Nuclear and Particle Physics
... Compare this to the mass of a proton or neutron in your formula sheet ...
... Compare this to the mass of a proton or neutron in your formula sheet ...
Lesson 15: Nuclear Quest - Highline Public Schools
... Changes in the nucleus of an atom can change the identity of an element. Alpha particle: A particle composed of two protons and two neutrons, equivalent to the nucleus of a helium atom. Beta particle: An electron emitted from the nucleus of an atom during beta decay. Gamma ray: A form of high-energy ...
... Changes in the nucleus of an atom can change the identity of an element. Alpha particle: A particle composed of two protons and two neutrons, equivalent to the nucleus of a helium atom. Beta particle: An electron emitted from the nucleus of an atom during beta decay. Gamma ray: A form of high-energy ...
Chapter 4 The Liquid Drop Model
... 2. Surface term: The nucleons at the surface of the ‘liquid drop’ only interact with other nucleons inside the nucleus, so that their binding energy is reduced. This leads to a reduction of the binding energy proportional to the surface area of the drop, i.e. proportional to A2/3 −aS A2/3 . 3. Coul ...
... 2. Surface term: The nucleons at the surface of the ‘liquid drop’ only interact with other nucleons inside the nucleus, so that their binding energy is reduced. This leads to a reduction of the binding energy proportional to the surface area of the drop, i.e. proportional to A2/3 −aS A2/3 . 3. Coul ...
Chapter 16 – Nuclear Energy
... • Radiation: alpha particles, beta particles and gamma rays given off in the decaying of unstable nuclei. ...
... • Radiation: alpha particles, beta particles and gamma rays given off in the decaying of unstable nuclei. ...
Nuclear chemistry – the study of nuclear reactions and their uses in
... Strong nuclear forces exist between nucleons. The belt of stability, where all stable nuclei are found, ends at element 83; anything with 84 or more protons are radioactive. Radioactive decay depends to a large extend on its neutron-to-proton ratio. i. Nuclei above the belt of stability (high neutro ...
... Strong nuclear forces exist between nucleons. The belt of stability, where all stable nuclei are found, ends at element 83; anything with 84 or more protons are radioactive. Radioactive decay depends to a large extend on its neutron-to-proton ratio. i. Nuclei above the belt of stability (high neutro ...
Chapter 14
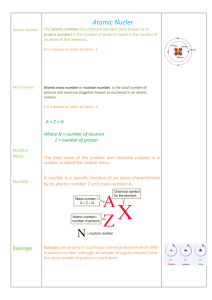
... When a neutron is converted into a proton, this is an example of _________. This is the process by which one element changes into another element. Atoms of the same element with a different number of neutrons are called _. The atomic number of an element is equal to _____________. This is the smalle ...
... When a neutron is converted into a proton, this is an example of _________. This is the process by which one element changes into another element. Atoms of the same element with a different number of neutrons are called _. The atomic number of an element is equal to _____________. This is the smalle ...
Chapter 9: Nuclear Changes
... Chapter 9: Nuclear Changes - ____________- the process by which an unstable nucleus emits one or more particles or energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation - _____ ________- process radioactive materials undergo - radioactive materials have an unstable nucleus - become stable by undergoing nu ...
... Chapter 9: Nuclear Changes - ____________- the process by which an unstable nucleus emits one or more particles or energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation - _____ ________- process radioactive materials undergo - radioactive materials have an unstable nucleus - become stable by undergoing nu ...
Atoms - Red Hook Central Schools
... straight through the gold foil as if it wasn’t even there! 2. The nucleus of the atom is small, dense, and positively charged ...
... straight through the gold foil as if it wasn’t even there! 2. The nucleus of the atom is small, dense, and positively charged ...
File
... The atomic mass units of hydrogen isotopes are: 1 amu 2 amu 3 amu An isotope’s names is usually followed by the ...
... The atomic mass units of hydrogen isotopes are: 1 amu 2 amu 3 amu An isotope’s names is usually followed by the ...
Atomic Theory Handout CNS 8
... Bohr began to work on the problem of the atom's structure. Ernest Rutherford had recently suggested the atom had a miniature, dense nucleus surrounded by a cloud of nearly weightless electrons. There were a few problems with the model, however. For example, according to classical physics, the electr ...
... Bohr began to work on the problem of the atom's structure. Ernest Rutherford had recently suggested the atom had a miniature, dense nucleus surrounded by a cloud of nearly weightless electrons. There were a few problems with the model, however. For example, according to classical physics, the electr ...
Standard A
... LG (b) EARLY HISTORY OF ATOMIC MODEL: Know the contributions made by Dalton, Thomson, Millikan, Rutherford and Chadwick as well as the experiments the lead to the discovery of the atom and its subatomic particles. ...
... LG (b) EARLY HISTORY OF ATOMIC MODEL: Know the contributions made by Dalton, Thomson, Millikan, Rutherford and Chadwick as well as the experiments the lead to the discovery of the atom and its subatomic particles. ...
Atomic Structure Study Guide
... high voltage vacuum tube – was made up of ____________ charged particles, which had a smaller mass/charge ratio than any known atom. This showed that ______________ particles existed, and therefore atoms were not indivisible. These particles are now known as _____________. His student, Rutherford, s ...
... high voltage vacuum tube – was made up of ____________ charged particles, which had a smaller mass/charge ratio than any known atom. This showed that ______________ particles existed, and therefore atoms were not indivisible. These particles are now known as _____________. His student, Rutherford, s ...
Ch 21 Nuclear - coolchemistrystuff
... Radioactive series (or nuclear disintegration series): a series of nuclear reactions that begins with an unstable nucleus and terminates with a stable one Magic numbers: nuclei with 2, 8, 20, 28, 50, or 82 protons or 2, 8, 20, 28, 50, 82, or 126 neutrons; results in very stable nuclei Nuclei wit ...
... Radioactive series (or nuclear disintegration series): a series of nuclear reactions that begins with an unstable nucleus and terminates with a stable one Magic numbers: nuclei with 2, 8, 20, 28, 50, or 82 protons or 2, 8, 20, 28, 50, 82, or 126 neutrons; results in very stable nuclei Nuclei wit ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.