* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download chem_intro
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
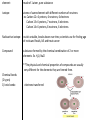
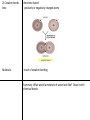
Essential Question: What are the differences and similarities among living things? Unit: Chemistry of Life, Chapter 2 Atom: basic unit of matter, made of 3 subatomic particles (smaller than atom) Proton: positively charged subatomic particle, found in nucleus, number of protons = mass number, where it is found on periodic table Neutron: neutrally charged subatomic particle, found in nucleus Nucleus: center of atom Electrons: negatively charges subatomic particle ex. Carbon atom element: made of 1 atom, pure substance isotope: atoms of same element with different numbers of neutrons ex. Carbon 12= 6 protons, 6 neutrons, 6 electrons Carbon 13= 6 protons, 7 neutrons, 6 electrons Carbon 14= 6 protons, 8 neutrons, 6 electrons Radioactive isotope: nuclei unstable, breaks down over time, scientists use for finding age of rocks and fossils, kill and treat cancer Compound: substance formed by the chemical combination of 2 or more elements. Ex. H20, NaCl **The physical and chemical properties of compounds are usually very different for the elements they are formed from. Chemical bonds (2 types) 1) Ionic bonds: electrons transferred 2) Covalent bonds: Ions: electrons shared positively or negatively charged atoms Molecule: result of covalent bonding Summary: What would a molecule of water look like? Draw it with chemical bonds-