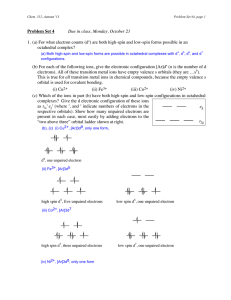
doc
... The top (anti-top) quark decays in 10-25 s and is not seen directly in the detector. However, one electron and 4 jets of particles are seen in the detector with energy and momentum given by (Ee,pe), (E1,p1), (E2,p2), (E3,p3) and (E4,p4), where bold font indicates a vector. In this case, the top quar ...
... The top (anti-top) quark decays in 10-25 s and is not seen directly in the detector. However, one electron and 4 jets of particles are seen in the detector with energy and momentum given by (Ee,pe), (E1,p1), (E2,p2), (E3,p3) and (E4,p4), where bold font indicates a vector. In this case, the top quar ...
pptx - Yale University
... In the last 25 years various manifestations of Scanning Probe Microscopy, such as AFM, STM, and SNOM, have enabled chemists to “feel” individual molecules and atoms. SPM techniques are not quite good enough yet to study how electrons are distributed in bonds. Because light is scattered predominantly ...
... In the last 25 years various manifestations of Scanning Probe Microscopy, such as AFM, STM, and SNOM, have enabled chemists to “feel” individual molecules and atoms. SPM techniques are not quite good enough yet to study how electrons are distributed in bonds. Because light is scattered predominantly ...
Viewing and Projection - MIT Computer Science and
... electric field may rotate. If the electric field is oriented in a particular constant direction it is called polarized. The behavior of reflection depend on how the incoming electric field is oriented relative to the surface at the point where the field makes contact. This variation in reflectance i ...
... electric field may rotate. If the electric field is oriented in a particular constant direction it is called polarized. The behavior of reflection depend on how the incoming electric field is oriented relative to the surface at the point where the field makes contact. This variation in reflectance i ...
Reflection - Animated Science
... In this case the two waves would cancel each other out - one says that destructive interference has occurred. At a point of constructive interference the net amplitude of the two waves is a maximum, whereas at a point of destructive interference, the net amplitude is a minimum. Of course, one could ...
... In this case the two waves would cancel each other out - one says that destructive interference has occurred. At a point of constructive interference the net amplitude of the two waves is a maximum, whereas at a point of destructive interference, the net amplitude is a minimum. Of course, one could ...
of the light. - Hss-1.us
... – If the two waves have the same amplitude (A) and wavelength (λ) the resultant waveform will have an amplitude between 0 and 2A depending on whether the two waves are in phase or out of phase. – In phase: Consider two waves that are in phase, with amplitudes A1 and A2. Their troughs and peaks line ...
... – If the two waves have the same amplitude (A) and wavelength (λ) the resultant waveform will have an amplitude between 0 and 2A depending on whether the two waves are in phase or out of phase. – In phase: Consider two waves that are in phase, with amplitudes A1 and A2. Their troughs and peaks line ...
Chapter 3: Planck`s theory of blackbody radiation
... the potential energy E of the pendulum is E = mgx = 1,492 · 10−6 J. Applying the quantum equation E = nhν, since in this case hν = 3,301 · 10−34 J, we find the numer of quanta to be n = 4,5 · 1027 !!! What is the moral of the story? To measure the discrete character of energy in a macroscopic system ...
... the potential energy E of the pendulum is E = mgx = 1,492 · 10−6 J. Applying the quantum equation E = nhν, since in this case hν = 3,301 · 10−34 J, we find the numer of quanta to be n = 4,5 · 1027 !!! What is the moral of the story? To measure the discrete character of energy in a macroscopic system ...
Chapter 2 Chemical context of Life
... Electrons in the outermost shell have the greatest amount of energy and are called valence electrons. They occupy the valence shell. See Fig. 2.9. Elements with the same number of electrons in their valence shell have similar chemical properties, e.g. K and Na; Cl and F. Electrons can change from on ...
... Electrons in the outermost shell have the greatest amount of energy and are called valence electrons. They occupy the valence shell. See Fig. 2.9. Elements with the same number of electrons in their valence shell have similar chemical properties, e.g. K and Na; Cl and F. Electrons can change from on ...