Exploring Sound and Light
... Sources that produce interesting sounds include fluorescent and neon lights and novelty LEDs. Since the solar cell is sensitive to infrared radiation, you can even listen to a television remote control device even though you can’t see the radiation emanating from it. Voice and music may also be tran ...
... Sources that produce interesting sounds include fluorescent and neon lights and novelty LEDs. Since the solar cell is sensitive to infrared radiation, you can even listen to a television remote control device even though you can’t see the radiation emanating from it. Voice and music may also be tran ...
Physics 213 — Problem Set 5 (Due before Feb. 26) Spring 1998
... Consider two thin, conducting, spherical shells as in Figure P25.76 of your text. The inner shell has a radius r1 = 15 cm and a charge of 10 nC. The outer shell has a radius r2 = 30 cm and a charge of −15 nC. Find (a) the electric field E and (b) the electric potential V in regions A, B, and C of th ...
... Consider two thin, conducting, spherical shells as in Figure P25.76 of your text. The inner shell has a radius r1 = 15 cm and a charge of 10 nC. The outer shell has a radius r2 = 30 cm and a charge of −15 nC. Find (a) the electric field E and (b) the electric potential V in regions A, B, and C of th ...
Topic 4 New Part 1 Oscillations and Waves solutions
... 6. Define the frequency of a wave and explain how wave frequency is measured. number of waves per sec = Hz = s-1 7. What is the period of a wave? Identify how the period of a wave relates to its frequency. T = duration of wave, how long the wave lasts T = 1/f 8. What factors affect the speed at whic ...
... 6. Define the frequency of a wave and explain how wave frequency is measured. number of waves per sec = Hz = s-1 7. What is the period of a wave? Identify how the period of a wave relates to its frequency. T = duration of wave, how long the wave lasts T = 1/f 8. What factors affect the speed at whic ...
Cold encounters: Electrons and molecules
... Two types of experiment have been developed. The first are those that form cold electrons or Rydberg atoms in situ with a target gas to study exclusively DA [3,4,5,7]. The exquisite precision of recent DA measurements is illustrated by data in [8J, involving CH 3 I + electron ~ 1- + CH 3, showing ho ...
... Two types of experiment have been developed. The first are those that form cold electrons or Rydberg atoms in situ with a target gas to study exclusively DA [3,4,5,7]. The exquisite precision of recent DA measurements is illustrated by data in [8J, involving CH 3 I + electron ~ 1- + CH 3, showing ho ...
Chapter 8: Conservation of Energy
... 21. Two masses are connected by a light string passing over a light frictionless pulley, as shown in Figure P8.21. The 5.00-kg mass is released from rest. Using the law of conW AC = - mg (dC – dA)= - 2×9.8×(5.0 -2.0) = -58.8 J servation of energy, (a) determine the speed of the 3.00F kg mass just as ...
... 21. Two masses are connected by a light string passing over a light frictionless pulley, as shown in Figure P8.21. The 5.00-kg mass is released from rest. Using the law of conW AC = - mg (dC – dA)= - 2×9.8×(5.0 -2.0) = -58.8 J servation of energy, (a) determine the speed of the 3.00F kg mass just as ...
Does light cause movement - Rochester Community Schools
... Light can travel through space which is why we see the light from stars (sun). ...
... Light can travel through space which is why we see the light from stars (sun). ...
1 - kurtniedenzu
... b. Stephen Jay Gould c. Throckmorton P. Guildersleeve d. Ernest B. Rutherford 15. Which numbered arrow in the diagram below gives the best indicator of the time at which the particle model of the atom became generally accepted by chemists and physicists? ...
... b. Stephen Jay Gould c. Throckmorton P. Guildersleeve d. Ernest B. Rutherford 15. Which numbered arrow in the diagram below gives the best indicator of the time at which the particle model of the atom became generally accepted by chemists and physicists? ...
Light - Edublogs
... Isaac Newton was the first to show that white light consists of every color light mixed together. He sent white light through a prism, which produced a rainbow of colors and then through a second prism, where it recombined to produce white light again. All the colors, on atop the other, combine to ...
... Isaac Newton was the first to show that white light consists of every color light mixed together. He sent white light through a prism, which produced a rainbow of colors and then through a second prism, where it recombined to produce white light again. All the colors, on atop the other, combine to ...
Chemical Reactions
... Electrical – results from the movement of charged particles Mechanical – directly involved in moving matter Radiant or electromagnetic – energy traveling in waves (i.e., visible light, ultraviolet light, and X-rays) ...
... Electrical – results from the movement of charged particles Mechanical – directly involved in moving matter Radiant or electromagnetic – energy traveling in waves (i.e., visible light, ultraviolet light, and X-rays) ...
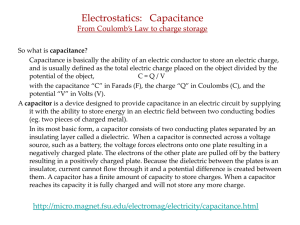
Slide 1
... Capacitance is basically the ability of an electric conductor to store an electric charge, and is usually defined as the total electric charge placed on the object divided by the potential of the object, C=Q/V with the capacitance “C” in Farads (F), the charge “Q” in Coulombs (C), and the potential ...
... Capacitance is basically the ability of an electric conductor to store an electric charge, and is usually defined as the total electric charge placed on the object divided by the potential of the object, C=Q/V with the capacitance “C” in Farads (F), the charge “Q” in Coulombs (C), and the potential ...
Students will be assessed on their ability to
... • Radio waves produced by moving electrons at transmitter • Induce current in receiver aerial ...
... • Radio waves produced by moving electrons at transmitter • Induce current in receiver aerial ...
The kinetic theory of electromagnetic radiation
... a mixture of them which will yield Planck’s energy distribution. A clue to the choice of infinite variety comes directly from observation of the photoelectric effect, for this indicates that, in interactions between matter and radiation, energy exchanges occur, at any frequency, ν, in integral multi ...
... a mixture of them which will yield Planck’s energy distribution. A clue to the choice of infinite variety comes directly from observation of the photoelectric effect, for this indicates that, in interactions between matter and radiation, energy exchanges occur, at any frequency, ν, in integral multi ...