Review 2 key - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]
... 7 Explain what the strong force is and the purpose of it. The strong force is the force that keeps the protons and neutrons in the nucleus. It holds them together even though all of the protons are positively charged and should be repel. 8 What is an isotope? Atoms of the same element that have di ...
... 7 Explain what the strong force is and the purpose of it. The strong force is the force that keeps the protons and neutrons in the nucleus. It holds them together even though all of the protons are positively charged and should be repel. 8 What is an isotope? Atoms of the same element that have di ...
12_physics_notes_ch13_nuclei
... • Binding Energy: a) It may be defined as the energy required to break a nucleus into its constituent protons and neutrons and to separate them to such a large distance that they may not interact with each ...
... • Binding Energy: a) It may be defined as the energy required to break a nucleus into its constituent protons and neutrons and to separate them to such a large distance that they may not interact with each ...
Chapter 8: Chemical Reactions and Physical Changes
... • Chemical equation: written description of a chemical reaction using symbols and formulas • Reactants: the elements or compounds present at the start of a reaction • Products: the elements or compounds formed during the reaction • Covalent compounds: compounds formed by the sharing of electrons ...
... • Chemical equation: written description of a chemical reaction using symbols and formulas • Reactants: the elements or compounds present at the start of a reaction • Products: the elements or compounds formed during the reaction • Covalent compounds: compounds formed by the sharing of electrons ...
Chapter 29: Nuclear Physics
... •Alpha rays are stopped by a few cm of air or about 0.02 mm of aluminum. •Beta-minus can penetrate a few cm into biological tissue. •Gamma ray absorption is based on probability so they can penetrate to varying depths. ...
... •Alpha rays are stopped by a few cm of air or about 0.02 mm of aluminum. •Beta-minus can penetrate a few cm into biological tissue. •Gamma ray absorption is based on probability so they can penetrate to varying depths. ...
Evolution of the Atomic Theory
... • 2. few particles were deflected when shot at the foil. • 3. rarely, one particle would come back almost directly at the alpha source ...
... • 2. few particles were deflected when shot at the foil. • 3. rarely, one particle would come back almost directly at the alpha source ...
Section 2 The Structure of the Atom Discovery of the Electron
... • An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains the chemical properties of that element. • The nucleus is a very small region located at the center of an atom. • The nucleus is made up of at least one positively charged particle called a proton and usually one or more neutral particles ...
... • An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains the chemical properties of that element. • The nucleus is a very small region located at the center of an atom. • The nucleus is made up of at least one positively charged particle called a proton and usually one or more neutral particles ...
General CHemistry Unit 2 Homework Notes
... Solids have a fixed shape. In a solid the particles are closely packed together. Each particle in a solid is held in one position and vibrates around that position. The particles in a liquid stay relatively close together, but they can move around each other. Gas particles are far apart; they move r ...
... Solids have a fixed shape. In a solid the particles are closely packed together. Each particle in a solid is held in one position and vibrates around that position. The particles in a liquid stay relatively close together, but they can move around each other. Gas particles are far apart; they move r ...
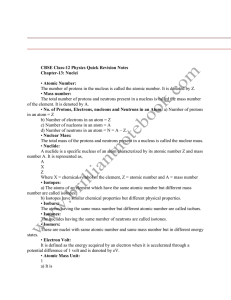
Stable Vs Unstable Isotopes
... Nuclear reactions are accompanied by tremendous energy changes as an unstable isotope spontaneously undergoes changes. ...
... Nuclear reactions are accompanied by tremendous energy changes as an unstable isotope spontaneously undergoes changes. ...
Chemistry Student Guided Notes
... The sum of the protons and the neutrons in an atom’s nucleus is its Draw the diagram from the PowerPoint of the element chlorine to illustrate how atomic numbers and atomic mass are listed in the periodic table of the elements. ...
... The sum of the protons and the neutrons in an atom’s nucleus is its Draw the diagram from the PowerPoint of the element chlorine to illustrate how atomic numbers and atomic mass are listed in the periodic table of the elements. ...
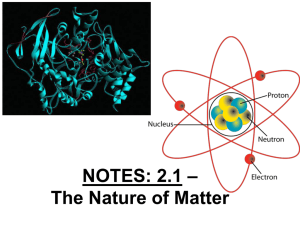
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.
![Review 2 key - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000860497_1-e3bea510ba504d09bc42d6f5e4936390-300x300.png)