RAD 107 HOMEWORK 4
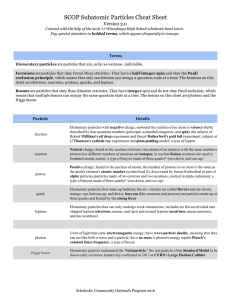
... 2. Because each chemical element corresponds to precisely one value of the atomic number, nuclides can also be identified by the symbol for the element followed by the mass number (i.e. without also specifying the atomic number). For example, instead of 146 C we can write C-14 or Carbon-14. Write ea ...
... 2. Because each chemical element corresponds to precisely one value of the atomic number, nuclides can also be identified by the symbol for the element followed by the mass number (i.e. without also specifying the atomic number). For example, instead of 146 C we can write C-14 or Carbon-14. Write ea ...
HW1
... • Many body phenomena governed by Pauli principle • Phase transitions (crystal lattice), symmetry breaking, Higgs mechanism, shape coexistence, crustal structures • Temperature, surface tension • Periodic table • Binding energy, shell structure and magic numbers • Molecular and nuclear shapes, colle ...
... • Many body phenomena governed by Pauli principle • Phase transitions (crystal lattice), symmetry breaking, Higgs mechanism, shape coexistence, crustal structures • Temperature, surface tension • Periodic table • Binding energy, shell structure and magic numbers • Molecular and nuclear shapes, colle ...
View Outline
... A student who fails to take two (2) long examinations shall automatically incur the grade of “5” unless he drops the subject. No student may be exempted from the finals if he/she fails to take one (1) long examination. A student who tails to take the finals shall be given the grade of “5” unless his ...
... A student who fails to take two (2) long examinations shall automatically incur the grade of “5” unless he drops the subject. No student may be exempted from the finals if he/she fails to take one (1) long examination. A student who tails to take the finals shall be given the grade of “5” unless his ...
Lecture 15
... Thus we see that all atoms have an ionization energy, which is the threshold for exciting an atom in the ground state to the lowest unbound state. This converts the atom to a positive ion. In general, this will change the chemical nature of the atom. If the atom is in a chemical compound, (as it wou ...
... Thus we see that all atoms have an ionization energy, which is the threshold for exciting an atom in the ground state to the lowest unbound state. This converts the atom to a positive ion. In general, this will change the chemical nature of the atom. If the atom is in a chemical compound, (as it wou ...
Standard Model history (2008)
... or can we recognize patterns or symmetries in their nature (charge, mass, flavor) or the way they behave (decays)? ...
... or can we recognize patterns or symmetries in their nature (charge, mass, flavor) or the way they behave (decays)? ...
Orbital-Orbital Coupling
... Solving the Schrodinger Equation in this case can be very hard. But we can approximate the solution as the product of singleparticle wave functions: ...
... Solving the Schrodinger Equation in this case can be very hard. But we can approximate the solution as the product of singleparticle wave functions: ...
Modern Physics P age | 1 AP Physics B
... 6. According to the Bohr model of the atom, electrons orbit the nucleus in definite orbits. According to the laws of classical physics, this model would be impossible because (A) the positively charged nucleus attracts the electrons (B) Coulomb's law applies (C) accelerating electrons radiate energy ...
... 6. According to the Bohr model of the atom, electrons orbit the nucleus in definite orbits. According to the laws of classical physics, this model would be impossible because (A) the positively charged nucleus attracts the electrons (B) Coulomb's law applies (C) accelerating electrons radiate energy ...
Chapter 42
... The magnitude of the angular momentum of an electron moving in a circle of radius r is L = me v r The direction of L is perpendicular to the plane of the circle In the Bohr model, the angular momentum of the electron is restricted to integer multiples of h ...
... The magnitude of the angular momentum of an electron moving in a circle of radius r is L = me v r The direction of L is perpendicular to the plane of the circle In the Bohr model, the angular momentum of the electron is restricted to integer multiples of h ...
Thesis Presentation Mr. Joshuah T. Heath Department of Physics
... One of the simplest conceptual models in quantum statistical physics is a gas of noninteracting particles with bosonic symmetry. In the grand canonical ensemble, particle number and temperature are in equilibrium with an external reservoir and an exact analytical expression can be derived for the pa ...
... One of the simplest conceptual models in quantum statistical physics is a gas of noninteracting particles with bosonic symmetry. In the grand canonical ensemble, particle number and temperature are in equilibrium with an external reservoir and an exact analytical expression can be derived for the pa ...