Parts of Speech - cloudfront.net
... The flowers smelled good. (but NOT, “She smelled the flowers”). ...
... The flowers smelled good. (but NOT, “She smelled the flowers”). ...
notes as word document
... 1. A NOUN NAMES A PERSON, PLACE, THING, OR IDEA. IT CAN BE PROPER OR COMMON, COLLECTIVE, CONCRETE, OR ABSTRACT, SINGULAR OR PLURAL. NOUNS HAVE PERSON (first, second, third), NUMBER (singular/plural), GENDER (masculine, feminine, neuter), AND CASE (nominative, possessive, objective). 2. A VERB IS A W ...
... 1. A NOUN NAMES A PERSON, PLACE, THING, OR IDEA. IT CAN BE PROPER OR COMMON, COLLECTIVE, CONCRETE, OR ABSTRACT, SINGULAR OR PLURAL. NOUNS HAVE PERSON (first, second, third), NUMBER (singular/plural), GENDER (masculine, feminine, neuter), AND CASE (nominative, possessive, objective). 2. A VERB IS A W ...
verbs - East Penn School District
... One of the most popular animal fables is a story about an owl who becomes a god to its fellow creatures. Because the owl can see in the dark and can answer questions with a few pat phrases, the other animals decide it is the wisest creature in the world. They follow in the owl’s footsteps and mimic ...
... One of the most popular animal fables is a story about an owl who becomes a god to its fellow creatures. Because the owl can see in the dark and can answer questions with a few pat phrases, the other animals decide it is the wisest creature in the world. They follow in the owl’s footsteps and mimic ...
Parts of Speech
... • Modifies adjectives (i.e. really cute), verbs (extremely fast), and other adverbs (very easily) • Answers the question “How?”, “When?”, “Where?”, or “To what extent?” • NOT, NEVER, OFTEN, and ALWAYS are always adverbs ...
... • Modifies adjectives (i.e. really cute), verbs (extremely fast), and other adverbs (very easily) • Answers the question “How?”, “When?”, “Where?”, or “To what extent?” • NOT, NEVER, OFTEN, and ALWAYS are always adverbs ...
Tricky bits….
... A run-on sentence, with no punctuation or conjunction between "five" and "we": It is nearly half past five we can not reach the town before dark. A run-on sentence where some independent clauses are missing parts of speech, so that one clause "morphs" into the next: I was interested in bought one ...
... A run-on sentence, with no punctuation or conjunction between "five" and "we": It is nearly half past five we can not reach the town before dark. A run-on sentence where some independent clauses are missing parts of speech, so that one clause "morphs" into the next: I was interested in bought one ...
Glossary of grammatical terms
... undergoes the action of the verb in a direct way, is said to be the direct object, while him, the recipient of the giving, is the indirect object. An object can be a noun or noun phrase, e.g. the keys, or a pronoun, e.g. him. Passive and active A sentence such as The police caught the thief La poli ...
... undergoes the action of the verb in a direct way, is said to be the direct object, while him, the recipient of the giving, is the indirect object. An object can be a noun or noun phrase, e.g. the keys, or a pronoun, e.g. him. Passive and active A sentence such as The police caught the thief La poli ...
Parts of Speech
... very, now, then, there, up, down, certainly, however, etc.) *Adverbs usually answer the questions: how? When? Where? To what extent? And many adverbs are formed by adding –ly to an adjective (e.g. Quickly) ...
... very, now, then, there, up, down, certainly, however, etc.) *Adverbs usually answer the questions: how? When? Where? To what extent? And many adverbs are formed by adding –ly to an adjective (e.g. Quickly) ...
WALT – Describe what an auxiliary verb is and
... (Compound verb = is waiting, Adverb = probably) Fill in the missing word Fish is usually ______ with chips. I am not ______ well today Emily will usually _______ chocolate ice cream ...
... (Compound verb = is waiting, Adverb = probably) Fill in the missing word Fish is usually ______ with chips. I am not ______ well today Emily will usually _______ chocolate ice cream ...
hablar....................... hablando
... Estoy hablando................................................... I am speaking. Juan está comiendo............................................ John is eating. María está escribiendo una carta......................... Mary is writing a letter. In order to form the present progressive, you must know ...
... Estoy hablando................................................... I am speaking. Juan está comiendo............................................ John is eating. María está escribiendo una carta......................... Mary is writing a letter. In order to form the present progressive, you must know ...
Grammar and Usage Student Help Desk
... Traditional members keep cattle on their farms. (both are plural) o Person – 1st, 2nd, 3rd Visitors realize they can learn from other cultures. (3rd person) **Do not use YOU with 1st and 3rd persons. o Gender – masculine or feminine Laura Mansfield teaches her students at Hopi High. (both are femini ...
... Traditional members keep cattle on their farms. (both are plural) o Person – 1st, 2nd, 3rd Visitors realize they can learn from other cultures. (3rd person) **Do not use YOU with 1st and 3rd persons. o Gender – masculine or feminine Laura Mansfield teaches her students at Hopi High. (both are femini ...
eportfolio part 2
... 4. Intonation: Informal and conversational. While asking a question this way, the phrase remains as a statement, but your intonation rises, especially near the end. Questions that ask for specific information: Begin with an interrogative word: 1. Interrogative adverbs: Combien, comment, où, pourquoi ...
... 4. Intonation: Informal and conversational. While asking a question this way, the phrase remains as a statement, but your intonation rises, especially near the end. Questions that ask for specific information: Begin with an interrogative word: 1. Interrogative adverbs: Combien, comment, où, pourquoi ...
kno20710_app_547
... Mis libros y mi computadora están allí. My books and my computer are over there. ...
... Mis libros y mi computadora están allí. My books and my computer are over there. ...
HS4 – LOS USOS DIFERENTES DEL PRONOMBRE “SE” Perhaps
... (s)he does not have to claim responsibility. An indirect object pronoun will be used to refer to the person involved in the occurrence and the verb will match the subject (thing or things) involved. Your verb will be conjugated in the third person singular or plural. If you want to be even more spec ...
... (s)he does not have to claim responsibility. An indirect object pronoun will be used to refer to the person involved in the occurrence and the verb will match the subject (thing or things) involved. Your verb will be conjugated in the third person singular or plural. If you want to be even more spec ...
Verbs
... • Verb- A verb is a word that shows action or state of being. The action may be physical or mental. – State of being Ex. ...
... • Verb- A verb is a word that shows action or state of being. The action may be physical or mental. – State of being Ex. ...
verbs - Cuyamaca College
... – May show action [jump, hop, skip] – May link [is, was will be, appeared] – May be compound [has been, will have, is going] – Might be infinite [to go, to listen] **However a gerund is not an active verb [ing verb without helping verb isn’t main verb] ...
... – May show action [jump, hop, skip] – May link [is, was will be, appeared] – May be compound [has been, will have, is going] – Might be infinite [to go, to listen] **However a gerund is not an active verb [ing verb without helping verb isn’t main verb] ...
Mrs. Ray*s TAG Language Arts Class
... Relative pronouns introduce adjective clauses. That, which, who, whom, whose Indefinite pronouns refer to a person, place, thing, or idea that my not be specifically named. Examples: all, another, both, each, few, many, most, much, neither, nobody, other, several. ...
... Relative pronouns introduce adjective clauses. That, which, who, whom, whose Indefinite pronouns refer to a person, place, thing, or idea that my not be specifically named. Examples: all, another, both, each, few, many, most, much, neither, nobody, other, several. ...
Latin Summer Assignment Latin III Mr. Pasquinelli 2016 If you have
... (1) Indicates that the subject is the doer of the action (2) [Subject] “Is doing” or “Does” b) Passive (1) Indicates that the subject is the receiver of the action (but still in the nominative case) (2) [Subject] “Is being done by” or “Is done by” (3) NB: The translation examples above are for ...
... (1) Indicates that the subject is the doer of the action (2) [Subject] “Is doing” or “Does” b) Passive (1) Indicates that the subject is the receiver of the action (but still in the nominative case) (2) [Subject] “Is being done by” or “Is done by” (3) NB: The translation examples above are for ...
Grammar Blog 2 More Basics. The last blog said that a verb and its
... 1. Nouns can be described by one or more adjectives: e.g. a clever boy, a small red book, outstanding beauty. 2. Verbs can be described by one or more adverbs (usually ending in Cly). e.g. The door slammed loudly. He answered clearly and precisely. He runs fast.) 3. Adverbs can also describe adjecti ...
... 1. Nouns can be described by one or more adjectives: e.g. a clever boy, a small red book, outstanding beauty. 2. Verbs can be described by one or more adverbs (usually ending in Cly). e.g. The door slammed loudly. He answered clearly and precisely. He runs fast.) 3. Adverbs can also describe adjecti ...
PARTS OF SPEECH: Components of Language
... common to proper. • Mildred watched television most of the time. ...
... common to proper. • Mildred watched television most of the time. ...
Verbs
... verbs) – join the subject and the predicate and do not show action themselves. They tell you more about the subject rather than what the subject is doing. The most common linking verbs are forms of to be. Examples: am, is, are, was, were, fear, look, smell, taste, appear, become Example sentences: ...
... verbs) – join the subject and the predicate and do not show action themselves. They tell you more about the subject rather than what the subject is doing. The most common linking verbs are forms of to be. Examples: am, is, are, was, were, fear, look, smell, taste, appear, become Example sentences: ...
2014 Fall pre ap exam review
... Example: she, he, them, us, we, etc. Subject: Who or what a sentence is about, it’s always a noun or pronoun. -compound subject: When you have two or more subjects doing the same thing. Verb: What the subject is doing. -action verb: When the subject is performing an action (physical or mental). Exam ...
... Example: she, he, them, us, we, etc. Subject: Who or what a sentence is about, it’s always a noun or pronoun. -compound subject: When you have two or more subjects doing the same thing. Verb: What the subject is doing. -action verb: When the subject is performing an action (physical or mental). Exam ...
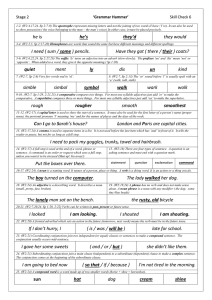
Check 6 Answers - Tranmere Park Primary School
... 1-2. (W2:4,17,24. Sp 2:7-9) The apostrophe represents missing letters and not the joining of two words (I have / I’ve). It can also be used to show possession ( the voice belonging to the man – the man’s voice) In either case, it must be placed precisely. ...
... 1-2. (W2:4,17,24. Sp 2:7-9) The apostrophe represents missing letters and not the joining of two words (I have / I’ve). It can also be used to show possession ( the voice belonging to the man – the man’s voice) In either case, it must be placed precisely. ...