Participles vs Gerunds vs Verbs
... conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing or speaking. a. Explain the function of verbals (gerunds, participles, infinitives) in general and their function in particular sentences. ...
... conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing or speaking. a. Explain the function of verbals (gerunds, participles, infinitives) in general and their function in particular sentences. ...
FUNCTIONS OF ADJECTIVES
... The word 'people' by itself is a general reference to some group of human beings. If someone says 'these people', we know which group they are talking about, and if they say 'a lot of people' we know how big the group is. 'These' and 'a lot of' are determiners in these sentences. ...
... The word 'people' by itself is a general reference to some group of human beings. If someone says 'these people', we know which group they are talking about, and if they say 'a lot of people' we know how big the group is. 'These' and 'a lot of' are determiners in these sentences. ...
TIV Exam Format CLC
... Noun & verb tables. (11 marks) All five declensions (regulars only), including neuters. All four conjugations: active indicative in the present, imperfect, future, perfect, pluperfect, future perfect; passive indicative in the present, imperfect, future; active subjunctive in the present, imperfect, ...
... Noun & verb tables. (11 marks) All five declensions (regulars only), including neuters. All four conjugations: active indicative in the present, imperfect, future, perfect, pluperfect, future perfect; passive indicative in the present, imperfect, future; active subjunctive in the present, imperfect, ...
Eight parts of speech
... The most common way to form an adverb is to add the letters 'ly' to the adjective. Not always, though! Examples: quietly, softly, rapidly ...
... The most common way to form an adverb is to add the letters 'ly' to the adjective. Not always, though! Examples: quietly, softly, rapidly ...
Multi Sensory Grammar
... house, past the house, near the house, etc. These are all prepositional phrases. • A prepositional phrase begins with a preposition and ends with either a noun or pronoun. The preposition is underlined in green and the entire prepositional phrase is circled in green. ...
... house, past the house, near the house, etc. These are all prepositional phrases. • A prepositional phrase begins with a preposition and ends with either a noun or pronoun. The preposition is underlined in green and the entire prepositional phrase is circled in green. ...
File
... A pronoun is a word used to take the place of a noun. A pronoun is used as a noun. Through the use of pronouns, one may avoid repeating name words: Mary has lost her book. The box has lost its handle. Ruth saw the boys and talked to them. VERBS A verb is a word used to express action, being, or stat ...
... A pronoun is a word used to take the place of a noun. A pronoun is used as a noun. Through the use of pronouns, one may avoid repeating name words: Mary has lost her book. The box has lost its handle. Ruth saw the boys and talked to them. VERBS A verb is a word used to express action, being, or stat ...
Parts of Speech
... object, or a part of a phrase. Some nouns are harder-to-define objects such as emotions, countries, and ideals (justice, for instance). For instance, patriotism, or love of one’s country, is a noun. The –ism ending on “patriotism” shows that the word is a noun. Subjects in sentences can be difficult ...
... object, or a part of a phrase. Some nouns are harder-to-define objects such as emotions, countries, and ideals (justice, for instance). For instance, patriotism, or love of one’s country, is a noun. The –ism ending on “patriotism” shows that the word is a noun. Subjects in sentences can be difficult ...
Latin Summer Assignment Latin III Mr. Pasquinelli 2016 If you have
... 4. Can be used as a demonstrative “that” (We haven’t seen it used this way very often.) D. Reflexive Pronouns 1. Used when the object is the same as the subject. “I trust myself.” 2. 1st and 2nd Person reflexives are the same as the 1st and 2nd personal pronouns 3. 3rd Person Reflexives have spe ...
... 4. Can be used as a demonstrative “that” (We haven’t seen it used this way very often.) D. Reflexive Pronouns 1. Used when the object is the same as the subject. “I trust myself.” 2. 1st and 2nd Person reflexives are the same as the 1st and 2nd personal pronouns 3. 3rd Person Reflexives have spe ...
Grammar Cheat Sheet 3 - Bowling Green City Schools
... ALMOST ALWAYS begins with to but doesn’t have to have the word to when words associate with the following are present in the sentence: feel, hear, help, let, make, see, and watch. Word often ending in “ing” or ed, d, t, en, n Function mainly as adjectives (modifies a noun or pronoun) and sometimes a ...
... ALMOST ALWAYS begins with to but doesn’t have to have the word to when words associate with the following are present in the sentence: feel, hear, help, let, make, see, and watch. Word often ending in “ing” or ed, d, t, en, n Function mainly as adjectives (modifies a noun or pronoun) and sometimes a ...
APP-Writing-Glossary-L1-and-2
... Note that a morpheme like "-s" can just be a single phoneme and does not have to be a whole syllable. Technique ...
... Note that a morpheme like "-s" can just be a single phoneme and does not have to be a whole syllable. Technique ...
Verbals
... A geruNd is a verbal ending in -ing that is used as a Noun. 2. A gerund phrase consists of a gerund plus modifier(s), object(s), and/or ...
... A geruNd is a verbal ending in -ing that is used as a Noun. 2. A gerund phrase consists of a gerund plus modifier(s), object(s), and/or ...
the basics
... Verb phrase- a main verb and its helping verbs The snow has been falling for three days. Gerund phraseGerund-verb ending in –ing; acts as subject, DO, OP, and PN The boy escaped his brother by hiding under his bed. Infinitive phraseInfinitive-verb form that begins with the word to and functions as a ...
... Verb phrase- a main verb and its helping verbs The snow has been falling for three days. Gerund phraseGerund-verb ending in –ing; acts as subject, DO, OP, and PN The boy escaped his brother by hiding under his bed. Infinitive phraseInfinitive-verb form that begins with the word to and functions as a ...
Kirby`s POS "beachball" ppt.
... Betty is pretty. Linking! Betty=pretty. Links adjective pretty to Betty. Betty answered the phone. Action! She physically picked up her phone. ...
... Betty is pretty. Linking! Betty=pretty. Links adjective pretty to Betty. Betty answered the phone. Action! She physically picked up her phone. ...
Infinitives - WordPress.com
... shift waiting tables at the neighborhood café. (To sleep – subject; noun) Wherever Melissa goes, she always brings a book to read in case conversation lags or she has a long wait. (to read – adjective modifying book) More examples on page ...
... shift waiting tables at the neighborhood café. (To sleep – subject; noun) Wherever Melissa goes, she always brings a book to read in case conversation lags or she has a long wait. (to read – adjective modifying book) More examples on page ...
for whom - Wikispaces
... A conjunction is a word used to join words or groups of words. Ex. And, but, or, nor, for, so, yet… Both girls and boys went to the park for a ...
... A conjunction is a word used to join words or groups of words. Ex. And, but, or, nor, for, so, yet… Both girls and boys went to the park for a ...
NOUN - SchoolNotes
... Verbs are words that express action or condition. Action verbs tell what a person, place, or thing is doing. Run, think, decide, read, and go are action verbs. Linking verbs tell what a person, place, or thing is. Is, are, was, were, seem, and become are linking verbs. Helping verbs have two or more ...
... Verbs are words that express action or condition. Action verbs tell what a person, place, or thing is doing. Run, think, decide, read, and go are action verbs. Linking verbs tell what a person, place, or thing is. Is, are, was, were, seem, and become are linking verbs. Helping verbs have two or more ...
Language Functions and Forms: A Brief Summary
... In oral language some common functions may include: • giving instructions • making requests • defending an argument ...
... In oral language some common functions may include: • giving instructions • making requests • defending an argument ...
Simple sentences - WritingSecondarySubjects
... place and I was extremely happy about all that but I did not know anyone there at all. ...
... place and I was extremely happy about all that but I did not know anyone there at all. ...
Notes: Prepositions, Subjects and Verbs
... word being a preposition. ) In order for it to be a preposition, it must be followed by an object of a preposition, a noun or pronoun which answers the question who or what following the prep. Examples: I went by the store. By what? The store. By the store is a prepositional phrase. Practice: From t ...
... word being a preposition. ) In order for it to be a preposition, it must be followed by an object of a preposition, a noun or pronoun which answers the question who or what following the prep. Examples: I went by the store. By what? The store. By the store is a prepositional phrase. Practice: From t ...
BASIC VERB CONJUGATION A verb in its unchanged form
... pieces of info you can get from a conjugated verb are: WHO is doing it, WHEN it is done, and WHAT the action is. Verbs have 2 main parts- the “stem”/ “root” which tells you what the action is, and the ending which tells you who is doing it and when the action takes place. There are three kinds of ve ...
... pieces of info you can get from a conjugated verb are: WHO is doing it, WHEN it is done, and WHAT the action is. Verbs have 2 main parts- the “stem”/ “root” which tells you what the action is, and the ending which tells you who is doing it and when the action takes place. There are three kinds of ve ...
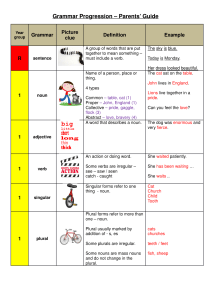
Parents` Guide to Grammar: Progression
... They include articles (a / an, the), possessive pronouns, demonstratives (this / that, those / these) and quantifiers (some, many, no etc) and numbers. Contains a subject and a verb. ...
... They include articles (a / an, the), possessive pronouns, demonstratives (this / that, those / these) and quantifiers (some, many, no etc) and numbers. Contains a subject and a verb. ...
DELHI PUBLIC SCHOOL, SRINAGAR REVISION WORKSHEET
... Some other examples of pronouns are I, he, she, it, we, they, yours, he, her, us, you and them. Personal pronouns: For example: I, me, you, your, he, she These are also known as personal pronouns. They are used to refer to ourselves, people we are talking to and people whom we are talking about. We ...
... Some other examples of pronouns are I, he, she, it, we, they, yours, he, her, us, you and them. Personal pronouns: For example: I, me, you, your, he, she These are also known as personal pronouns. They are used to refer to ourselves, people we are talking to and people whom we are talking about. We ...
Parts of Speech and Parts of a Sentence
... But if your sentence does not have both a subject and verb after the conjunction, your sentence does not need a comma, for example: Mickey [subject] likes [verb] going to the beach and ...
... But if your sentence does not have both a subject and verb after the conjunction, your sentence does not need a comma, for example: Mickey [subject] likes [verb] going to the beach and ...
Parts of Speech
... Adverbs give more information about verbs – they show how an action is happening, e.g: ...
... Adverbs give more information about verbs – they show how an action is happening, e.g: ...