Chemistry: The Nature of Matter
... Energy Levels of Electrons ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ More distant an electron is from the nucleus, the greater the energy possible in the atom Different states of energy are called energy levels or ...
... Energy Levels of Electrons ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ More distant an electron is from the nucleus, the greater the energy possible in the atom Different states of energy are called energy levels or ...
Radioactivity
... • 7.4 understand that alpha and beta particles and gamma rays are ionising radiations emitted from unstable nuclei in a random process • 7.5 describe the nature of alpha and beta particles and gamma rays and recall that they may be distinguished in terms of penetrating power • 7.6 describe the effec ...
... • 7.4 understand that alpha and beta particles and gamma rays are ionising radiations emitted from unstable nuclei in a random process • 7.5 describe the nature of alpha and beta particles and gamma rays and recall that they may be distinguished in terms of penetrating power • 7.6 describe the effec ...
Nuclear atom 1 - schoolphysics
... Nuclear and atomic physics 1 1. Describe briefly the two conflicting theories of the structure of the atom. 2. Why was the nuclear model of Rutherford accepted as correct? 3. What would have happened if neutrons had been used in Rutherford’s experiment? Explain your answer. 4. What would have happen ...
... Nuclear and atomic physics 1 1. Describe briefly the two conflicting theories of the structure of the atom. 2. Why was the nuclear model of Rutherford accepted as correct? 3. What would have happened if neutrons had been used in Rutherford’s experiment? Explain your answer. 4. What would have happen ...
Nuclear Energy
... nucleus into two smaller nuclei. The fuel is a large unstable atom such as Uranium-235. When the neutron hits the U-235 nucleus, the nucleus splits apart into two smaller nuclei and 2 or more neutrons. ...
... nucleus into two smaller nuclei. The fuel is a large unstable atom such as Uranium-235. When the neutron hits the U-235 nucleus, the nucleus splits apart into two smaller nuclei and 2 or more neutrons. ...
Atomic Structure - Sierra Vista Chemistry
... them. All elements must contain identically charged electrons. Atoms are neutral, so there must be positive particles in the atom to balance the negative charge of the electrons Electrons have so little mass that atoms must contain other particles that account for most of the mass ...
... them. All elements must contain identically charged electrons. Atoms are neutral, so there must be positive particles in the atom to balance the negative charge of the electrons Electrons have so little mass that atoms must contain other particles that account for most of the mass ...
notes ch 39 1st half Atomic Nucleus and Radioactivity
... 39.1 Atomic Nucleus cont. • The strong force is only strong enough to hold things together at very small distances. • When the number of protons increases in a nucleus, then the number of neutrons needed to hold the nucleus together must get larger too. • At small atomic numbers, the number of neut ...
... 39.1 Atomic Nucleus cont. • The strong force is only strong enough to hold things together at very small distances. • When the number of protons increases in a nucleus, then the number of neutrons needed to hold the nucleus together must get larger too. • At small atomic numbers, the number of neut ...
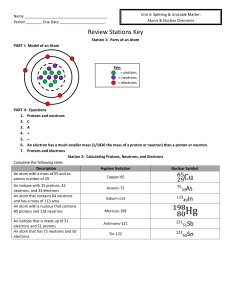
Name Period ______ Due Date Review Stations Key Station 1
... 2. a If the isotope had a long half-life, it would stay in your body causing radiation poisoning or cancer. ...
... 2. a If the isotope had a long half-life, it would stay in your body causing radiation poisoning or cancer. ...
Atomic Structure
... them. All elements must contain identically charged electrons. Atoms are neutral, so there must be positive particles in the atom to balance the negative charge of the electrons Electrons have so little mass that atoms must contain other particles that account for most of the mass ...
... them. All elements must contain identically charged electrons. Atoms are neutral, so there must be positive particles in the atom to balance the negative charge of the electrons Electrons have so little mass that atoms must contain other particles that account for most of the mass ...
24.5 Nuclear Equations - The Free Learning Channel
... 3. There are six known quarks: up, down, charmed, strange, top, and bottom. Protons and neutrons are each made of only up and down quarks, and they are made of three quarks each. The up quark carries a charge of + 23 , and the down quark carries a charge of − 31 . Determine by the final charge on the ...
... 3. There are six known quarks: up, down, charmed, strange, top, and bottom. Protons and neutrons are each made of only up and down quarks, and they are made of three quarks each. The up quark carries a charge of + 23 , and the down quark carries a charge of − 31 . Determine by the final charge on the ...
power point notes
... - he was studying light emission when he discovered that uranium emits energy by itself ...
... - he was studying light emission when he discovered that uranium emits energy by itself ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.