Atoms and Radioisotopes
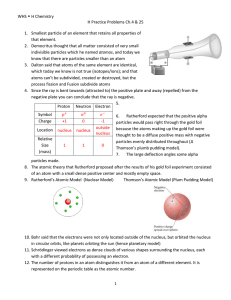
... contains over 99% of its mass. Atoms are mostly empty space. Atomic number and mass number The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom. Every atom has the same number of protons and electrons, because they need to be electrically neutral. The electrons in an atom have almost no mass. So th ...
... contains over 99% of its mass. Atoms are mostly empty space. Atomic number and mass number The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom. Every atom has the same number of protons and electrons, because they need to be electrically neutral. The electrons in an atom have almost no mass. So th ...
• Bond: come together • Charge: there is either a positive or negative
... Unit: the chemical formula with the least number of elements outof the set of empirical fo rmulas having the same proportion of ions as elements. ...
... Unit: the chemical formula with the least number of elements outof the set of empirical fo rmulas having the same proportion of ions as elements. ...
Chapter 21: Nuclear Chemistry
... Spontaneously emit particles and electromagnetic radiation This can transform the unstable nucleus into a stable one - the emitted radiation carries off extra energy e.g., decay of uranium-238 by spontaneous emission of particles: ...
... Spontaneously emit particles and electromagnetic radiation This can transform the unstable nucleus into a stable one - the emitted radiation carries off extra energy e.g., decay of uranium-238 by spontaneous emission of particles: ...
VOCABULARY name, date, hour: Fill in the number of each term
... ___ positively charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom ___ stable, orbiting particle of an atom with a negative charge ___ substance that is a mixture of two or more metals ___ columns of the periodic table; also known as groups ___ number of protons carried by the nucleus of an atom ___ el ...
... ___ positively charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom ___ stable, orbiting particle of an atom with a negative charge ___ substance that is a mixture of two or more metals ___ columns of the periodic table; also known as groups ___ number of protons carried by the nucleus of an atom ___ el ...
Ion- an atom or molecule with a net electric charge due to the loss or
... Ground State- The lowest energy state of an atom or other particle. Excited electron- An electron in an atom that has absorbed some energy, which has put it into a higher energy state. An excited electron will usually decay back to its resting level and release of a packet of energy (a photon). Spec ...
... Ground State- The lowest energy state of an atom or other particle. Excited electron- An electron in an atom that has absorbed some energy, which has put it into a higher energy state. An excited electron will usually decay back to its resting level and release of a packet of energy (a photon). Spec ...
Chemistry Standard 2A-Nucleus Section 20.1
... c. number of neutrons b. atomic number d. neutron-to-proton ratio 5. What is the process in which an unstable atomic nucleus emits charged particles or energy or both? Page answer is found ____________ a. radioactivity c. decomposition b. oxidation d. none of the above 6. When the ____ is not large ...
... c. number of neutrons b. atomic number d. neutron-to-proton ratio 5. What is the process in which an unstable atomic nucleus emits charged particles or energy or both? Page answer is found ____________ a. radioactivity c. decomposition b. oxidation d. none of the above 6. When the ____ is not large ...
Pre-Knowledge: Chemistry and Physics Vocabulary Atomic Number
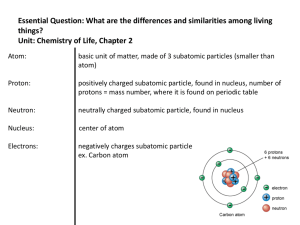
... The sum of the number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus of an atom. Nucleus The small “core” of the atom, where most of its mass and all of its positive charge is concentrated. Except for ordinary hydrogen (which has only a proton), atomic nuclei consist of protons and neutrons. For this reason ...
... The sum of the number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus of an atom. Nucleus The small “core” of the atom, where most of its mass and all of its positive charge is concentrated. Except for ordinary hydrogen (which has only a proton), atomic nuclei consist of protons and neutrons. For this reason ...
Nuclear Physics - Coweta County Schools
... For atoms larger than iron, they have less mass when they separate than when they are held together (fission) Iron is stable and undergoes neither fission ...
... For atoms larger than iron, they have less mass when they separate than when they are held together (fission) Iron is stable and undergoes neither fission ...
1. Nucleons Protons and neutrons 2. Nuclide A atom in
... type of radioactive decay called electron capture, an inner orbital electron is captured by the nucleus of its own atom. • Gamma rays- high energy emr waves emitted from a nucleus as it changes from ground state to excited state. ...
... type of radioactive decay called electron capture, an inner orbital electron is captured by the nucleus of its own atom. • Gamma rays- high energy emr waves emitted from a nucleus as it changes from ground state to excited state. ...
nuclear chemistry
... Nucleons can undergo 2 other types of decay o Positron emission ( same mass as an electron but positive charge) o Electron capture ( nuleus captures an electron from the electron cloud) NUCLEAR STABILITY Nuclei undergo decay to achieve stability If an isotopes mass number is greater than its a ...
... Nucleons can undergo 2 other types of decay o Positron emission ( same mass as an electron but positive charge) o Electron capture ( nuleus captures an electron from the electron cloud) NUCLEAR STABILITY Nuclei undergo decay to achieve stability If an isotopes mass number is greater than its a ...
Atomic nucleus
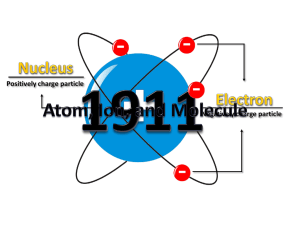
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.