An algebraic approach to Arabic sentence structure (2003).
... Pregroup grammars have been used to study sentence structure in a number of European languages [3,5,8,9]. We here turn to Arabic [1,2,6] as our first example of a non-European (and non-Indo-European) language. As it turned out, for the fragment of Arabic we investigated, only a small part of the alg ...
... Pregroup grammars have been used to study sentence structure in a number of European languages [3,5,8,9]. We here turn to Arabic [1,2,6] as our first example of a non-European (and non-Indo-European) language. As it turned out, for the fragment of Arabic we investigated, only a small part of the alg ...
Parts of Speech Review
... Pick out the adverb(s) in the following sentences. 1. My friend secretly sent me a text. 2. Finally, my boyfriend showed up. 3. I was too short to ride the roller coaster. 4. I was so happy that I had finished my homework so quickly. ...
... Pick out the adverb(s) in the following sentences. 1. My friend secretly sent me a text. 2. Finally, my boyfriend showed up. 3. I was too short to ride the roller coaster. 4. I was so happy that I had finished my homework so quickly. ...
Verbals Handout
... Traveling might satisfy your desire for new experiences. (subject) They do not appreciate my singing. (direct object) Birds can escape from dangers by flying. (object of the preposition) ...
... Traveling might satisfy your desire for new experiences. (subject) They do not appreciate my singing. (direct object) Birds can escape from dangers by flying. (object of the preposition) ...
Prepositional Phrase: A preposition plus its object and modifiers
... Prepositional Phrase: A preposition plus its object and modifiers. Prepositions To, around, under, over, like, as, behind, with, outside, etc. Prepositional phrases may function as adjectives or as adverbs. Adjective prepositional phrases tell which one, what kind, how many, and how much, or give ot ...
... Prepositional Phrase: A preposition plus its object and modifiers. Prepositions To, around, under, over, like, as, behind, with, outside, etc. Prepositional phrases may function as adjectives or as adverbs. Adjective prepositional phrases tell which one, what kind, how many, and how much, or give ot ...
Stiahnuť prednášku
... Possessive - my / mine, you / yours, their / theirs 2.RELATIVE PRONOUNS - which, that – for inanimate - who, whom – for animate - whose – for both 3.INTERROGATIVE PRONOUNS - what, whom - which – for inanimate - who – for animate 4.DEMONSTRATIVE PRONOUNS - this, those, these, that ...
... Possessive - my / mine, you / yours, their / theirs 2.RELATIVE PRONOUNS - which, that – for inanimate - who, whom – for animate - whose – for both 3.INTERROGATIVE PRONOUNS - what, whom - which – for inanimate - who – for animate 4.DEMONSTRATIVE PRONOUNS - this, those, these, that ...
Grammatical and Punctuation Feature
... to as the ‘future tense’. But this usage changes the meaning of the word ‘tense’ so that it no longer refers only to the use of ...
... to as the ‘future tense’. But this usage changes the meaning of the word ‘tense’ so that it no longer refers only to the use of ...
Grammar and Punctuation Revision
... to as the ‘future tense’. But this usage changes the meaning of the word ‘tense’ so that it no longer refers only to the use of ...
... to as the ‘future tense’. But this usage changes the meaning of the word ‘tense’ so that it no longer refers only to the use of ...
Noun and Pronoun Cases
... A noun is said to be in the nominative case if it is the subject of a verb. (SUBJECT is the person or the thing who or which carries out the action of the verb in the sentence) Examples: • Mr. Green is an intelligent man. Mr. Green is a proper noun in nominative case. • The painter paints the portra ...
... A noun is said to be in the nominative case if it is the subject of a verb. (SUBJECT is the person or the thing who or which carries out the action of the verb in the sentence) Examples: • Mr. Green is an intelligent man. Mr. Green is a proper noun in nominative case. • The painter paints the portra ...
Unit 3 Lesson 3 (sec 4) - Ms. De masi Teaching website
... The player [whom we cheered for] was replaced. (we cheered for whom – object of preposition) ...
... The player [whom we cheered for] was replaced. (we cheered for whom – object of preposition) ...
subject(ed) verb(ing) agreement(s)
... 8) 8. Nouns such as scissors, tweezers, trousers, and shears require plural verbs. (There are two parts to these things.): - These scissors are sharp! (SCISSORS = ARE) - Those trousers are on fire! (TROUSERS = ARE) 9) In sentences beginning with there is or there are, the subject follows the verb. S ...
... 8) 8. Nouns such as scissors, tweezers, trousers, and shears require plural verbs. (There are two parts to these things.): - These scissors are sharp! (SCISSORS = ARE) - Those trousers are on fire! (TROUSERS = ARE) 9) In sentences beginning with there is or there are, the subject follows the verb. S ...
1. Parts of Speech
... The names of persons, places, things, feelings, or ideas. Nouns usually answer the questions who or what. Nouns are divided into proper nouns and common nouns. Do you know what is the difference between them? ...
... The names of persons, places, things, feelings, or ideas. Nouns usually answer the questions who or what. Nouns are divided into proper nouns and common nouns. Do you know what is the difference between them? ...
Noun Clauses - rauscherspace
... a. Action Verbs: show the action that the subject performs b. Linking Verbs: link/connect the subject to nouns, pronouns or adjectives later in the sentence ...
... a. Action Verbs: show the action that the subject performs b. Linking Verbs: link/connect the subject to nouns, pronouns or adjectives later in the sentence ...
Perfect tense - Aquinas Spanish Wiki
... which means that it has an auxiliary verb (helping verb) and a past participle. This is the same in English, where the helping verb is “have” or “has” as in “I have spoken”; “she has spoken”. In Spanish, the helping verb is “haber” which means “to have”. NB: don’t confuse “haber” with “tener” (to ha ...
... which means that it has an auxiliary verb (helping verb) and a past participle. This is the same in English, where the helping verb is “have” or “has” as in “I have spoken”; “she has spoken”. In Spanish, the helping verb is “haber” which means “to have”. NB: don’t confuse “haber” with “tener” (to ha ...
Parts of Speech - Cloudfront.net
... Do not refer to a specific person, place, or thing. They usually do not have antecedents: “Many of the fans had arrived at 6 a.m.” Some pronouns can also function as adjectives: “Several people had to wait in the rain.” (adjective) “Several of the fans waited anxiously in line.” (pronoun) ...
... Do not refer to a specific person, place, or thing. They usually do not have antecedents: “Many of the fans had arrived at 6 a.m.” Some pronouns can also function as adjectives: “Several people had to wait in the rain.” (adjective) “Several of the fans waited anxiously in line.” (pronoun) ...
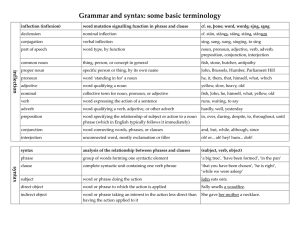
Grammar and syntax: some basic terminology
... word specifying the relationship of subject or action to a noun phrase (which in English typically follows it immediately) ...
... word specifying the relationship of subject or action to a noun phrase (which in English typically follows it immediately) ...
verbs - Amy Benjamin
... to illustrate how a word can change its forms, adapting itself to more than one part of speech. Not all words follow the same morphology. It’s interesting to see how words morph into different forms. The morphology chart is great for grammar lessons, vocabulary expansion, and spelling. ...
... to illustrate how a word can change its forms, adapting itself to more than one part of speech. Not all words follow the same morphology. It’s interesting to see how words morph into different forms. The morphology chart is great for grammar lessons, vocabulary expansion, and spelling. ...
Nouns – people, places, things, and ideas
... *Remember, the same noun can be categorized in more than one way. For example, boy is a singular, common noun, as well as a concrete noun. Nouns have many roles in a sentence. Sometimes they can act as adverbs and adjectives, but their main jobs in a sentence are to be the subject, direct object, in ...
... *Remember, the same noun can be categorized in more than one way. For example, boy is a singular, common noun, as well as a concrete noun. Nouns have many roles in a sentence. Sometimes they can act as adverbs and adjectives, but their main jobs in a sentence are to be the subject, direct object, in ...
1. Simple subject is the main noun or pronoun in the
... 1. Simple subject is the main noun or pronoun in the complete subject. 2. Complete subject includes all the words that tell whom or what a sentence is about. 3. Compound subject has two or more simple subjects that have the same predicate and are joined by and or or. 4. Complete predicate consists o ...
... 1. Simple subject is the main noun or pronoun in the complete subject. 2. Complete subject includes all the words that tell whom or what a sentence is about. 3. Compound subject has two or more simple subjects that have the same predicate and are joined by and or or. 4. Complete predicate consists o ...
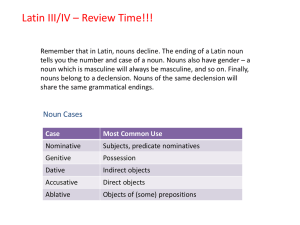
Latin II – Review Time!!!
... Nouns of the first declension are generally feminine in gender. The exceptions are nouns such as nauta, agricola, and poeta which describe occupations which would generally be held by men. The characteristic vowel of the first declension is -a-, and a first declension noun can be recognized by its g ...
... Nouns of the first declension are generally feminine in gender. The exceptions are nouns such as nauta, agricola, and poeta which describe occupations which would generally be held by men. The characteristic vowel of the first declension is -a-, and a first declension noun can be recognized by its g ...
Repaso: C4G2 Verbs with reflexive pronouns and direct objects 1.
... 3. Irregular: romper -> ____________: broke abrir -> _______________: open ...
... 3. Irregular: romper -> ____________: broke abrir -> _______________: open ...
Gerund
... The popular US President John Kennedy was known for his eloquent and inspirational speeches. - - essential so no commas - - there have been more than one President, so “Kennedy” is essential to the meaning ...
... The popular US President John Kennedy was known for his eloquent and inspirational speeches. - - essential so no commas - - there have been more than one President, so “Kennedy” is essential to the meaning ...
Nouns
... A common noun is a general name for a person, place, thing, or idea. A proper noun names a particular person, place, thing, or idea. Note: Proper nouns always begin with a capital letter. Common nouns begin with a capital letter only when they come at the beginning of a sentence. ...
... A common noun is a general name for a person, place, thing, or idea. A proper noun names a particular person, place, thing, or idea. Note: Proper nouns always begin with a capital letter. Common nouns begin with a capital letter only when they come at the beginning of a sentence. ...
Parts of Speech
... words expressed within the same syntactic rule. A non-local dependency is an instance in which two words can be syntactically dependent even though they occur far apart in a sentence (e.g., subject-verb agreement; long-distance dependencies such as wh-extraction). Non-local phenomena are a challenge ...
... words expressed within the same syntactic rule. A non-local dependency is an instance in which two words can be syntactically dependent even though they occur far apart in a sentence (e.g., subject-verb agreement; long-distance dependencies such as wh-extraction). Non-local phenomena are a challenge ...