, past tense verb, gerund/present participle verb, past participle verb, sing. present, non-3d verb, 3rd person sing. present wh-determiner wh-pronoun possessive wh-pronoun ...
Subject-Verb Agreement Identifying the Subject
... Identifying the Subject In all of the examples listed above, the subject noun is placed directly next to its verb, and so it is rather simple to determine which type of verb to use. However, in some sentences, the subject is separated from its verb by additional phrases or clauses. To find the subje ...
... Identifying the Subject In all of the examples listed above, the subject noun is placed directly next to its verb, and so it is rather simple to determine which type of verb to use. However, in some sentences, the subject is separated from its verb by additional phrases or clauses. To find the subje ...
Noun, Adjective, and Adverb Clauses
... Usually connected to the word it modifies by one of the relative pronouns (that which, who, whom, or whose). Sometimes, it is connected by a relative adverb (after, before, since, when, where, or why). ...
... Usually connected to the word it modifies by one of the relative pronouns (that which, who, whom, or whose). Sometimes, it is connected by a relative adverb (after, before, since, when, where, or why). ...
Nouns II - PageFarm.net
... A subject is that which initiates an action; in other words, who or what is initiating whatever is being done. • Example: The postman left Harry a letter. A predicate noun is normally placed after the verb: it answers the question what? or who? and it refers to or renames the subject of the sentence ...
... A subject is that which initiates an action; in other words, who or what is initiating whatever is being done. • Example: The postman left Harry a letter. A predicate noun is normally placed after the verb: it answers the question what? or who? and it refers to or renames the subject of the sentence ...
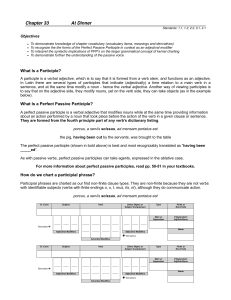
Chapter 33
... There are also future active participles: In English: the frog about to jump In Latin these are made by adding –urbefore the ending of the p.p.p. They are declined as 1st-2nd declension ...
... There are also future active participles: In English: the frog about to jump In Latin these are made by adding –urbefore the ending of the p.p.p. They are declined as 1st-2nd declension ...
DGP Sentence 8
... o Example: We have been taking notes all day. She will be cold today. Modifies a noun using a, an, or the ...
... o Example: We have been taking notes all day. She will be cold today. Modifies a noun using a, an, or the ...
Lecture 3. Phrases
... May contain one or more postmodifiers, which provide more information on the head, such as (see UGE [p. 60] for a more comprehensive list): ...
... May contain one or more postmodifiers, which provide more information on the head, such as (see UGE [p. 60] for a more comprehensive list): ...
Grammar Study Sheet
... A pronoun is a word that takes the place of a noun or nouns. The words he, she, it, we, you, and they are pronouns. Emmett is a vet. He helps animals. He takes the place of the noun Carlos. Robbie and Evelyn are zookeepers. They also help animals. They take the place of the nouns Robbie and Evelyn. ...
... A pronoun is a word that takes the place of a noun or nouns. The words he, she, it, we, you, and they are pronouns. Emmett is a vet. He helps animals. He takes the place of the noun Carlos. Robbie and Evelyn are zookeepers. They also help animals. They take the place of the nouns Robbie and Evelyn. ...