ch 11 Data Network Connectivity
... Transparent bridging - a bridge begins polling a network to learn about its physical topology as soon as it is installed on the network. ...
... Transparent bridging - a bridge begins polling a network to learn about its physical topology as soon as it is installed on the network. ...
Ethernet, IP and TCP
... address to the host, sending it the network mask and the gateway address as well. • Internet providers work like that to save address space. • Problem: some services require IP addresses to be stable. They can not be run in such a setting. ...
... address to the host, sending it the network mask and the gateway address as well. • Internet providers work like that to save address space. • Problem: some services require IP addresses to be stable. They can not be run in such a setting. ...
Data Network Connectivity
... Transparent bridging - a bridge begins polling a network to learn about its physical topology as soon as it is installed on the network. ...
... Transparent bridging - a bridge begins polling a network to learn about its physical topology as soon as it is installed on the network. ...
Network Routing Algorithms
... – a subset of the subnet that includes all routers but contains no loops. ...
... – a subset of the subnet that includes all routers but contains no loops. ...
Network Routing Algorithms
... – a subset of the subnet that includes all routers but contains no loops. ...
... – a subset of the subnet that includes all routers but contains no loops. ...
Geo-distributed Messaging with RabbitMQ
... Inter-node communication security (transport protocol encryption and authentication) The secondary quality attributes to achieve are: ...
... Inter-node communication security (transport protocol encryption and authentication) The secondary quality attributes to achieve are: ...
PowerPoint
... (1) When nodes are in motion, links can be obstructed by intervening objects. (2) When nodes must conserve power, links are shut down periodically. • Network partition : When no path exists between source and destination, it is perfectly possible that two nodes may never be part of the same connecte ...
... (1) When nodes are in motion, links can be obstructed by intervening objects. (2) When nodes must conserve power, links are shut down periodically. • Network partition : When no path exists between source and destination, it is perfectly possible that two nodes may never be part of the same connecte ...
WorldNet Data Warehouse Albert Greenberg albert
... Goal? In operational IP networks, improve performance and make more efficient use of network resources, by better matching the resources with traffic demands How? By integrating – traffic measurement – network modeling – selection and configuration of network management and control mechanisms. ...
... Goal? In operational IP networks, improve performance and make more efficient use of network resources, by better matching the resources with traffic demands How? By integrating – traffic measurement – network modeling – selection and configuration of network management and control mechanisms. ...
IP MULTICAST
... source S to group G, it first checks in the standard unicast routing table that the incoming interface is the one that is used for sending unicast packets toward S. If this is not the case, it drops the packets and sends back a “prune (S,G)” message on the incoming interface. • The router will then ...
... source S to group G, it first checks in the standard unicast routing table that the incoming interface is the one that is used for sending unicast packets toward S. If this is not the case, it drops the packets and sends back a “prune (S,G)” message on the incoming interface. • The router will then ...
Introduction to Decision Mathematics
... Euler realized that the problem could be solved in terms of the degrees of the nodes. The degree of a node is the number of edges touching it; in the Königsberg bridge graph, three nodes have degree 3 and one has degree 5. Euler proved that a circuit of the desired form is possible if and only if th ...
... Euler realized that the problem could be solved in terms of the degrees of the nodes. The degree of a node is the number of edges touching it; in the Königsberg bridge graph, three nodes have degree 3 and one has degree 5. Euler proved that a circuit of the desired form is possible if and only if th ...
ppt - NOISE
... • Reliable Delivery: Guarantee to deliver the frame to the other end of the link without error. • Flow Control: The link layer can provide mechanisms to avoid overflowing the buffer • Error Correction: Determining where errors have occurred and then correcting those errors. ...
... • Reliable Delivery: Guarantee to deliver the frame to the other end of the link without error. • Flow Control: The link layer can provide mechanisms to avoid overflowing the buffer • Error Correction: Determining where errors have occurred and then correcting those errors. ...
PowerPoint
... • mcast forwarding tree: tree of shortest path routes from source to all receivers – Dijkstra’s algorithm ...
... • mcast forwarding tree: tree of shortest path routes from source to all receivers – Dijkstra’s algorithm ...
Sensors, Databases and Flash Storage
... neighboring node (remote cache hit), forwards the request to the neighboring node with the largest residual energy • If the request can not be satisfied by this mediator node, then it does not forward it recursively to its own mediators, since this will be done by the routing protocol, e.g., AODV • ...
... neighboring node (remote cache hit), forwards the request to the neighboring node with the largest residual energy • If the request can not be satisfied by this mediator node, then it does not forward it recursively to its own mediators, since this will be done by the routing protocol, e.g., AODV • ...
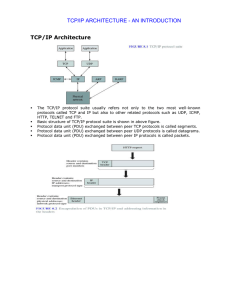
TCP/IP Architecture TCP/IP ARCHITECTURE
... IP address needs to be resolved to physical address at each IP network interface Example: Ethernet uses 48-bit addresses o Each Ethernet network interface card (NIC) has globally unique Medium Access Control (MAC) or physical address o First 24 bits identify NIC manufacturer; second 24 bits are ...
... IP address needs to be resolved to physical address at each IP network interface Example: Ethernet uses 48-bit addresses o Each Ethernet network interface card (NIC) has globally unique Medium Access Control (MAC) or physical address o First 24 bits identify NIC manufacturer; second 24 bits are ...
Valiant Load-Balancing in Backbone Networks
... Each packet needs look up only once in the backbone Each flow is evenly split over N paths Routing decisions are local ...
... Each packet needs look up only once in the backbone Each flow is evenly split over N paths Routing decisions are local ...
Basic Network Concepts
... • The more bytes there are in each address, the more addresses there are available and the more devices that can be connected to the network simultaneously. ...
... • The more bytes there are in each address, the more addresses there are available and the more devices that can be connected to the network simultaneously. ...
ppt
... accomplished via “link state broadcast” all nodes have same info computes least cost paths from one node (‘source”) to all other nodes gives forwarding table for that node iterative: after k iterations, know least cost path to k dest.’s ...
... accomplished via “link state broadcast” all nodes have same info computes least cost paths from one node (‘source”) to all other nodes gives forwarding table for that node iterative: after k iterations, know least cost path to k dest.’s ...
Chapter 9 Slides - Hafr Al-Batin Community College (HBCC)
... networks in which bridges pass frames along one hop at a time based on tables associating end nodes with bridge ports. The operation and presence of these bridges is transparent to network end nodes. Transparent bridges interconnect like-media LANs (for example, all Ethernet) to form the appearance ...
... networks in which bridges pass frames along one hop at a time based on tables associating end nodes with bridge ports. The operation and presence of these bridges is transparent to network end nodes. Transparent bridges interconnect like-media LANs (for example, all Ethernet) to form the appearance ...
Fluid Networking Description
... time. • Very small so it uses up limited bandwidth. • Each node – has no network knowledge – follows instructions (if any) provided on policy routing and maximum port bandwidth – processes each packet at wire speed in hardware Copyright 2006 Modern Systems Research ...
... time. • Very small so it uses up limited bandwidth. • Each node – has no network knowledge – follows instructions (if any) provided on policy routing and maximum port bandwidth – processes each packet at wire speed in hardware Copyright 2006 Modern Systems Research ...
System Model
... want to get the maximum revenue in the network and when their utility is less than zero, they will give up the opportunity to use the ...
... want to get the maximum revenue in the network and when their utility is less than zero, they will give up the opportunity to use the ...