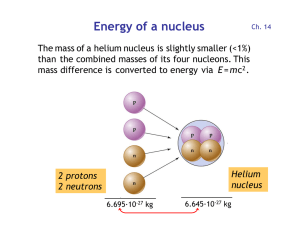
Energy of a nucleus
... • All elements heavier than iron/nickel are created during a supernova explosion, which has enough thermal energy to form nuclei with higher energy per nucleon. ...
... • All elements heavier than iron/nickel are created during a supernova explosion, which has enough thermal energy to form nuclei with higher energy per nucleon. ...
available here
... Atomic structure and bonding related to properties of materials Nuclide notation. Isotopes and relative atomic mass. Ions. Ionic bonding. ...
... Atomic structure and bonding related to properties of materials Nuclide notation. Isotopes and relative atomic mass. Ions. Ionic bonding. ...
Introduction to Radioactivity and Radioactive decay
... nucleus. Atoms with very low atomic numbers have about the same number of neutrons and protons; as Z gets larger, however, stable nuclei will have more neutrons than protons. Eventually, a point is reached beyond which there are no stable nuclei: the bismuth nucleus with 83 protons and 126 neutrons ...
... nucleus. Atoms with very low atomic numbers have about the same number of neutrons and protons; as Z gets larger, however, stable nuclei will have more neutrons than protons. Eventually, a point is reached beyond which there are no stable nuclei: the bismuth nucleus with 83 protons and 126 neutrons ...
Historical Development of atomic theory
... Quarks were first theorized forty years ago, followed by gluons about half a decade later. Three quarks and a host of gluons, so-called because they glue quarks together, are found in each proton and neutron. The nucleus, in turn, is comprised of one or more protons and may also contain neutrons. Th ...
... Quarks were first theorized forty years ago, followed by gluons about half a decade later. Three quarks and a host of gluons, so-called because they glue quarks together, are found in each proton and neutron. The nucleus, in turn, is comprised of one or more protons and may also contain neutrons. Th ...
File
... atom: The smallest particles that make up matter. proton: a subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is located in the nucleus of an atom. (The number of protons in the nucleus is the atomic number, which determines the identity of an element.) neutron: a subatomic particle that has no ...
... atom: The smallest particles that make up matter. proton: a subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is located in the nucleus of an atom. (The number of protons in the nucleus is the atomic number, which determines the identity of an element.) neutron: a subatomic particle that has no ...
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions C Kapler ` , , I 27 O//#W SELF
... — In ions, the number of protons is always greater than the number of electrons. — An atom has always more subatomic particles than an ion. The number of true statements is a. 0 b. 1 c. 2 d. 3 e. 4 9. In a chemical reaction, if an atomic particle carries a positive charge, then the atom has a. lost ...
... — In ions, the number of protons is always greater than the number of electrons. — An atom has always more subatomic particles than an ion. The number of true statements is a. 0 b. 1 c. 2 d. 3 e. 4 9. In a chemical reaction, if an atomic particle carries a positive charge, then the atom has a. lost ...
California Chemistry Standards Test
... 2. hydrocarbons and polymers 3. amino acids building blocks of matter Nuclear Processes-(2) 1. protons and neutrons in the nucleus (forces) 2. fusion and fission 3. isotopes of elements are radioactive 4. radioactive decay (alpha, beta, and gamma)-know how nucleus changes Investigation & Experimenta ...
... 2. hydrocarbons and polymers 3. amino acids building blocks of matter Nuclear Processes-(2) 1. protons and neutrons in the nucleus (forces) 2. fusion and fission 3. isotopes of elements are radioactive 4. radioactive decay (alpha, beta, and gamma)-know how nucleus changes Investigation & Experimenta ...
Nucleus
... The nucleus is in the center of the atom Contains protons and neutrons Almost all the mass is contained in the nucleus Nucleus is very small compared to the actual atom If the atom were the size of a stadium the nucleus would be a marble Nucleus is very dense A nucleus the size of a pea would we ...
... The nucleus is in the center of the atom Contains protons and neutrons Almost all the mass is contained in the nucleus Nucleus is very small compared to the actual atom If the atom were the size of a stadium the nucleus would be a marble Nucleus is very dense A nucleus the size of a pea would we ...
Glossary - Angelfire
... Isotope - Isotopes of the same element have the same number of "PROTONS" but different numbers of "NEUTRONS". If two atoms have different numbers of protons then they must also have different numbers of electrons in order to be electrically neutral. They therefore have different chemical properties ...
... Isotope - Isotopes of the same element have the same number of "PROTONS" but different numbers of "NEUTRONS". If two atoms have different numbers of protons then they must also have different numbers of electrons in order to be electrically neutral. They therefore have different chemical properties ...
Quiz 3-6 fy13 - Nuclear Chemistry practice
... What thickness of what material is the minimum necessary to stop a beta particle? A. three feet of concrete B. three inches of lead C. sheet of aluminum foil D. sheet of paper E. beta particles cannot be stopped ...
... What thickness of what material is the minimum necessary to stop a beta particle? A. three feet of concrete B. three inches of lead C. sheet of aluminum foil D. sheet of paper E. beta particles cannot be stopped ...
Isotope Half-Life Radiation Emitted
... http://library.thinkquest.org/06aug/01200/Graphics/705px-Nuclear_fireball.jpg ...
... http://library.thinkquest.org/06aug/01200/Graphics/705px-Nuclear_fireball.jpg ...
2nd Semester Review
... 4. Circle the correct atomic particle for each of the following: Defines an atom Protons Neutrons Electrons Isotopes: same type of atom with different number of Protons Neutrons Determines how atoms combine Protons Neutrons Electrons Ions: same type of atom with different number of Protons Neutrons ...
... 4. Circle the correct atomic particle for each of the following: Defines an atom Protons Neutrons Electrons Isotopes: same type of atom with different number of Protons Neutrons Determines how atoms combine Protons Neutrons Electrons Ions: same type of atom with different number of Protons Neutrons ...
The arrangement of the subatomic particles within the atom
... y Atomic mass { This number is the mass of the nuclear particles ...
... y Atomic mass { This number is the mass of the nuclear particles ...
Atomic Structure Note Page
... a. The overall (net) charge of the nucleus is positive. i. The overall (net) charge of the nucleus is equal to the number of protons. b. There is an attractive force between protons and electrons. i. Opposites attract and like charges repel one another. c. Atoms have a Neutral Charge because the num ...
... a. The overall (net) charge of the nucleus is positive. i. The overall (net) charge of the nucleus is equal to the number of protons. b. There is an attractive force between protons and electrons. i. Opposites attract and like charges repel one another. c. Atoms have a Neutral Charge because the num ...
Scientists` Consensus Ideas Atomic Structure and Nuclear Interactions
... nuclear reactions or nuclear interactions. Nuclear reactions release enormous quantities of energy compared to chemical reactions. 14. Some elements change into other elements as a result of nuclear reactions. Physical and chemical interactions do not convert one element into another element. 15. Nu ...
... nuclear reactions or nuclear interactions. Nuclear reactions release enormous quantities of energy compared to chemical reactions. 14. Some elements change into other elements as a result of nuclear reactions. Physical and chemical interactions do not convert one element into another element. 15. Nu ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.