Wireless Audio Conferencing System (WACS)
... address when only its Internet Layer (IP) or Network Layer address is known. uses a simple message format that contains one address resolution request or response Once local network recognized, the server or networking device returns a response containing the required address. ...
... address when only its Internet Layer (IP) or Network Layer address is known. uses a simple message format that contains one address resolution request or response Once local network recognized, the server or networking device returns a response containing the required address. ...
route1
... N denotes set of nodes in the graph l (i, j) denotes non-negative cost (weight) for edge (i, j) s denotes this node M denotes the set of nodes incorporated so far C(n) denotes cost of the path from s to node n ...
... N denotes set of nodes in the graph l (i, j) denotes non-negative cost (weight) for edge (i, j) s denotes this node M denotes the set of nodes incorporated so far C(n) denotes cost of the path from s to node n ...
Document
... Additional problems: a) Two stations communicate via a 1Mb/s satellite link with a propagation delay of 270ms. The satellite serves merely to retransmit data received from one station to another, with neglidgible switching delay. Using HDLC frames of 1024 bits with 3bit sequence numbers, what is the ...
... Additional problems: a) Two stations communicate via a 1Mb/s satellite link with a propagation delay of 270ms. The satellite serves merely to retransmit data received from one station to another, with neglidgible switching delay. Using HDLC frames of 1024 bits with 3bit sequence numbers, what is the ...
Instant Conferencing Service
... Larger geographic coverage More cost-effective (economy of scales) More redundancy at the physical connectivity level Higher aggregate back-plane throughput EdgeNet2006 Summit ...
... Larger geographic coverage More cost-effective (economy of scales) More redundancy at the physical connectivity level Higher aggregate back-plane throughput EdgeNet2006 Summit ...
Kuliah Komunikasi Data
... defines the way in which computers, printers, and other devices are connected. A network topology describes the layout of the wire and devices as well as the paths used by data transmissions. ...
... defines the way in which computers, printers, and other devices are connected. A network topology describes the layout of the wire and devices as well as the paths used by data transmissions. ...
Part I: Introduction - University of Pittsburgh
... CD – detect collision while sending and cancel it CA – avoid collision by getting permission first Ethernet and Wi-Fi? ...
... CD – detect collision while sending and cancel it CA – avoid collision by getting permission first Ethernet and Wi-Fi? ...
Visualisation and Analysis of Real Time Application Behaviour in a
... schemes • Evaluation of the behaviour of real time applications would benefit from an ability to assess the “quality of reproduction” when subjected to a particular network scheme ...
... schemes • Evaluation of the behaviour of real time applications would benefit from an ability to assess the “quality of reproduction” when subjected to a particular network scheme ...
Solutions
... paths to other network nodes, but their link state updates are yet to reach their neighbors. Is there a possibility of packets looping in the network? Why? [2 points] Yes. There is a possibility of looping. After A and B do the recomputation, the shortest A—B path is through C, but C still thinks th ...
... paths to other network nodes, but their link state updates are yet to reach their neighbors. Is there a possibility of packets looping in the network? Why? [2 points] Yes. There is a possibility of looping. After A and B do the recomputation, the shortest A—B path is through C, but C still thinks th ...
Peer-to-Peer Streaming
... placing minimal demands on the peers Goal: help a server tide over crises such as flash crowds rather than replace the server with a pure P2P system ...
... placing minimal demands on the peers Goal: help a server tide over crises such as flash crowds rather than replace the server with a pure P2P system ...
classful addressing - E Learning UPN Veteran Yogyakarta
... 127.0.0.1, which points to yourself] ...
... 127.0.0.1, which points to yourself] ...
mat379.sp05.ExamAnswers
... i. Mention and briefly describe two features of the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) that make it more suitable for routing in the global Internet than either the Routing Information Protocol (RIP) or the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Protocol. BGP allows policy routing. In other words, routers can c ...
... i. Mention and briefly describe two features of the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) that make it more suitable for routing in the global Internet than either the Routing Information Protocol (RIP) or the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Protocol. BGP allows policy routing. In other words, routers can c ...
Here is the Power Point Presentation on Chord
... The first large peer-to-peer network was Napster As we went over in class, Napster relied on a central server to store all routing information, so it was only sort of peer-to-peer ...
... The first large peer-to-peer network was Napster As we went over in class, Napster relied on a central server to store all routing information, so it was only sort of peer-to-peer ...
Communication - Princeton University
... No Backbone Changes: Mobile IP • Mobile node has home address & care-of address ...
... No Backbone Changes: Mobile IP • Mobile node has home address & care-of address ...
ppt - MIT
... finds a path to the destination and forwards packets along that path • Difference between routing and forwarding • Routing is finding the path • Forwarding is the action of sending the packet to the next-hop toward its destination ...
... finds a path to the destination and forwards packets along that path • Difference between routing and forwarding • Routing is finding the path • Forwarding is the action of sending the packet to the next-hop toward its destination ...
1-up PPT
... finds a path to the destination and forwards packets along that path • Difference between routing and forwarding • Routing is finding the path • Forwarding is the action of sending the packet to the next-hop toward its destination ...
... finds a path to the destination and forwards packets along that path • Difference between routing and forwarding • Routing is finding the path • Forwarding is the action of sending the packet to the next-hop toward its destination ...
Ethernet - Inst.eecs.berkeley.edu
... • 48-bit address • Address assigned when NIC card is manufactured. • Packets can be sent to Single address – Unicast All stations on network – Broadcast (address = all 1s.) Subset of stations – Multicast • Broadcast (address = all 1s.) All receivers accepts unicast / broadcats. • Half addresses rese ...
... • 48-bit address • Address assigned when NIC card is manufactured. • Packets can be sent to Single address – Unicast All stations on network – Broadcast (address = all 1s.) Subset of stations – Multicast • Broadcast (address = all 1s.) All receivers accepts unicast / broadcats. • Half addresses rese ...
Artificial Intelligence in Networking: Ant Colony Optimization
... Determines a path before packets are sent, and then sends all packets along that path ...
... Determines a path before packets are sent, and then sends all packets along that path ...
Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol
... – Initially, assume that every host on the network is part of the Multicast group (TRPB) – Per Source-Group Multicast delivery tree – Reverse Path Forwarding check – Poison Reverse • Determine downstream interfaces to forward the packet on ...
... – Initially, assume that every host on the network is part of the Multicast group (TRPB) – Per Source-Group Multicast delivery tree – Reverse Path Forwarding check – Poison Reverse • Determine downstream interfaces to forward the packet on ...
Universität Stuttgart Communication Networks II Sample Solution
... No, IP routing provides only a single path from source to destination. Therefore, only up to 10 Mbit/s can be reached by modifying the link cost ...
... No, IP routing provides only a single path from source to destination. Therefore, only up to 10 Mbit/s can be reached by modifying the link cost ...
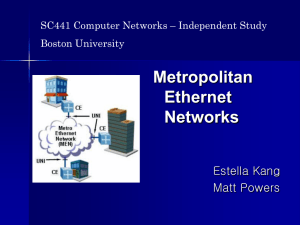
Metro Ethernet Networks
... Explosion of Internet traffic and IP services demand for rapid scalability and dynamic functionality ...
... Explosion of Internet traffic and IP services demand for rapid scalability and dynamic functionality ...