Estructuras Gramaticales Leccion 6 with blanks
... iii. Adjectives that express a __________________________________ about the modified noun are usually placed before the noun. iv. __________, _____________, and ___________indefinite adjectives and ________ and _________ numbers are also placed before the noun. v. The adjectives _________ and ______ ...
... iii. Adjectives that express a __________________________________ about the modified noun are usually placed before the noun. iv. __________, _____________, and ___________indefinite adjectives and ________ and _________ numbers are also placed before the noun. v. The adjectives _________ and ______ ...
SAT 5: Identifying Sentence Errors
... Answers the question “Who” “John”, “Mary”, “He”, “She”, “It” ...
... Answers the question “Who” “John”, “Mary”, “He”, “She”, “It” ...
(2)
... when they is a group of boys or boys and girls, and ellas for ‘they’ Usted- Use when speaking when its only girls. to a person you don’t know Ustedes- Use ustedes formally when in Spain; use it in L.A. somone older, or someone with any group of people to whom you want to show ...
... when they is a group of boys or boys and girls, and ellas for ‘they’ Usted- Use when speaking when its only girls. to a person you don’t know Ustedes- Use ustedes formally when in Spain; use it in L.A. somone older, or someone with any group of people to whom you want to show ...
Parts of Speech and Parts of a Sentence
... • Sentences in the perfect tense include two events or actions, such as: I had finished my homework [event one] before my boyfriend arrived [event two]. For present perfect tense, another action is assumed, for example, the sentence: “I have studied for two hours” implies that I will do more study ...
... • Sentences in the perfect tense include two events or actions, such as: I had finished my homework [event one] before my boyfriend arrived [event two]. For present perfect tense, another action is assumed, for example, the sentence: “I have studied for two hours” implies that I will do more study ...
COMMON MISTAKES IN GRAMMAR Faulty Parallelism
... When it was her turn, she nervously walks up to the stage and begins her speech. When it was her turn, she nervously walked up to the stage and began her speech. ...
... When it was her turn, she nervously walks up to the stage and begins her speech. When it was her turn, she nervously walked up to the stage and began her speech. ...
COMMON MISTAKES IN GRAMMAR Faulty Parallelism
... When it was her turn, she nervously walks up to the stage and begins her speech. When it was her turn, she nervously walked up to the stage and began her speech. ...
... When it was her turn, she nervously walks up to the stage and begins her speech. When it was her turn, she nervously walked up to the stage and began her speech. ...
Parts of Speech:
... 1) Subject—tells who or what the sentence is about. Is a noun or a pronoun. 2) Predicate—tells what the subject is or does. The verb is found in the predicate. A) Action Verbs--Action: A verb that expresses action-this may be physical or mental. The action verb tells what the subject does (jump, kis ...
... 1) Subject—tells who or what the sentence is about. Is a noun or a pronoun. 2) Predicate—tells what the subject is or does. The verb is found in the predicate. A) Action Verbs--Action: A verb that expresses action-this may be physical or mental. The action verb tells what the subject does (jump, kis ...
Name - Humble ISD
... EXAMPLE: Laura is sweet. In this sentence, the verb is _________the subject Laura to the idea that she is sweet. ...
... EXAMPLE: Laura is sweet. In this sentence, the verb is _________the subject Laura to the idea that she is sweet. ...
Mandatos en “usted” - Mahtomedi High School
... For regular verbs, to form an affirmative or negative command do the following: 1) Take the present tense yo form of the verb. 2) Drop the –o ending (or oy in the verb estar) 3) For –ar verbs add an e For -er/-ir verbs add an a ...
... For regular verbs, to form an affirmative or negative command do the following: 1) Take the present tense yo form of the verb. 2) Drop the –o ending (or oy in the verb estar) 3) For –ar verbs add an e For -er/-ir verbs add an a ...
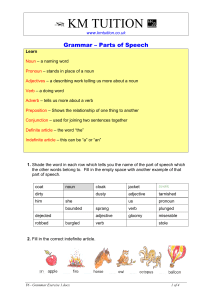
Grammar Exercise 1
... Pronoun – stands in place of a noun Adjectives – a describing work telling us more about a noun Verb – a doing word Adverb – tells us more about a verb Preposition – Shows the relationship of one thing to another Conjunction – used for joining two sentences together Definite article – the word “the” ...
... Pronoun – stands in place of a noun Adjectives – a describing work telling us more about a noun Verb – a doing word Adverb – tells us more about a verb Preposition – Shows the relationship of one thing to another Conjunction – used for joining two sentences together Definite article – the word “the” ...
Nouns and Pronouns
... My cat am a Siamese. On Tuesday mornings I is at class. The city prune the trees in the park on request. The sun rise in the east. Several vines climbs up the porch wall. These questions is easy. Usually, I writes with my right hand. Scientists searches for the causes of illness. Do the movie end ha ...
... My cat am a Siamese. On Tuesday mornings I is at class. The city prune the trees in the park on request. The sun rise in the east. Several vines climbs up the porch wall. These questions is easy. Usually, I writes with my right hand. Scientists searches for the causes of illness. Do the movie end ha ...
Pronombres de objetos directos
... When the sentence is negative (using “no”), direct object pronouns come before the verb, but after the no. ...
... When the sentence is negative (using “no”), direct object pronouns come before the verb, but after the no. ...
Grammar Study Sheet
... subject–verb–object in its simplest, unmarked declarative statements. B. Interrogative sentences invert word order. C. English also sees some use of the OSV (object-subject-verb) word order, especially when making comparisons using pronouns that are marked for case. D. Far more rare, but still somet ...
... subject–verb–object in its simplest, unmarked declarative statements. B. Interrogative sentences invert word order. C. English also sees some use of the OSV (object-subject-verb) word order, especially when making comparisons using pronouns that are marked for case. D. Far more rare, but still somet ...
Unit 2: Verbs, Adverbs, Prepositions, Conjunctions and Interjections
... How can you tell if it is an adverb or adjective? • Adjectives ALWAYS modify a noun or pronoun, so look at what it is describing • Adverbs always modify a verb, adjective or other adverb, so see what it is describing ...
... How can you tell if it is an adverb or adjective? • Adjectives ALWAYS modify a noun or pronoun, so look at what it is describing • Adverbs always modify a verb, adjective or other adverb, so see what it is describing ...
Parts of Speech - The Latin Library
... We found our way until the sun set. We found our way because there was a full moon. Preposition - a word that shows the relationship between a noun or pronoun and another word in the sentence (in, on, towards, with, by, etc.). · In Latin, as in English, prepositions are almost always placed before ( ...
... We found our way until the sun set. We found our way because there was a full moon. Preposition - a word that shows the relationship between a noun or pronoun and another word in the sentence (in, on, towards, with, by, etc.). · In Latin, as in English, prepositions are almost always placed before ( ...
parts of speech
... sentence that expresses action or being. Action verbs tell what the subject does.(sing) ...
... sentence that expresses action or being. Action verbs tell what the subject does.(sing) ...
Parts of speech 2
... sentence that expresses action or being. Action verbs tell what the subject does.(sing) ...
... sentence that expresses action or being. Action verbs tell what the subject does.(sing) ...
parts of speech here
... Ex/ Used intensively – She herself was not hurt. Relative – who, whom, which, that, whose Used to introduce subordinate clauses The people who live there are on vacation. Interrogative – who, whom, which, what, whose Used to ask questions Ex/ Who borrowed my pen? Demonstrative – this, these, that, t ...
... Ex/ Used intensively – She herself was not hurt. Relative – who, whom, which, that, whose Used to introduce subordinate clauses The people who live there are on vacation. Interrogative – who, whom, which, what, whose Used to ask questions Ex/ Who borrowed my pen? Demonstrative – this, these, that, t ...
The FOUR LEVELS OF ANALYSIS
... THERE HAS TO BE SOMETHING THAT IS EITHER DOING SOMETHING OR BEING SOMETHING: • The whale, upon the waves, crimson with gore, gnashed the sailors. ...
... THERE HAS TO BE SOMETHING THAT IS EITHER DOING SOMETHING OR BEING SOMETHING: • The whale, upon the waves, crimson with gore, gnashed the sailors. ...
Verbal
... Verbals A verbal is sort of an off-duty verb that looks like a verb but functions as another part of speech in a sentence. o There are three types of verbals: gerunds, participles and infinitives. Gerunds are –ing verbs that function as nouns. o Example: Swimming is a good form of exercise. Pa ...
... Verbals A verbal is sort of an off-duty verb that looks like a verb but functions as another part of speech in a sentence. o There are three types of verbals: gerunds, participles and infinitives. Gerunds are –ing verbs that function as nouns. o Example: Swimming is a good form of exercise. Pa ...
Parts of Speech
... (justice, for instance). For instance, patriotism, or love of one’s country, is a noun. The –ism ending on “patriotism” shows that the word is a noun. Subjects in sentences can be difficult to locate under certain conditions. The following link may provide some helpful tips to understand and locate ...
... (justice, for instance). For instance, patriotism, or love of one’s country, is a noun. The –ism ending on “patriotism” shows that the word is a noun. Subjects in sentences can be difficult to locate under certain conditions. The following link may provide some helpful tips to understand and locate ...