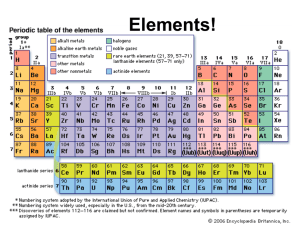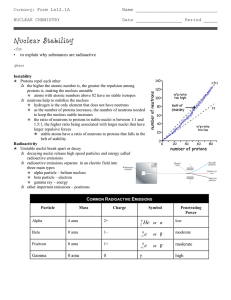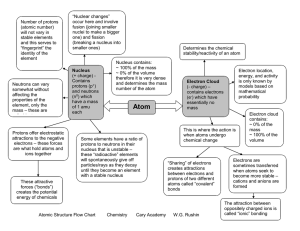
19.1 Reinforcement WKT to project
... 1. How is the chemical symbol of an element determined? 2. Of what are atoms composed? 3. Are electrons, protons, or neutrons the smallest particles? If not, what are? 4. How many types of quarks are there and what is the name of one of them? 5. Why do scientists use models to study atoms? 6. Why ha ...
... 1. How is the chemical symbol of an element determined? 2. Of what are atoms composed? 3. Are electrons, protons, or neutrons the smallest particles? If not, what are? 4. How many types of quarks are there and what is the name of one of them? 5. Why do scientists use models to study atoms? 6. Why ha ...
Atomic Nucleus web
... • arrangements of the fundamental particles (proton, neutron) in the different energy shells (levels) • describe the structure of the nucleus in terms of energy levels • the shells for protons and for neutrons are independent of each other • nuclei with certain number of nucleons have higher binding ...
... • arrangements of the fundamental particles (proton, neutron) in the different energy shells (levels) • describe the structure of the nucleus in terms of energy levels • the shells for protons and for neutrons are independent of each other • nuclei with certain number of nucleons have higher binding ...
nuclear chemistry notes 1
... Elements 93-110 are man-made radioactive elements. Since these man-made atoms are so big, they can be created by combining two smaller atoms together. The protons and neutrons combine into one large nucleus. ...
... Elements 93-110 are man-made radioactive elements. Since these man-made atoms are so big, they can be created by combining two smaller atoms together. The protons and neutrons combine into one large nucleus. ...
Matter Vocab Part 4
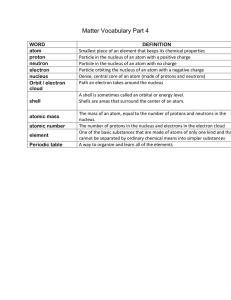
... Particle in the nucleus of an atom with a positive charge Particle in the nucleus of an atom with no charge Particle orbiting the nucleus of an atom with a negative charge Dense, central core of an atom (made of protons and neutrons) Path an electron takes around the nucleus A shell is sometimes cal ...
... Particle in the nucleus of an atom with a positive charge Particle in the nucleus of an atom with no charge Particle orbiting the nucleus of an atom with a negative charge Dense, central core of an atom (made of protons and neutrons) Path an electron takes around the nucleus A shell is sometimes cal ...
Document
... MICTOA SAMS __________________________________________________ 2. the smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of an element MOATS _________________________________________________________ 3. positively charged particle in the atom TORPNO ____________________________________________ ...
... MICTOA SAMS __________________________________________________ 2. the smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of an element MOATS _________________________________________________________ 3. positively charged particle in the atom TORPNO ____________________________________________ ...
14-2 Notes Atomic number
... Isotopes-atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons Mass of the protons and neutrons make up the nuclear mass of the atom Carbon-12, Carbon-13, Carbon-14 If proton # = neutron # then it is a stable atom Mass number = proton # + neutron # Strong nuclear force--holds protons tog ...
... Isotopes-atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons Mass of the protons and neutrons make up the nuclear mass of the atom Carbon-12, Carbon-13, Carbon-14 If proton # = neutron # then it is a stable atom Mass number = proton # + neutron # Strong nuclear force--holds protons tog ...
Section 25.2 Name_____________________
... 3. Use the following word bank to complete the section below: atomic number nuclear bombardment ...
... 3. Use the following word bank to complete the section below: atomic number nuclear bombardment ...
25.2 section summary
... transmutation. This process can occur by radioactive decay or when particles bombard the nucleus of an atom. All of the elements with atomic numbers above 92, trasuranium elements have been synthesized in nuclear reactors or accelerators. Transmutation reaction sometime occurs spontaneously. ...
... transmutation. This process can occur by radioactive decay or when particles bombard the nucleus of an atom. All of the elements with atomic numbers above 92, trasuranium elements have been synthesized in nuclear reactors or accelerators. Transmutation reaction sometime occurs spontaneously. ...
Nuclear Stability
... q the higher the atomic number is, the greater the repulsion among protons is, making the nucleus unstable p atoms with atomic numbers above 82 have no stable isotopes q neutrons help to stabilize the nucleus p hydrogen is the only element that does not have neutrons p as the number of protons incre ...
... q the higher the atomic number is, the greater the repulsion among protons is, making the nucleus unstable p atoms with atomic numbers above 82 have no stable isotopes q neutrons help to stabilize the nucleus p hydrogen is the only element that does not have neutrons p as the number of protons incre ...
Unit 6 Science Vocabulary Emily 6th
... 5. an arrangement of the elements in order of their atomic numbers such that elements with similar properties fall in the same group 6. the smallest particle into which an element can be divided. 7. uncharged particles that are found within the nucleus of an atom. 8. the center of an atom made up of ...
... 5. an arrangement of the elements in order of their atomic numbers such that elements with similar properties fall in the same group 6. the smallest particle into which an element can be divided. 7. uncharged particles that are found within the nucleus of an atom. 8. the center of an atom made up of ...
Atomic Structure Flow Chart Chemistry Cary Academy W.G. Rushin
... ~ 0% of the volume therefore it is very dense and determines the mass number of the atom ...
... ~ 0% of the volume therefore it is very dense and determines the mass number of the atom ...
Name
... 9. The conversion of an atomic nucleus of one element into an atomic nucleus of another element through a loss or gain in the number of protons. 10. High-energy radiation emitted by the nuclei of radioactive atoms. 11. Nuclear fusion produced by high temperature. Down 2. The force of interaction bet ...
... 9. The conversion of an atomic nucleus of one element into an atomic nucleus of another element through a loss or gain in the number of protons. 10. High-energy radiation emitted by the nuclei of radioactive atoms. 11. Nuclear fusion produced by high temperature. Down 2. The force of interaction bet ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.