Terms to Know
... gain and loss of electrons that orbit an atomic nucleus, but do not involve any change in the nucleus itself Positrons : The positron is the antiparticle of the electron. It has the same mass and the same quantity of electric charge as does the electron, but its electric charge is positive rather th ...
... gain and loss of electrons that orbit an atomic nucleus, but do not involve any change in the nucleus itself Positrons : The positron is the antiparticle of the electron. It has the same mass and the same quantity of electric charge as does the electron, but its electric charge is positive rather th ...
Atomic Structure and Forces
... Electrical Force (aka electromagnetic force) Action – Based on charges of particles. Like forces repel, opposite forces attract Effect of distance – long-range force, can act over distance, gets slightly weaker as distance increases Strength – Second strongest of the 4 fundamental forces Strong Forc ...
... Electrical Force (aka electromagnetic force) Action – Based on charges of particles. Like forces repel, opposite forces attract Effect of distance – long-range force, can act over distance, gets slightly weaker as distance increases Strength – Second strongest of the 4 fundamental forces Strong Forc ...
SIMPLE NUCLEAR REACTIONS
... A neutron is fired at a large nucleus (usually uranium-235). It is absorbed briefly which makes the unstable isotope of uranium-236. This then splits into two or more smaller nuclei releasing neutrons and energy in the process. The products are radioactive. Ex. uranium-235 + neutron [uranium-236] ...
... A neutron is fired at a large nucleus (usually uranium-235). It is absorbed briefly which makes the unstable isotope of uranium-236. This then splits into two or more smaller nuclei releasing neutrons and energy in the process. The products are radioactive. Ex. uranium-235 + neutron [uranium-236] ...
L37 - University of Iowa Physics
... • the neutrons and protons have about the same mass, and are each about 2000 times more massive than the electrons • the nucleus accounts for about 99.9% of the total mass of the atom • the neutrons have no charge what role do they play???? ...
... • the neutrons and protons have about the same mass, and are each about 2000 times more massive than the electrons • the nucleus accounts for about 99.9% of the total mass of the atom • the neutrons have no charge what role do they play???? ...
Basic Physics Concepts Useful in Astronomy
... If Object A exerts a force on Object B, then Object B must exert a force on Object A that is equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction Atoms o Everything in the Universe is made up of atoms o Atoms are made up of smaller particles o Atoms are held together by the positively charged nucleus and ...
... If Object A exerts a force on Object B, then Object B must exert a force on Object A that is equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction Atoms o Everything in the Universe is made up of atoms o Atoms are made up of smaller particles o Atoms are held together by the positively charged nucleus and ...
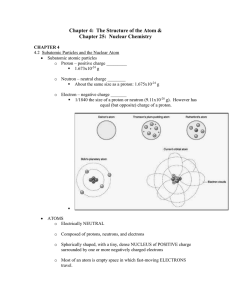
Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom &
... 4.2 Subatomic Particles and the Nuclear Atom Subatomic atomic particles o Proton – positive charge _________ 1.673x10-24 g o Neutron – neutral charge ________ About the same size as a proton: 1.675x10-24 g o Electron – negative charge _______ 1/1840 the size of a proton or neutron (9.11x10-2 ...
... 4.2 Subatomic Particles and the Nuclear Atom Subatomic atomic particles o Proton – positive charge _________ 1.673x10-24 g o Neutron – neutral charge ________ About the same size as a proton: 1.675x10-24 g o Electron – negative charge _______ 1/1840 the size of a proton or neutron (9.11x10-2 ...
Unit 1 - cloudfront.net
... Cathode rays have identical properties regardless of the element used to produce them. All elements must contain identically charged electrons. Atoms are neutral, so there must be positive particles in the atom to balance the negative charge of the electrons Electrons have so little mass that a ...
... Cathode rays have identical properties regardless of the element used to produce them. All elements must contain identically charged electrons. Atoms are neutral, so there must be positive particles in the atom to balance the negative charge of the electrons Electrons have so little mass that a ...
Atoms Study Guide
... Electron – NEGATIVELY CHARGED (-) particle; discovered by Thomson; least mass of all atomic particles Electron cloud – the region where electrons are likely to be found Isotope – atom with same # of protons, different # of neutrons; # of protons NEVER changes in an isotope Mass number – the sum of p ...
... Electron – NEGATIVELY CHARGED (-) particle; discovered by Thomson; least mass of all atomic particles Electron cloud – the region where electrons are likely to be found Isotope – atom with same # of protons, different # of neutrons; # of protons NEVER changes in an isotope Mass number – the sum of p ...
nuclear chemistry - La Salle High School
... daughter nucleus that is in an excited state; the excited state is unstable and goes to a lower-energy state by releasing energ y in the form of gamma rays. ...
... daughter nucleus that is in an excited state; the excited state is unstable and goes to a lower-energy state by releasing energ y in the form of gamma rays. ...
Nuclear Physics
... Nuclear force is short range: as nucleus grows nuclear bonds are saturated and nuclei interact only with neighbors => Ebinding almost constant ...
... Nuclear force is short range: as nucleus grows nuclear bonds are saturated and nuclei interact only with neighbors => Ebinding almost constant ...
GCSE C1.1 PPT Structure of atoms - School
... Identify each of the three subatomic particles – protons, neutrons and electrons Recall location, mass and charge of each of the three subatomic particles Identify the numbers of protons, neutrons and electrons for each element in the periodic table up to atomic number 20 – calcium ...
... Identify each of the three subatomic particles – protons, neutrons and electrons Recall location, mass and charge of each of the three subatomic particles Identify the numbers of protons, neutrons and electrons for each element in the periodic table up to atomic number 20 – calcium ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.